Introduction
The Ministry of Justice is one of the most important organs of the government in the United Arab Emirates. The ministry is headed by the minister of justice, Sultan Saeed Al Badi (Ulrichsen, 2017). The main responsibility of this ministry is to oversee operations of the court system in a way that would ensure that all residents of the UAE could have justice within the shortest period possible. The body appoints judges, prosecutors, translators, and other legal experts needed in order for the court system to function normally (Grose, 2016). Operations within the ministry have evolved over the years as it moves towards technology-based data management systems to help improve efficiency in its operations.
The analysis of the firm’s operations identified the problem within the firm to be the poor thought process that lacks creativity and innovation. It was evident that the ministry has a rigid system where everyone is expected to follow a specific pattern of undertaking their responsibilities, leaving little room for them to embrace innovativeness. Most of the new decisions at this government department are often made by senior officers.
Woolcock, Pritchett, & Andrews (2017) explain that creativity and innovativeness are not defined by one’s position in an organization. Sometimes the best idea may be given by some of the junior employees within the firm. As such, when the system fails to allow these junior officers to express their views freely, then creativity would become less common, as witnessed in this ministry. The current lack of creativity means that this organization would end up ignoring international best practices that can lower the cost of operations and improve efficiency.
The purpose of this report is to define three ways that the ministry can use to solve the identified problem. The researcher seeks to find creative problem-solving processes that the department can use to address the concern. The context of this problem solving is to create a system that would promote creativity within this organization. The pertinent issue has been identified as a rigid system that makes it impossible for the department to embrace creativity in its operations.
The main constraint the department may face when trying to address the problem is the strict culture. Grose (2016) explains that local culture defines the relationship between junior employees and top managers. As such, the targeted audience is the top ministry officials who have the power to create an environment where junior employees can try new practices in their operations without fear of being punished.
Analysis of the Problem
The process of selecting the problem was based on the views of members of the public about the performance of this department. It was considered appropriate to select an issue that has a profound impact on the overall performance of the company. The lack of creativity and innovativeness in the thought processes of the company was considered a significant problem because it denies it the opportunity to cut the cost of operation and improve efficiency in its operations. Ulrichsen (2017) explains that in modern society technology plays a critical role in lowering the cost of operation. However, it is not easy for an entity to embrace emerging technologies if it has a rigid system of operation.
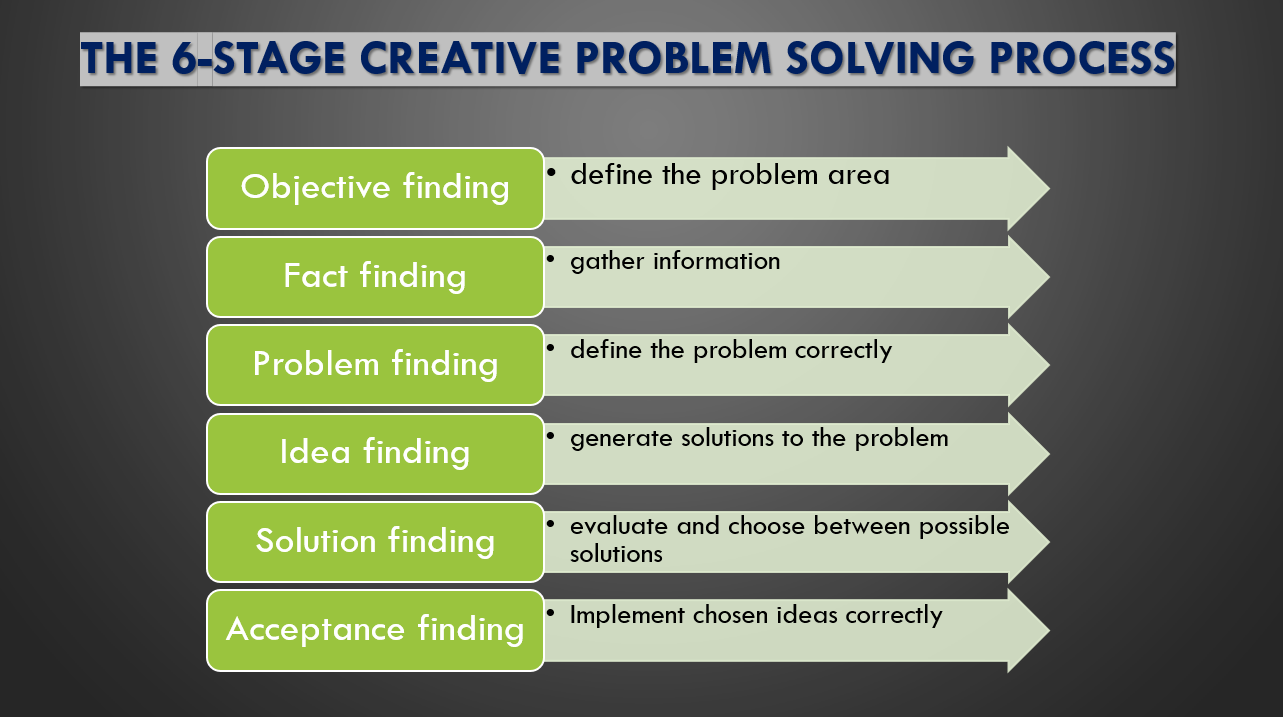
When conducting a critical evaluation of the identified issue with this ministry, it is necessary to use methodological approaches to problem-solving that would highlight steps the management can take to find an effective solution. The 6-stage creative problem-solving process was considered the most relevant methodology that can be used to define and address the identified problem. This method identifies six stages that should be used to define and solve a problem within a given organization.
