- Introduction
- The Issues of Medication Compliance in Australia
- Description of the System Design
- The Major Components of the System
- The Intended Users of the System
- Interface Changes to Accommodate Different Users
- Design Innovation that Enhances the Efficient and Safe Practice of Managing
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The problem of insufficient patients’ compliance to the medication regimens remains a burning health care issue in Australia. Millions of patients miss their medications on a regular basis that leads to the worsened patient outcomes and increased costs of care. The following project will observe the scope of the problem along with its causes and will provide the IT solution applicable to the needs of both patients and health care providers.
The Issues of Medication Compliance in Australia
Patients’ incompliance with medication is as dangerous and costly as the majority of illnesses (Currie et al., 2016). Medication compliance in patients in Australia is connected with the following major issues:
- missing medications in case of relief;
- poor knowledge of certain medicines storage rules (Grover, Armour, Van Asperen, Moles, & Saini, 2013).
One of the health issues that illustrate the situation is asthma. Since asthma is a chronic condition, it cannot be fully cured but it can be significantly improved if properly managed with the help of medications (National Asthma Council Australia, 2014). In Australia, asthma is getting a health issue of special concern given that over two million people are already affected by the disease (National Asthma Council Australia, 2014).
Moreover, the rate of asthma incidence in the country is one of the highest in the world (National Asthma Council Australia, 2014). Asthma is also a huge concern in the youngest age category since one of eight children is likely to be diagnosed with this disorder at a certain moment of their lives (Grover et al., 2013).
According to National Asthma Council Australia (2014), over fifty percent of patients having asthma reported to have over one case of medications missing a week during the periods of relief. Over thirty percent of these patients stated that they lacked knowledge on proper storage regimen for keeping their asthma drugs (National Asthma Council Australia, 2014). The example of asthma medications demonstrates that patients with the chronic illnesses tend to forget to take their medicines quite often. Research conducted by Currie et al. (2016) supports this conclusion by stating that patients with acute illnesses have higher adherence rates to the medications they have been prescribed.
Overall, insufficient adherence to medications in Australian people causes further problems decreasing effectiveness of the country’s healthcare system including complications, poor therapeutic outcomes in patients, and low degree of care cost-effectiveness (Hatah, Braund, Tordoff, & Duffull, 2014). The problem is especially the case in the rural southern territories of Australia (Hatah et al., 2014).
Description of the System Design
In order to provide a solution to the problem of insufficient compliance to the medication regimen in Australian residents, this project aims to offer the IT system application for the use by both patients and health care professionals. This application will target the main problems and barriers that prevent patients in Australia from being fully complaint to their medications.
The major problems associated with patients’ incompliance to medicines are forgetfulness and loss of medical scripts. Another problem that is in connection with the issue is poor knowledge of storage techniques by patients with the lack of medical knowledge. The outcome of this problem is the loss of the medical value of a drug, and therefore, even if the patient continues to use this drug timely, the benefit is reduced.
Other common barriers include language barrier, insufficient education and especially insufficient education in the area of health care and health promotion, and ineffective patient-doctors communication (Schrijvers, Uitslager, Schuurmans, & Fischer, 2013). To address these problems, the application design will be maximally simplified and laconic to make it easy to use to all clients. This is especially the case for the patients’ menu to allow them convenient usage of the tool even if they have poor knowledge of medical terms as well as if they have language barriers. Another option the system will provide is using the application for all family members. As such, one account will provide a chance to serve all family members who will like to do so.
The purpose of the application is to provide the patient an opportunity to connect one’s primary care provider and pharmacist when consultation is needed and ensure the client does not miss the due time to take the medications prescribed. In the application interface, the data on all medications prescribed to every specific client is available along with the time and dosage of its use and the remaining period of its intake. In addition, with the use of this application, a client may connect one’s pharmacist to inform that he or she got low of the medicine and intend to come to borrow ore on a specific date agreed.
Approaching this application from the point of view of a physician, its benefit is an option for the patient’s care provider to see all the medications one is currently on to avoid any side effects and possible threats. In addition, the application will provide a health care provider with an option to fill in the information regarding the complication and side effects the patient had as a result of therapy with certain types of drugs. This option will help the specialist to make the right decisions in future to avoid the side effects and choose the medication proving the optimal outcomes for each particular client.
The Major Components of the System
The major components of the offered system are the main interface with the two buttons for patients and for medical specialists. Appearing in their menu, the patients find the options they may use including the list of their medications, the time of intake, the remaining period of medication, the dosage, and an option to connect the care provider, and pharmacist (see Fig. 1).
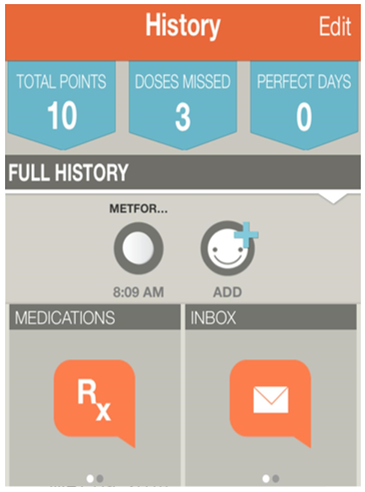
The menu for the health care providers will make available the options to overview the profiles of their patients that contain data on all the medications they are currently on, the status of their compliance to the medical regimen, and a way to connect the patient online along with one’s personal contacts including the phone number and home address.
