Abstract
Softwood Limited has internal and external sources of funds available for expansion. Each source comes with costs and specific bottlenecks. In addition, each has a unique impact on the company’s financial statements. Bank loan seems more attractive than other sources in terms of the amount that can be raised. A financial plan is fundamental to the planned expansion. The firm should efficiently manage cash, debtors, creditors, and inventory to avoid income flow problems. The machine supplied by XYZ limited is suitable because it adds value to the shareholders. Softwood’s financial position in terms of efficiency, profitability, and gearing has improved. However, the company’s liquidity is at stake.
Introduction
Expansion of a firm can be very costly. Softwood Ltd. desires to expand its business to cover the international market. Funds are needed to modernise and expand its operations. The expansion process should be carefully planned to ensure success. The firm should consider the effects of the various available financing options bearing in mind the need to increase the shareholders value.
Sources of Finance for the Business
The company has two broad sources of finance at its disposal: internal and external sources. The major internal financial resources include debt collection, sale of inventory and non-current assets, and retained earnings (Dlabay & Burrow 2007). As at December 2013, Softwood Ltd. had trade receivables amounting to £350000. As such, the debtors can be used to generate short-term finance for expansion.
The company’s inventory and net non-current assets by the end of 2013 were valued £312000 and £1735000 respectively. The stock would provide quick short-term finance, while the fixed assets would cater for medium-term financial needs (Dlabay & Burrow 2007). By the close of 2013, the firm had £860000 as retained earnings. Softwood Ltd. can use the same for short term financing of the expansion initiative.
Softwood Ltd. can benefit from various external sources of finance. They include equity, bank loan, leases, hire purchases, and trade credits (Dlabay & Burrow, 2007). The company also has the option of authorising and issuing more shares. The two partners can invest personal funds in the firm or allow other investors to come in.
Softwoods Ltd. can also engage in lease financing, which is an external source of funds. The strategy brings together the property owner, the lessor, and the person paying for the right to use it [the lessee] (McLaney 2006). In this arrangement, the company will pay periodic payments (lease rental) in exchange for the right to use plant or machinery.
The firm has two leasing options available. The two are operating and finance leases. The former runs for a short term, usually less than the asset’s economic life. In addition, the lessor services the equipment and retains ownership. The lessee services the asset and has a buying option.
Softwood Ltd. has the option of engaging in hire purchase or trade credits as external sources of finance. The former is an instalment credit where the asset’s ownership passes to the hirer upon settling the last payment (Neff 2003). The firm can also consider expanding its trade credit. The option is short-term finance, usually payable within thirty days.
Implications of the Different Sources of Financing
The various sources of funding options available for Softwood Ltd. have different implications on the company’s business. For instance, retained earnings are suitable because no cash payments are required. In addition, they do not involve issue costs associated with debentures and new shares (McLaney 2006).
Reinvestment of profit has opportunity cost implications. It denies the providers of equity dividends. As such, managers need to convince the common stockholders to accept reduced dividends. The cost of finance generated from within the company is less costly compared to external sources. However, the number of funds raised through internal sources may be limited, creating the need for external financing (McLaney 2006).
Bank loans may be the short or medium term. The company will be more dependent on borrowings today than it was in the past. A raised debt-equity ratio implies declining financial stability. There also exists long-term bank lending (mortgage), usually for the acquisition of property. If the firm opts for the bank loan, the debt-equity will rise (McLaney 2006).
Issuing shares will affect the ownership structure of the company. Issuance of equity would lead to dilution of control. The current shareholders will have to share ownership and control with the incoming investors. In relation to leasing finance, the lessee charges rentals on the income statement. The finance lease proportionately increases the total assets and liabilities. Nevertheless, the company’s gearing level will rise. In addition, the company may incur lease rentals, as well as repair and maintenance costs, depending on the leasing option (Neff 2003). Trade credits are suitable for cash flow management without interest charges. Overreliance on this source of financing may lead to liquidity problems (Dlabay & Burrow 2007). If the current liabilities are more than half of the current assets, the firm may run bankrupt.
Appropriate Sources of Finance for Softwood Ltd.
