A problematic situation relevant to the workplace
I will be relating my understanding of workplace metaphors to the organisation where I have been working for the past three years, the Student Support Centre at City University, London. The Student Centre affords academic services like free consultation and tuition to a campus of about 7,000 students. Here racial minorities are about 23% and 48% are females. Very specifically my role in the organisation should focus on the Additional Instruction program.
There is a necessity at the institute to amplify student retention. So, the institute has taken up this academic assistance program. The program objects classes, which are usually hard for students to pass. Being an Additional Instruction (AI) leader, my function is to act as a “model student”. I go to class, read consigned material and prepare notes then I conduct out-of-class group learning sessions. In this session, I help the group to progress with the course material. In support of the last two years, I have been serving as an AI leader targeting the course Management 214.
In the first observation of the physical ambience of the room where I work, anyone can suppose that it’s a casual place of learning. The room accommodation in the Student Support Centre is grand sized. Dozens of tables and chairs are detached all the way through the room in order to have room for more than a few tutoring groups at the same time. The walls are decorated with pictures and sporting inspirational quips which are motivational to students.
Table and Chairs are in large quantity and can be grouped together to lodging either big or small groups of students with short notice without any difficulty. Blackboards can be stimulated around to meet specific tutorial group needs. Thus, it has become a confidential intimate and informal area where students can conduct a tutorial session for their development. This assists in maintenance with the trust that the Additional Instruction sittings be supposed to be casual and informal.
Outsized casement with changeable blinds let for the proper light to filter through. The wall carpet grants warmth and lessens absorbs sound. As a whole, the physical surroundings let somebody to inviting a contented and homely impression that would be encouraging to student learning. The casualness of the big room is unlike the more structured classroom environment. Hence custody with the organisation cultural certainty that out-of-class learning assisted by the ’peer leader’ is less unfriendly and more favourable to student learning.
In the organisational surroundings where I work, the right of entry to funds and money is inadequate. There is scarcity, especially to allocate something as needed frivolous for the program. However, it’s accurately that my supervisor does. She positions for herself and all the AI leaders to overcome on an all-operating cost paid trip/workshop typically to a very tempting locale in the city, where we have to travel. This is moderately consideration that we are part-time transitory workers.
There are numerous part-time employees functioning at the university in many other departments. Some of them even working with the same ability those educational assistants have. But none of the groups enjoys such privileges and benefits as them. How is my boss competent to obtain this trip? The response lies in the acceptance and use of organisational basis of power.
Let’s investigate the source of recognised power my supervisor owns. She holds charisma, warmth and grace persona characteristics. She is methodically liked and appreciated by her associates, personnel and students. She has grained several exceptional employee awards from the organization as well as some other community awards. This individuality seems to justify her weight to exercise some authority in influencing to approve these trips.
Major and Minor Metaphor Relevant to the Situation
The temperament and task of organisational metaphors are that they allow us to enhanced understanding of organisations and management. Applying the metaphors to real existence workplace situations polish our capability to competently and spontaneously create a wide range of options and potential interpreting and resolving organisational problems.
The Major perception of the organisation as an organism metaphor is to understand the significance of the organisation and its correlation to the environment. In other expressions, the metaphor appreciates that the organisation is an open system. It is like liquefied and persistently undergoing alteration in affiliation to its surroundings. This can happen externally and internally. The metaphor is applicable and can be supported where I work. For example, the City University has taken into deliberation the demographics and requirements of the population to whom it affords education.
On a greater level, the academy has taken the external temperament of the environment into deliberation. Evidence of this is its expansion to the Bar Vocational course. The university is providing training and teaching in a field that is increasing and growing among the general population. More legal professionals will be in demand to care for boomers. On a more internal level, the college recognises that many of its students, in order to be accepted into such programs as legal professionals must first complete courses, which are typically difficult. In operating the AI program, the university has taken up a new innovative strategy that renovates the normal way students are taught and be taught.
The program aimed at high-risk courses to a certain extent than high-risk students. The AI program objects to those classes where 40% or above of the students fail. As a result, fulfilling a need to assist the students to pass the class. They also learn precious study practice and skills, which would maintain them motivated to continue their studies. This will revolve around boosting student enrolment and tuition dollars.