Addressing the algorithm of the application usage, the user will need to choose one’s account, then one will need to proceed to the current date, and he or she will see the list of medications for the current moment. History of medications intake can also be seen as well as the history of communication with the care providers and pharmacists. In addition, the application will provide a clear plan of medicines intake along with the dosage and timing if more than one medicine is used at the same time.
This solution is very important for the chronically ill people who may miss their medications due to the complexity of their treatment regimen and multiple components it may include. The patient interface will have the option to change the user if one account is shared by more than one family member. At that, upon the user request, privacy settings can be installed on the account so that the client could choose an option of not allowing other family members navigate through one’s account.
For clients to modulate the emergency issues when they appear in the circumstances when the energy charging is unavailable or similar issues of electronic devices usage arise, the application system features an option of generating the list of medication for the chosen time period and sending it to printing. This solution appeared to be helpful for users as it was demonstrated by the situations when people survived a natural disaster, fire or other emergency situation and were left without electricity for some time (Berry & Schleser, 2014).).
The Intended Users of the System
The intended users of the system are patients, physicians, and pharmacists. While patients are the primary clients the system is intended for, physicians and pharmacists can also benefit from using the system by having the stable connection with their customers and tracking their adherence rates to the prescribed medication regimen. In addition, the patients’ family members may have access to the system to extend help to their aged or somehow disabled family members in remaining adherent to their medication regiment despite the limitations their condition may place on them.
Interface Changes to Accommodate Different Users
The system will have two different interfaces: one for the patients and one for the physicians and pharmacists. The patients’ interface will have more options aiming to make it convenient for the user to keep on track of one’s medication regimen, while the health care providers’ interface will be focused on tracking the patients’ adherence to the medication regimen, communicating with them, and storing data on the side effects of particular medications the patients have identified.
Besides, the health care providers will be able to keep the record of the dates when patients will need the refilling of their drugs. In addition, physicians will be able to trace the information on patients’ allergies, as well as they will always have access to other useful data on the patient profile such as emergency contacts or patients’ professional status to make sure the chosen medicine corresponds to the client’s needs.
Design Innovation that Enhances the Efficient and Safe Practice of Managing
Medication Compliance
The design innovation that enhances the efficient and safe practice of managing medication compliance is the elaboration of the application design in such a way that allows using it with the help of a variety of IT devices ranging from the smartphones and ending with desktop computer. The smartphones of various kinds are the primary intended devices for this application. However, research on the availability of such devices in Australian families demonstrated that in the older users, these devices may not be readily available (Berry & Schleser, 2014).
Since these users are also the most active users of medications because their health condition is vulnerable to the higher number of threats, it is important to develop the versions of these applications for other devices such as lap tops of desktop computers.
Another innovation option for the application is the improved security system that will allow a better level of information protection. Australian legislation has the strict regulations as for the patients’ personal information protection. To meet these requirements and address the advancements made by security hackers, the application will implement the sophisticated system of data encryption utilized in combination with the encodings program component installed on user accounts. This barrier aims to hamper the hackers capable of unlocking the user accounts with the technique of password selection since even if they are able to enter the personal cabinet they will need a decoding component to be installed on their device.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it should be noted that patients’ insufficient adherence to the medication regimen remains the central health care issue that affects the health of the nation as well the health care cost effectiveness in Australia. The problem is especially serious in the patients who are on medication due to the chronic conditions as compared to those that take drugs due to the acute problems. This project has observed the illustration of the state of affairs with the patients who have been diagnosed with asthma.
To provide assistance to the patients, physicians, and pharmacists, this paper has proposed an application aiming to help each participant of the medication process achieve better results. The offered system has the two types of interfaces: the patients’ interface and health care providers’ interface. Each of these system components has addressed the needs of the categories of users mentioned above correspondingly.
References
Berry, M., & Schleser, M. (Eds.). (2014). Mobile media making in an age of smartphones. Sydney: Palgrave Macmillan.
Currie, C. J., Peyrot, M., Morgan, C. L., Poole, C. D., Jenkins-Jones, S., Rubin, R. R.,… & Evans, M. (2012). The impact of treatment noncompliance on mortality in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 35(6), 1279-1284.
Grover, C., Armour, C., Van Asperen, P. P., Moles, R. J., & Saini, B. (2013). Medication use in Australian children with asthma: user’s perspective. Journal of Asthma, 50(3), 231-241.
Hatah, E., Braund, R., Tordoff, J., & Duffull, S. B. (2014). A systematic review and meta‐analysis of pharmacist‐led fee‐for‐services medication review. British Journal Of Clinical Pharmacology, 77(1), 102-115.
National Asthma Council Australia.(2014). Australian Asthma Handbook – Quick Reference Guide,Version 1.0. National Asthma Council Australia, Melbourne. Web.
Schrijvers, L. H., Uitslager, N., Schuurmans, M. J., & Fischer, K. (2013). Barriers and motivators of adherence to prophylactic treatment in haemophilia: a systematic review. Haemophilia, 19(3), 355-361.