A macroeconomy is initially in equilibrium but not at full employment.
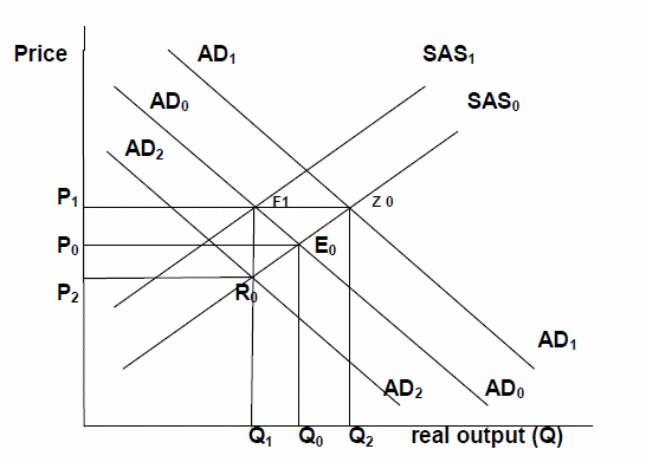
Where
- P: price,
- AD: aggregate demand,
- AS: Aggregate supply
- R0, E0, and Z0 refers to short-run equilibriums.
An increase in international oil prices
In figure 1, the economy is in short-run equilibrium at the point E with quantity Q0 and price P0 an increase in international oil prices has the effect of shifting the aggregate supply curve inwards and to the left. The aggregate supply curve will, therefore move from AS0 to AS1. Oil is an input good; many consumer goods and services use oil or oil products as inputs in the production process. When the global price of oil increases, therefore, producers of the final goods and services are forced to cut on the supply at all existing price levels.
It is the decrease in aggregate supply that is arising from the increase in the price of oil that shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve SAS0 inwards to the left to SAS1. The overall output level reduces from Q0 to Q1. The decrease in the level of output will push up prices from the original P0 to a new price P1. There is a shift in the short-run equilibrium from the original E0 to the new F1 (Barro, 2008).
An Appreciation in the Value of Foreign Exchange Rate of the Local Currency
When a countrys domestic currency appreciates, it becomes expensive relative to the other currencies. This, in turn, implies that for the other countries to buy its exports, they have to incur an extra cost because the local currency becomes dearer. On the other hand, imports to the country, become less expensive as the a given volume of the domestic currency can buy more of the other countrys products and services (Boyes & Melvins, 2010).
Because the exports are more expensive, less of the local goods and services are exported at the same time imports into the country will increase (net exports decrease). Given that net exports are a function of aggregate demand, the total demand in the economy reduces, causing an inward shift in the total demand curve from AD0 to AD2. Suppliers of goods and services will react to the fall in demand by reducing both the general price level for goods and services (P0 to P2) and the volume of output (Q0 to Q1). A new level of equilibrium is attained in the short-run (F1).
America falls back into recession
The effect on the local economy will depend on whether America is a major trading partner or not. If it is a major trading partner, the recession in America will result in a drop in the aggregate demand for goods and services as the disposable income reduces, less of the local countrys exports will be demanded. This has the effect of the shift in the aggregate demand curve to the left from AD0 to AD2. Because supply exceeds demand, prices will drop from the original P0 to P2 at the same time, output reduces from Q0 to Q2.
The country’s main exports fall in price while the goods the country imports from abroad rise in price
From a macroeconomics perspective, the net exports of a country (exports – imports) form part of the aggregate demand. As a result, a fall in the relative price of exports will make the countrys exports more attractive, thereby increasing the net exports and real gross domestic product. At the same time, the increase in the price of imports makes the imports more expensive and therefore there less is demanded. Overall, the countries net exports will increase, thereby increasing its real gross domestic product. The total demand shifts to the right from AD0 to AD1, and the price increases from P0 to P1 the real GDP increases from Q0 to Q2. The economy attains a new short-run equilibrium at the point Z0.
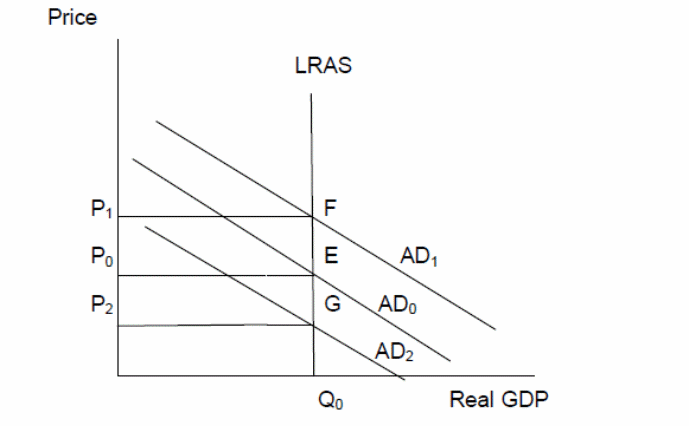
Where:
- LRAS- the long-run aggregate supply,
- AD- aggregate demand,
- G, E, F-long run equilibriums
- P- is the price level, and the economy operates at full employment (Arnold, 2010).
Effects Of Oil Price increase in the long run
In the long run, real GDP is a function of factor inputs (capital and labour). Price, therefore, does not affect the long-run output; hence the long-run supply curve is vertical, and the economy operates at full employment (Arnold, 2010). Because the price has no effect on the long-run supply curve, we can conclude that oil price increases in the world market have no effect on the long-run equilibrium.
LR appreciation of the local currency and recession in America
The economy is initially at equilibrium at point E, when the value of the local currency appreciates, imports increase and exports reduce simultaneously. The net export is a component of aggregate demand [(C + I + G + (X -IM)]. Therefore, when net exports reduce, the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left from AD0 to AD2, the price reduces from P0 to P2 while the real output level remains fixed at Q0. The effect is the same when America falls into a recession.
LR fall in export price and rise in import price
The increase in net exports (X-IM) will boost the total demand in the economy. The aggregate demand curve will shift outward and to the right from the original AD0 to AD1. This increase is accompanied by a rise in the price level from the initial P0 to P1. The rise in price leads to inflationary pressures in the economy in the long-term.
References
Arnold, R. (2010). Macroeconomics. New York. NY: Cengage Learning.
Barro, R. (2008). Macroeconomics. New York, NY: Cengage Learning.
Boyes, W. & Melvins, M. (2010). Macroeconomics. New York, NY: Cengage Learning.