The school proclaims that the AI program optimistically influences not only individual students but extensive organisational development as well. This unremitting exchange with the environment has allowed the college to be distinct as an ‘open system’ where the connection between the environment and the internal implementation of the system is accepted as being symbiotic. There is a state of communication and mutual reliance in a situation where the university needs student and earnings tuition dollars to be succeeding. Students needed to be unbeaten in their academic activities in order to struggle in the job market. The AI program helps the university to uphold a ‘good fit’ among the organisation and its environment.
The psychic prison metaphor of the organisation discovers the avenues of instinctively trapped by exacting ways of thinking hence making change difficult. This metaphor looks into the hidden human psyche of the insensible mind in order to appreciate a certain magnitude of organisational life. One can pertain a psychoanalytical, Freudian perception of analysis to be aware of how employees’ individuality traits have a consequence on the organisation.
The culture metaphor describes an organisation as an extremely survival cultural phenomenon. The organisations should expand a culture based on similar factors that organisations particular stage of growth, know-how and yet its history. Within the organisation, subcultures should begin, and outline of culture will be shaped through the assembled realities of the members who share knowledge viewpoint, dreams and day-to-day practice.
The trait that constructs the culture metaphor is that organisations will develop a distinct type of corporate culture. The convinced aspects of culture are as values, beliefs, norms and even language should form an outline of shared meanings that give an organisation a separate personality. The information about the organisation’s corporate culture can be achieved by observing its day-to-day performance.
The organisation’s own unique cultural flavour is formed with the everyday life experiences of the people in it. In order to investigate the culture metaphor of my existing workplace at the Student Support Center, I would go to check up its daily representation like values, norms, images, beliefs and physical impressions to find out the culture programmed in the organisational philosophy.
Selection & Justification of the Methodology to Resolve the Problem
The first issue in this question concerns to the conceptualization of problematic situation that is relevant to the workplace. For instance, Skarlicki, F. et al (1999) refer to the problematic situation as a disciplinary behaviour enacted in response to an unjust situation. On the other view, Robinson & Bennett (1995) has described the problematic situation of the workplace as a socially abnormal response that violates organisational norms and terrorises the welfare of the organisation. Robinson et al (1995) and Neuman and Baron (1998) recommended that problematic situations of the workplace consist of an interpersonal and an organisational aspect. R. J. Bennett & Robinson (2000) has presented a two-factor model based on the scheme that there are expected to be different correlates of individual and organisational objectives.
Douglas & Martinko (2001) and Hepworth & Towler (2004) have sustained to merge interpersonal and organisational dimensions of problematic situations of the workplace. More likely Lee & Allen (2002); Miles et al (2002) and Spector & Fox (2005) have supported the specific nature of the workplace would provide an effective solution by System of Systems Methodologies (SoSM).
The System of Systems Methodology (SOSM) is considered to have the temperament of the pecking order with the system of System Engineering (SE) as a sub-system of SOSM. SOSM methodology applies to problem situations in which interests conflict exists. In SOSM methodology, the interest coordination process replaces the learning process of Checkland’s Soft Systems Methodology (SSM). SOSM is comprehensive throughout addition to ISSM and system group of problems situation stand on the origins. Subsequently, I use extensive SOSM to make a straight Total Systems Intervention (TSI) to Additional Instruction (AI) of Student Support Centre (SSC) at City University, London project where I work with. This has examined the theory and promoted the project liveliness as well.
