Introduction
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) is a substance extracted from Propolis. Propolis is a substance collected by honeybees from tree and flower buds. Propolis has a long history of medical use. It is only until recently when Caffeic acid phenethyl ester was isolated from propolis that revelation on why propolis has been used as a medicine for such a long time came to light. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester has been shown to be a very interesting substance with very unique properties including healing properties and association with different diseases.
Natural Sources for CAPE
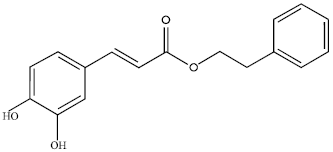
Natural sources for CAPE include propolis (LeBlanc et al. 14637); CAPE was for the first time isolated from propolis and examined by Grunberger in 1988 (Roos 7). Propolis, also referred to as bee glue, is a substance collected by bees from plants specifically from the buds. The composition of propolis depends on where it is collected from geographically as well as from which plants it is collected. Plant buds can also serve as natural sources for CAPE (Iraz et al. 69). The following is a molecular structure of CAPE.
Health Benefits of CAPE
CAPE has been in use for a long time even at a time when its mechanism of working was not at all understood. As a folk medicine, but in the crude form as propolis, it has been used in “exhibiting anti-mitogenic, anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral and immune-modulatory properties” (Lin et al. 26). According to Demestre et al., it was also used in “treatment of infection, wound and inflammation as well as for preparing mummies” (1). Wang et al. also noted that it was used in curing of allergic and asthma related cases (39). These health benefits are discussed as follows.
Anti-oxidative properties of CAPE: These properties in CAPE were illustrated as early as 1993. In 2005, the properties were shown in action in various biological systems (Roos 8).
Anti-inflammatory and chemo-preventive properties of CAPE: As early as 1993, studies showed the inhibition property of CAPE on 5-lipoxygenase. More recent studies in 2004 also showed the inhibitory property of CAPE on cyclooxygenase. Extensive studies further showed that CAPE effectively inhibits the nuclear transcription factor kB (NF-kB) thus significantly illustrating how CAPE fights inflammation (Roos 8).
Cardiovascular effects and CAPE: CAPE has been shown to “inhibit chlamydophila pneumonia-induced ICAM-1 up-regulation in human endothelial cells” (Roos 8). Other studies on cardiovascular effects of CAPE have been carried out on rat models with promising results (Roos 8).
Proliferation and CAPE: Studies have shown Caffeic acid phenethyl ester to have anti-proliferative properties. These properties have been shown to work in “vascular smooth muscle cells, chorioallantoic membrane in chick embryo” (Roos 9).
Studies on CAPE are still going on and a lot more is still being discovered. In their study Chen et al. acknowledged that CAPE’s beneficial properties can be applied in many uses. Their study showed that CAPE acted as protector of “661W cells (in vitro) against H2O2– mediated cell death and in albino rats (in vivo) against various light conditions” (Chen et al. 1325).
CAPE Metabolism
Anti-Cancer mechanism
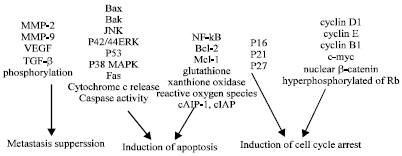
It has been shown that CAPE is used in inducing “apoptosis, G1 or G2 cell cycle arrest and necrosis” (Lin et al. 29). Furthermore, CAPE has been shown to “suppress development, growth and metastasis of tumors in animal models” (Lin et al. 29). It is observed that the ability of CAPE to limit the motility and invasiveness of cancerous cells is a factor of the concentration of CAPE and the kind of cells in question. Experiments have achieved a concentration of 5.0 μg mL-1 in human serum. Unfortunately, this concentration is still too low to remove all the cancerous cells known (Lin et al. 29).
Studies have also shown that CAPE blocks the process of conversion of “normal cells to cancerous cells” (Lin et al. 29). It has also been shown to “induce cell cycle arrest in CREF” (Lin et al. 29). Human cancer cell lines proliferation has been shown to be suppressed through CAPE treatment. CAPE stimulates Bcl-2-associated X protein to “induce apoptosis in many cancer types” (Lin et al. 29).
The anti-cancer ways that CAPE has been shown to work are illustrated in the diagram below.
Diseases related to CAPE
Diabetes and CAPE
Several studies carried out have shown that CAPE can help to reduce diabetic activities. This has been shown to be possible through its antioxidant property. For instance, diabetes mellitus has been known to increase “oxidative stress in cardiac tissue” (Okutan et al. 191) but CAPE has been shown to have an “ameliorating effect on the oxidative stress” (Okutan et al. 191). Park and Min have also shown CAPE to assist in healing diabetic rats by ameliorating IGF secretion (Park and Min 1741).