Considering the various costs associated with financing options, Softwood Ltd. can combine more than one source of finance. Recommended alternatives for the company include long term bank loans and issuance of shares. Long term loans provide the desired finances in a timely manner, depending on the agreement with the lending bank. In addition, the issuance of shares is suitable since the company is looking towards a larger market. Venturing into the international market may eventually necessitate Softwood shareholders to relinquish some of their ownership rights or share them with other stakeholders.
Cost of Different Sources of Finance
As a source of finance, debt collection is not associated with any costs. However, the amount of funds that can be raised through this option is very limited. In addition, receivables can only be used in the short run. Like debt collection, sale of assets hardly involves any costs. However, this approach will not raise adequate funds to pay for the plant.
Retained earnings are suitable because no cash payments are required. In addition, the earnings do not involve issuance costs associated with debentures and new shares. Issuance of common stock would require Softwood to pay dividends to the investors. Furthermore, the firm would have to incur issue costs.
Reinvestment of profit has opportunity cost implications. It denies the providers of equity dividends. Softwood Ltd. will incur interest charges on the bank loan. In addition, the company may have to use its non-current assets as collateral for the loan. Lease finance and hire purchase are expensive. The company pays more for these options than for cash purchase. If the firm opts to expand through trade credit, it will have to forfeit trade discounts (Dlabay & Burrow 2007).
Importance of Financial Planning
A financial plan is the pillar of prosperity in business (Dlabay & Burrow 2007). It is a road map for the company’s financial affairs. It gives the firm a long-range view. Since it is long-term oriented, a financial plan will enable Softwood Ltd. to plan for investments that will enhance expansion.
Financial roadmaps also enable a firm to continually improve and gain a competitive edge. In essence, the plans are vital for cash management, especially in projected expansions. The plan will help Softwood Ltd. to deal with the cycles associated with revenue generation. It will shield the firm from cash constraints. Furthermore, it will enable the company to establish a cash reserve. The reserve will help Softwood to exploit opportunities that may emerge in the future (Neff 2003).
Financial planning helps managers to set measurable targets that can be compared against actual results during the operating year (Neff 2003). The plan helps the manager to keep track of the firm’s revenue under specific strategies. The trends in revenue will consequently assist the manager to efficiently allocate selling and marketing expenses. A sound financial roadmap will help the manager to identify the most relevant expenditures. Such expenses can enhance efficiency, improve productivity, and support market penetration. In addition, planning is essential to the prioritisation process.
Lack of a financial plan exposes a company to strategic, compliance, financial and operational risks (Dlabay & Burrow 2007). Strategic hazards are associated with working in a certain industry. For instance, a lack of financial planning may lead to hostile mergers and take-overs. Compliance risks, on the other hand, involve the failure to abide by the laid down laws and regulations. Companies have to meet the financial obligations related to employment, tax, health, and safety. Financial planning helps a firm to comply with these provisions.
A firm’s financial structure and transactions system expose it to fiscal risks. Such hazards include problems related to cash flows, interest and exchange processes, an over-dependence on one client. Lack of a financial plan makes it impossible for an enterprise to prioritise operational and administrative processes (McLaney 2006).
Information Needs of Various Decision-Makers
The management at Softwood Ltd. requires information on the company’s assets, liabilities, equity, income, expenses, and cash flows. Information on the prevailing and projected industrial and economic growth rates and changes is also essential in financial planning. The two sets of data will help the manager to make realistic projections of the firm’s income, financial position, and cash flow statement (McLaney 2006). In addition, the administrators require this information to ascertain past and present performance and project future goals.
Various stakeholders in Softwood Ltd. will require a variety of financial information from the company. For instance, investors and trade partners expect to be supplied with the balance sheets, cash flow statements, and profit and loss accounts. The information will help them determine whether or not to invest in the company. Accountants also require this data. The professionals provide the managers with baseline financial information needed to make decisions. Financial information is also needed by other stakeholders interested in the company. The stakeholders include competitors, the government, and suppliers.
Impact of Sources of Finance on Financial Statements
Debt collection will reduce the number of trade receivables and increase the cash or bank balance held by the company. The balance sheet figure will remain unchanged. However, if the company uses retained earnings, the available cash will be used to acquire the machinery. In the balance sheet, the number of fixed assets held will increase, while the total equity will diminish (McLaney 2006).