The first step is the objective finding where the relevant stakeholders are expected to define the problem area. As Scherdin (2016) observes, it is important to have a clear definition of the problem and areas that it affects. In this case, lack of creativity and innovativeness has been identified as the problem, and it affects almost every department within the Ministry of Justice.
The second step is fact-finding, where the problem-solving team is expected to gather relevant information from various sources. In this case, the team should find reasons why the ministry has failed to embrace creativity in its operations, and how the situation affects the normal operations of the ministry. It may be appropriate to define the financial and operational implications of the problem. The third stage is problem finding, where the team is expected to redefine the problem correctly based on the facts gathered. The team would go beyond stating the problem to identifying specific individuals or systems within the organization that has perpetuated the problem. In this case, an organizational culture that limits the ability of employees to try new processes was identified as the main problem that had to be addressed.
The next stage is idea finding, where the team is expected to generate solutions to the identified problem. Grose (2016) explains that when trying to find a solution, it is important to take into consideration the facts gathered. The proposed solution should directly target the source of the problem. If organizational culture was identified as the main source of the problem, the solution should focus on transforming it. In some cases, it may be necessary to propose two or three ways of solving the problem. The benefit of proposing more than one way of addressing the issue is that it gives the concerned parties different options that they can embrace to solve the problem.
The fifth step is to find the solution, which involves evaluating the provided alternatives and choosing the most appropriate one. When the management is offered two or more alternatives for solving the problem, it is expected to evaluate each one of them and select the one that they consider would work most effectively based on internal factors. As Scherdin (2016) observes, the management understands the internal system and can effectively evaluate different alternatives to select a method that would be less costly and easily acceptable to all or most of the stakeholders. Reasons why one is selected and others are rejected should be explained to ensure that the method receives the support of both junior and senior employees within the ministry.
The last step is the acceptance of the finding, where relevant officers would be expected to implement the chosen ideas correctly. At this stage, the team is expected to start by explaining to all the stakeholders why a given method of solving the problem was chosen (Vanfraechem, Pemberton, Ndahinda, 2014). The stakeholders will only accept the proposal if they feel it would improve operations within the ministry. Once the approval is given, the next important and sometimes challenging step is the implementation. The team will be tasked with actualizing the idea and ensuring that it delivers on its promise. Grose (2016) advises that such a stage may require the use of change management models to ensure that the transition is smooth and with the expected implications. The six stages are summarized in figure 1 below:
Creative Ideas for Problem Solving
When the problem is clearly defined, the next step is to find effective ways of solving it. Woolcock et al. (2017) argue that it is important to define creative ideas for solving the problem in a way that would have the desired impact. In this case, the researcher has identified three ways of solving the problem of lack of creativity and innovativeness in the thought processes at the company. The three solutions include brainstorming among all the stakeholders to find a mutually acceptable solution, embracing best practices that similar government departments have created in different parts of the world, and methods of thinking that specifically involve policy development by senior officials in the Ministry of Justice. It is necessary to discuss each of the three scenarios.
The first scenario involves inviting all the stakeholders to be involved in the process of solving the problem through a brainstorming process. Given a large number of employees in this ministry, it is not possible to have everyone in one forum. Instead, it would be necessary to have small manageable teams in different departments within the ministry discussing the problem and proposing possible ways of solving them.