Cancer and CAPE
CAPE has been shown to inhibit NF-kB mechanisms. In studying this inhibition property, studies have shown that CAPE can suppress “the proliferation of LNCaP, DU-145, and PC-3 human prostate cancer cells” (Chuu et al. 788). CAPE was also shown to inhibit “the growth of LNCaP xenografts in nude mice” (Chuu et al. 788). Lin et al. have also shown the potential of CAPE in treating many categories of cancer. They showed that the “anti-mitogenic, anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral and immuno-modulatory properties” (Lin et al. 26) of CAPE made it possible for the substance to be a potential medicine for cancer.
CAPE and Immune System
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester has been shown to have the potential to boost the immune system. Wang et al. carried out a study showing how CAPE inhibits various types of proteins in “mature healthy human MoDCs stimulated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and IL-12 p40, IL-10, IP-10 stimulated by crude mite extract” (Wang et al. 39). The study also showed that CAPE inhibited compounds which activated allergic reactions. In general, it was concluded that CAPE is vital in inhibition of “cytokine and chemokine production by MoDCs which might be related to the NF-κB signaling pathway” (Wang et al. 39).
Spinal Cord Injury and CAPE
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester has been shown to reduce spinal cord injury through its inhibitory activity. CAPE reduces secondary neuronal damage. It does this by enhancing the healing of locomotor function and reducing “the lesion size while suppressing the expression of the mRNAs for a pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β and the inflammatory enzymes, inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2” (Kasai et al. 1).
Brain aging and CAPE
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester has shown the potential to reduce brain aging through the process of HO-1 induction whereby neurons are given protection (Racchi et al. 4).
Angiogenesis and CAPE
Angiogenesis is biological activity that takes place at the time of development, reproduction and repairing of wounds. This process can at times be supportive to pathogenic activities in disease formation. It has been shown that CAPE can assist in the synthesis of inhibitors of angiogenesis (Basini et al. 186). This occurs by CAPE inhibiting new growth of blood vessels: it was shown that it blocked the “growth of vessels in angiogenesis bioassay” (Basini et al. 186).
Inflammatory and CAPE
Inflammation can be of two types – acute and systemic. Acute inflammation is physical and in most cases can be felt and seen while systemic inflammation is a serious problem which takes time to manifest slowly within the body. It often has no pain symptoms and therefore goes unnoticed. After a long time of systematic inflammation attacks, internal organs start to get damaged and chronic dieses attack the body (Understanding Inflammation 1).
Inflammation is brought about by NF-kappaB. CAPE inhibits inflammation by targeting NF-kappaB. It does this by inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB thus preventing inflammation (Toyoda et al. 1).
Intestinal ischemia reperfusion
This condition is associated with the white blood cells. The condition has the effect of increasing the volume of oxidative agents, e.g. xanthine oxidase. It also increases the reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Ozyurt et al. 198). This process causes more harm and is actually referred to as reperfusion injury.
CAPE heals intestinal ischemia reperfusion by using its “free radical scavenger properties” (Ozyurt et al. 198). CAPE will remove (scavenge on) the free radicals that are responsible for Intestinal ischemia reperfusion (Ozyurt et al. 198).
Myeloid Leukemia
Myeloid leukemia is actually a type of a cancer. This cancer starts from the bone marrow and spreads out to the other parts of the body. At the bone marrow when cells are attacked, those that become leukemic do not get to mature to the level on “functional non-dividing end cells” (Koeffler and Golde 348).
CAPE has been shown to kill tumor cells while sparing normal cells. In a study, it was shown that CAPE induces “mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia U937 cells” (Jin et al. 1).
Hypotension
This is a low blood pressure condition. It happens when the heartbeat slows down. When in this condition many organs in the body especially the heart and brain do not get enough blood supply (Ersin et al. 1).
CAPE has been shown to have hypotensive effects on rats. This has been shown to be through parasympathetic control mechanism. Therefore, CAPE may not be appropriate for treating hypotension but in the contrast may worsen the situation (Ersin et al. 1).
Neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is the nervous system poisoning which results from exposures to such agents as radiation treatment, heavy metals (lead, mercury), cosmetics etc. These poisons may kill the neurons and other cells that help to transmit impulses to and from the brain (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke 1).
Due to the inhibitory properties of CAPE, it “blocks 6-OHDA-induced neuronal death possibly by inhibiting 6-OHDA-induced free radical generation and blocking free radical-induced neurotoxicity in neurons” (Ma et al. 1).