The bank loan will increase the company’s liabilities in the balance sheet. Softwood will have to pay interest on the loan. The interest will be charged on the income statement. In addition, the cash received via the loan will be reflected in the cash-flow statement’s financing activities section.
Similarly, the finance lease will increase the liabilities, both current and long-term, in the balance sheet. The firm will be charging lease rentals and repair and maintenance costs on its income statement. The finance lease will appear in the financing activities section of the cash-flow statement.
The hire purchase arrangement will also increase the liabilities held by the firm. The company will be charging the instalments, repair, maintenance costs, and depreciation on the income statement. In addition, the trade credit option will raise the current liabilities owing to the firm in the balance sheet (McLaney 2006).
Cash Budget Analysis
Workings
Receipts from Sales
Purchases Payments
Variable Cost Payments
Fixed Expenses Cost Payments
Softwood Ltd.
Cash Budget for Twelve Months Ending 31st December 2015.
Healthy cash flows are crucial to the success of Softwood Ltd. The financial planning software will be vital in monitoring the company’s inflows and outflows (Ehrhardt & Brigham 2008). Cash flow management starts with an analysis of how the firm manages cash. A number of factors are taken into consideration with regards to the administration of cash flow. They include creditors, credit terms, debtors, and inventory. Once the manager obtains a comprehensive view of the company’s cash management, they should expedite the collection of inflow and delay outflows as much as possible. Improvements should be made on debt collection by making payment easy for the clients, as well as developing credit and collections policies.
The management of accounts payable can be improved by paying on time and extending and spreading payment schedules. Lastly, the firm should manage its inventory by monitoring daily sales and ensuring the inventory held matches the prevailing patterns (Hansen, Mowen & Guan 2007).
Establishing the Unit Cost
Working: Softwood Cost Statement. For the Year Ended 31st December 2015.
Unit Cost = Total Cost/ Annual Production
= £ 7605000/ 25000
= £ 304.20
The unit cost established above includes both variable and fixed expenses. At an annual output of 25000 units, Softwood should not price its furniture below £304.20.
Investment Appraisal
Option 1: ABC Ltd.
The firm’s discounted cash flows from operations within the next 5 years are as follows:
XYZ Ltd.
The firm’s five-year discounted cash-flows are as follows:
XYZ is the best supplier. Its machines generate positive net present cash flows at £165925. It improves the shareholders’ wealth and the firm’s market value. The machine from ABC Limited should be rejected because it gives rise to negative present cash flows (Lumb & Jones 2001).
Financial Statements
The primary function of income statements is to establish the net revenue generated during the financial year. The statement of financial position shows the assets held and the liabilities and equity used to finance the property. The receipts and payments are identified in the cash flow statement (Pizzey 2001). The format of a financial statement varies depending on the ownership structure of a given entity (Geddes 2002). The income statement of a partnership includes an appropriation section that shows how the profits are shared among the partners. A company’s declaration shows the dividends earned by the shareholders.
The statement of financial position in a partnership includes current accounts in the capital section. The accounts are used to adjust changes in capital. The statement of changes in equity is only prepared by limited liability companies. The cash flow declaration prepared by companies may include receipts from the share issue.
Comparative Financial Analysis
Financial reports differ from one company to the other. Four reporting formats are commonly used in contemporary organisations. The first is the balance sheet. It is used to reflect the financial status of the company. Others are income and cash flow reports. Finally, there is the statement that highlights changes in equity. The balance sheet indicates the financial position of the company at a particular date (Weygandt, Kimmel & Kieso 2007). It reflects assets, liabilities, and equity. Income statements communicate the company’s performance in terms of net loss or profit over a specified duration. Key elements include income and expenses.
Cash flow statements indicate the movement of cash and bank balances over a defined period of time (Weygandt et al. 2007). The movements are sorted out into operating, investing, and financing activities. The statement of changes in equity highlights the status of owner’s equity over time (Weygandt et al. 2007). It includes share capital repaid or issued during the duration and dividend payments. Net losses or profits and gains or losses in equity are also included. Impact of changes in accounting policy and correction of accounting errors are shown in this statement.
Businesses owned by single individuals do not require complex financial reports. The reason is that the information is meant for the owner only. The business structure is not complex, and income and balance sheets are not mandatory. Financial statements for partnerships and companies are prepared based on international standards.