Each of these small units can then select a representative that would represent their views to senior managers for the purpose of policy-making. This alternative is justifiable in a situation where there is the likelihood that stakeholders may reject policies they consider unfavorable to them. Involving them in solving the lack of creativity at the firm makes it possible for them to own the whole process. They will feel that the new policy is based on their views and that they have an obligation to support it.
The main challenge of using this strategy is that it may take a long to find an effective solution to the problem because of the large number of stakeholders involved (Woolcock et al., 2017). However, the team can address this challenge by ensuring that the problem is clearly defined and the desired solution clearly stated so that these stakeholders can have an understanding of what is expected of them. In such a way, it will take two to three forums for the stakeholders to share their ideas and come up with the best ways of solving the problem.
The second strategy of solving the problem is to embrace best practices that similar government departments created. According to Scherdin (2016), in the current globalized society, it is often advisable to monitor and understand what others are doing in a better way so that one can learn from them. The problem of lack of creativity and innovativeness in thought processes within the Ministry of Justice can be solved by reviewing what other countries are doing.
According to Grose (2016), the United States has one of the most robust justice systems where the independence of the judiciary is respected and views of different stakeholders are rarely taken for granted. The United States Department of Justice is also known for its creativity and ability to address different issues that emerge in society. The UAE’s Ministry of Justice can learn from the best practice presented by the US Department of Justice. It can borrow some of the policies in the country and find a way of making them relevant in the local context. The main challenge when using this strategy is that the socio-cultural and political system in the United States is significantly different from that in the United Arab Emirates.
Some policies may work in the US but may not be effective in the UAE (Balakrishnan, Moonesar, Awamleh, & Rowland-Jones, 2017). This problem can be addressed by modifying the borrowed policies to ensure that they reflect the local socio-cultural, political, and economic environment in the country.
The third alternative is to embrace methods of thinking that specifically involve policy-making by senior officials in the Ministry of Justice. This strategy is the direct opposite of the first proposal. Instead of allowing all the stakeholders to participate in finding the appropriate solution, senior ministry officials will be assigned that responsibility. The problem has already been identified as the lack of creativity and innovativeness in the general operations of the firm.
These officials would be required to address it. They can propose redefining the organizational culture to create room for junior employees to try new systems and practices as a way of promoting creativity. They can also propose the creation of innovation centers within the ministry where all stakeholders, irrespective of their positions, can share their ideas on how to improve operations within the firm. In these centers, the new ideas can be developed into policies and strategies that the ministry can use to transform its operations. The main challenge that the ministry can face when using this strategy is that junior employees may feel ignored.
They may feel that the ministry does not consider their views important. The problem can be solved by proposing policies that promote stakeholder involvement in future policy implementations. When they realize that the proposed solution creates room for them to be involved in future policy development, they will be less likely to reject the solution.
Conclusion
The Ministry of Justice plays a critical role in the socio-economic development in the United Arab Emirates. The government has remained committed to ensuring that the department is fully equipped and properly staffed to meet its obligations. It is unfortunate that a section of the community feels that it lacks creativity and innovation in its thought processes. In this study, the researcher has identified and explained the problem in detail, and proposed possible solutions, which would redefine the organizational culture and stimulate creativity and innovation within the department. The study has identified three possible solutions that this ministry can embrace.
First, it can involve all the stakeholders in different departments and units within the ministry to propose ways of solving the problem based on specific challenges that they face in their normal operations. Secondly, this department can embrace international best practices. The United States Department of Justice was identified as a good example that this ministry can learn from in an effort to promote creativity and innovativeness. The last strategy is for the top ministry officials to enact policies that would promote flexibility. The study has suggested the creation of an innovation center within the ministry to help nature new ideas.
References
Balakrishnan, M.S., Moonesar, I.A., Awamleh, R., & Rowland-Jones, R. (Eds.). (2017). UAE: Public policy perspectives. Bingley, UK: Emerald Publishing Limited.
Grose, M. (2016). Construction law in the United Arab Emirates and the Gulf. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Scherdin, L. (Ed.). (2016). Capital punishment: A hazard to a sustainable criminal justice system? London, UK: Routledge.
Ulrichsen, K.C. (2017). The United Arab Emirates: Power, politics and policy-making. New York, NY: Routledge.
Vanfraechem, I., Pemberton, A., Ndahinda, F.M. (Eds.). (2014). Justice for victims: Perspectives on rights, transition, and reconciliation. New York, NY: Routledge.
Woolcock, M., Pritchett, L., & Andrews, M. (2017). Building state capability: Evidence, analysis, action. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.