Introduction
Usually, a baseball with 216 raised and red stitches is thrown by a pitcher and then when the ball reaches the batter it curves and the batter then swings. The question that comes around is why did the baseball drop and what usually happens after the ball is thrown and goes right across the air?
Analyzing things
The first thing is to analyze how the ball was thrown and what kind of spin. The characteristic that features as the ball moves across the air, for example, curves, the slide has to do with the drag force or the air resistance. A result of spinning a ball creates the curveball. Games such as baseball would have been dull if there were no curves, knuckleballs, or sliders.
Usually, perception plays a great role in the throw of a curveball. Usually, there is a deviation of about 3.4 inches between the throw and the home plate. But, from the perspective of the batter and pitcher, the ball to them deviates 14.4 inches. This then shows the ball usually curves.
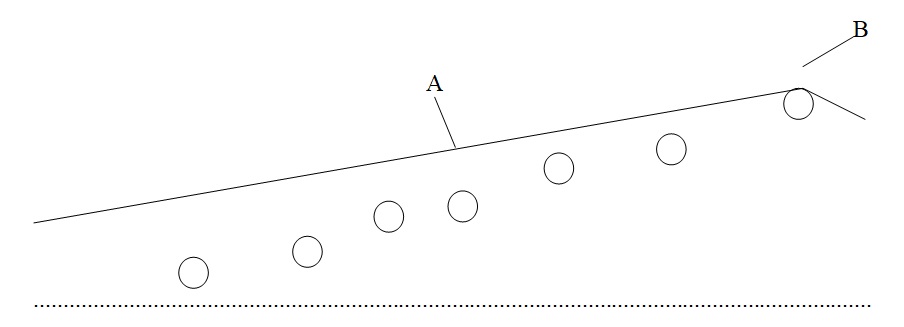
This is the trajectory of a curve ball which is thrown from a right handed pitcher to a batter.
- A: This is the maximum deviation from the straight line which is usually halfway from the pitcher to the home plate; it’s usually approximately 3.4 inches.
- B: This is the deflection at the home plate and is approximately 14.4 inches.
The story of the curveball is usually credited to Brooklyn Excelsior’s pitcher called Arthur “Candy” Cummings. He introduced a new thrown move called snapping the ball as he released it. This he did by snapping his wrist hence putting a spin on the projectile. When the ball moves against the air it causes an air stream which splits it into two lines one curving over the ball and the other under the ball.
When the ball is thrown it moves against the wind and at the top of the ball, it moves clockwise. This causes drag which increases the pressure, hence, forcing the ball downward. The lower point of the ball moves with the direction of the air stream causing low pressure and an increase in velocity. This then makes the ball be pulled downwards.
When the curveball is projected it moves both in rotation and translational velocity which then combines to produce pressure difference which occurs on both sides of the ball and this creates a lateral force called the Magnus effect. Usually, when an object moves through the air, the surface of the ball interacts with a thin layer called a boundary line. This then creates a low pressure or a wake region behind the moving ball. But, when the ball is moving, there is a point difference on the opposite sides of the ball.
There is an asymmetrical wake behind the ball due to the reflection on the flowing air sideways. A sideways deflection in the trajectory is observed when there is supposed to be equal and opposite momentum, this is so since energy cannot be destroyed or created. The phenomenal is directly depending on angular velocity vector, air density, cross-sectional ball area, and velocity vector.
Physics principles
There are a lot of important principles of physics that are usually associated with a curveball. This includes Bernoulli’s principle, Newton’s Third Law, and the Magnus effect. Newton’s third law states that “For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction” (Stan, 2002). In curveball, this rule is usually important because when the ball moves forward, there is a drag effect that slows down the curveball. On the other hand, Bernoulli’s principle states that “as the speed of moving air or water increases, the pressure within the fluid decreases”, (Johnnie, 2003). This then means that the curveball curves because there is an imbalance in pressure on each side or part of the ball. Magnus effect states that “for a spinning ball, the stitches on the ball will cause pressure on one side to be less than on its opposite side”, (Pijush, 2004). This effect is usually important since the stitches usually cause velocity which is higher on one side of the curveball, due to the imbalance of pressure will force the curveball to move to the side where the pressure is less.
Following the effect of air pressure and gravity, the curveball will fall due to a decrease in velocity. A pitcher usually applies a force that will make the ball reach the batter but it will be influenced by the force of gravity which will force the ball to go down. Usually, gravity makes associated objects go faster over certain periods. This means that when the ball tends to reach the home plate it curves downwards. A throw that drops half a foot after covering the have distance will fall another two feet when it reaches the second half. Usually, the pitcher is standing on the nearly one-foot mound which makes him a foot up than the batter.
Magnus force usually works on the principle of whether the air above it is laminar or turbulent. This then means that even if there is an increase of velocity during spinning it doesn’t affect Magnus’s force. When the ball velocity increases the air above the ball is laminar and after some time it changes to turbulent. This is due to the density and viscosity of the air and also the shape and the roughness of the ball. The turbulent air decreases the drag resulting in lower Magnus force. This usually occurs when the ball is nearing the home plate, hence, increases the drag. Then, the Reynolds number is usually used to show the point when the air turns turbulent.
An example of Magnus force calculation. In this case, the K coefficient is 2*10⁻⁶ and the velocity of the ball is 90 mph. The drag coefficient is 2 and the spin frequency is 1500 rpm.
Applying the Magnus formula:
F mag = K w V c = 2*10⁻⁶ * 1500 * 90 * 2 = 2 * 10⁻⁶ * 270,000 = 0.54
Conclusion
In the movement of a baseball, there is a lot of physics associated with the said movement. This includes various known laws and principles such as Newton, Bernoulli, and Magnus. Magnus force comes to frequent use in curveball through in terms of laminar or turbulent. When the Magnus force is less than the weight of the ball, then the ball will move upwards, else, vice versa. For this law to effectively take place the type of air stream should be considered and the type of the throw. If the ball doesn’t curve it is called a hanging ball. This type of ball is easily hit by the batter.
References
Damon, R. Guys, Dolls, and Curveballs: Damon Runyon on Baseball, New York: Caroll & Graf, 2005.
David, M. Physics for Game Developers, New York: O’Reilly, 2001.
John, R. Curveballs: Wacky Facts to Bat Around, California: Little Brown & Company, 1990.
Johnnie, T. The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Physics, London: Alpha Books, 2003.
Pijush, K. Fluid Mechanics, New York: Academic Press, 2004.
Stan, G. Physics Demystified, New York: McGraw- Hill Professional, 2002.