In limited liability companies, financial reports serve a number of purposes. For example, they show current and non-current assets held by the company. They also show the profits made and any debts owed to the firm. Partnerships also make use of financial statements. They are used to show the profits generated and earnings made by investors. The statement reflects balance sheets, cash flow, and income declarations.
Interpretation of Financial Statements
Gross profit margin

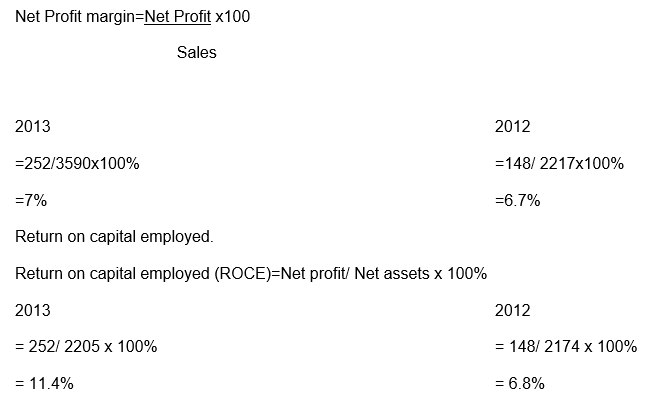
Net profit margin
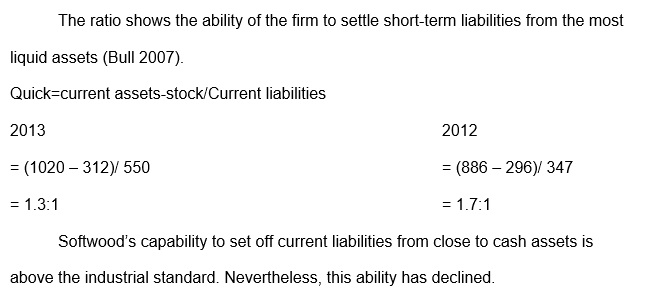
Current ratio

Quick ratio
Stock days
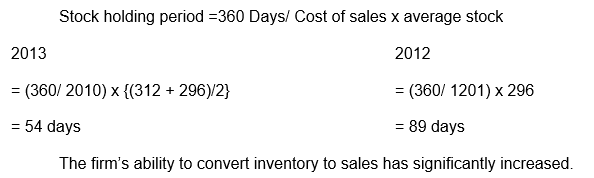
Receivables days

Debt-equity ratio

Conclusion
The planned business expansion is reasonable. The manager’s resolve to explore the sources of finance available to Softwood is needed to maximise the wealth of shareholders. Ratio analysis points to a stable financial position.
Recommendations
Softwood should finance the machine using bank borrowing. The machinery should be bought from XYZ Limited. The managers need to closely monitor the firm’s cash flows in the future.
References
Baker, H & Powell, G 2009, Understandingfinancialmanagement: a practical guide, Blackwell Publishing, Oxford.
Bull, R 2007, Financial ratios: how to use financial ratios to maximise value and success for your business, Elsevier, Oxford.
Dlabay, L & Burrow, J 2007, Business finance, Thompson, South-Western Australia.
Ehrhardt, M & Brigham, E 2008, Corporate finance: a focused approach, Cengage Learning, Mason.
Geddes, R 2002, Valuation and investment appraisal, Financial World Publishing, Canterbury.
Hansen, D, Mowen, M & Guan, L 2007, Cost management: accounting and control, Cengage Learning, Mason.
Lumb, S & Jones, C 2001, Fundamentals of investment appraisal, Thomson Learning, Pennsylvania.
McLaney, E 2006, Business finance: theory and practice, Prentice Hall, New Delhi.
Neff, C 2003, Corporate finance, innovation, and strategic competition, Springer, Berlin.
Pizzey, A 2001, Accounting and finance: a firm foundation, Cengage Learning, Mason.
Rohrich, M 2007, Fundamentals of investment appraisal: an illustration based on a case study, Textbook International, Oldenbourg.
Tracy, A 2012, Ratioanalysis fundamentals: how 17financial ratios can allow you to analyse any business on the planet, Elsevier, Oxford.
Weygandt, J, Kimmel, P, & Kieso, D 2007, Accounting principles, Wiley, Oxford.