Metastasis and Invasion
Metastasis is defined as the ability of the “cancerous cells to be spread from one organ to another” (Barts Cancer Institute 1). On the other hand, inversion has to do with “increased cellular motility, the production of enzymes with proteolytic activity and alteration in cell adhesion” (Barts Cancer Institute 1).
CAPE has been shown to control metastasis in oral cancer cells by “regulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway” (Peng et al. 1). CAPE also works against invasion of cancerous cells by inhibiting activation of NF-kappaB (Lee et al. 1).
Uveitis
Uvea is the middle layer of the eye. When this layer is irritated, it can swell and this swelling is referred to as uveitis. This condition can be brought about by “rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis, infection, or exposure to toxins” (PubMed Health 1).
CAPE was found to reduce inflammation in rat cells induced with uveitis. CAPE did this by suppressing LPS, protein concentration, and MPO levels in humor (Yilmaz et al. 1).
Works Cited
Barts Cancer Institute. Metastasis & Invasion. Barts Cancer Institute, 2012. Web.
Basini et al. “Antiangiogenic properties of an unusual benzo[k,l]xanthenes lignan derived from CAPE (Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester).” Invest New Drugs 30.1 (2012): 186-190. Print.
Chen et al. “Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects 661W cells from H2O2-mediated cell death and enhances electroretinography response in dim-reared albino rats.” Molecular Vision 18.1 (2012): 1325-1338. Print.
Chuu et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester suppresses the proliferation of human prostate cancer cells through inhibition of p70S6K and Akt signaling networks. National Library of Medicine, 2012. Web.
Demestre et al. “CAPE (Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester)-based Propolis Extract (Bio 30) Suppresses the Growth of Human Neurofibromatosis (NF) Tumor Xenografts in Mice.” Phytotherapy Research 1.1 (2008): 1-5. Print.
Ersin et al. Role of vagal activity on bradicardic and hypotensive effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE). Cardiovascular Toxicology, 2005. Web.
Iraz et al. “Dose Dependent Effects Of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester On Heart Rate And Blood Pressure In Rats.” Eur J Gen Med 2.2 (2005): 69-75. Print.
Jin et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia U937 cells. National Library of Medicine, 2008. Web.
Kasai et al. “Caffeic acid phenethyl ester reduces spinal cord injury-evoked locomotor dysfunction.” Biomedical Research 32.1 (2011): 1-7. Print.
Koeffler, Paul, and Golde Doln. “Human Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines: A review.” Blood 56.3 (1980): 344-350. Print.
LeBlanc et al. “Synthesis and Antiradical/Antioxidant Activities of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester and Its Related Propionic, Acetic, and Benzoic Acid Analogues.” Molecules 17.1 (2012): 14637-14650. Print.
Lee et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits invasion and expression of matrix metalloproteinase in SK-Hep1 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting nuclear factor kappa B. National Library of Medicine, 2008. Web.
Lin et al. “Anticancer effect of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester.” Pharmacologia 3.1 (2004): 26-30. Print.
Ma et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester blocks free radical generation and 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity. National Library of Medicine, 2006. Web.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. NINDS Neurotoxicity Information. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 2012. Web.
Okutan et al. Effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in diabetic rat heart. National Library of Medicine, 2005. Web.
Ozyurt et al. “Protective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.” Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 292.1 (2006): 197-203. Print.
Park, Saul, and Min Tom. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester ameliorates changes in IGFs secretion and gene expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. National Library of Medicine, 2005. Web.
Peng et al. Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Inhibits Oral Cancer Cell Metastasis by Regulating Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway. Hindawi, 2012. Web.
PubMed Health. Uveitis. National Library of Medicine, 2005. Web.
Racchi et al. “Alzheimer’s disease: new diagnostic and therapeutic tools.” Immunity & Ageing 5.7 (2008): 1-7. Print.
Roos, Thomas. “The polyphenols resveratrol and caffeic acid phenethyl ester: their influence on growth-related signaling pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells.” SIGILL, (2006): 1-135. Print.
Toyoda et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), a nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor, on Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis in Mongolian gerbils. National Library of Medicine, 2009. Web.
Understanding Inflammation. Understanding Inflammation. The Exercise Coach, 2012. Web.
Wang et al. “The effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on the functions of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells.” BMC Immunology 10.39 (2009): 1-13. Print.
Yilmaz et al. Effects of Caffeic acid phenethyl acid on endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats. National Library of Medicine, 2005. Web.