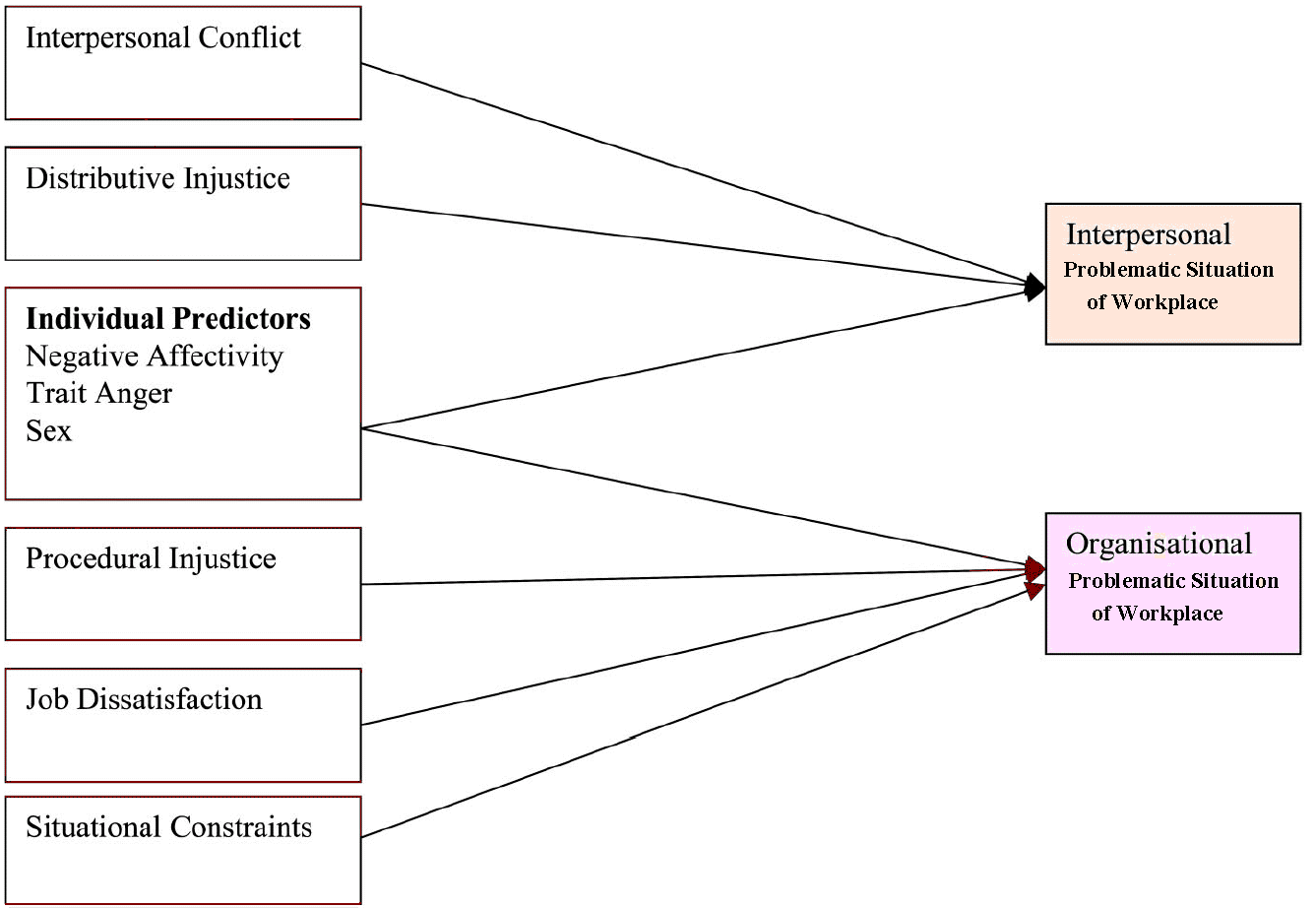
Individual and Situational Predictors
Douglas & Martinko (2001) have investigated concerns about the relative significance of individual factors in predicting workplace situations. Individual differences refer to stable personality traits and other factors that differ between people. Shoda & Mischel (1993) have shown that individuals do have stable predispositions to engage in certain behaviours that the manner in which an individual interprets a situation can vary as a function of these stable individual differences, suggesting an important role for individual differences in predicting workplace aggression.
Thus, the predictive role of individual and situational variants in explaining workplace situations leads to the target-specific situation put forward to the target specificity applies to situational variables. Individual variations are not aggravations rather reflect factors that predispose behave in certain ways in a workplace situation.
Individual Differences
Trait anger Theory linking anger to aggressive behaviour is the predisposition to respond to situations with hostility. Douglas & Martinko (2001) have provided both theoretical and empirical support for the link between trait anger and workplace situation. People high in trait anger are likely to be more easily provoked because of their tendency to perceive situations as frustrating.
Negative affectivity
Watson & Clark (1984) have presented Negative affectivity. It imitates the degree of individuals experience upsetting emotions like hostility, anxiety and fear. Individuals high with negative affectivity are additional sensitive and also more reactive to the negative events. Berkowitz (1993) argued that although people act aggressively when they feel bad (state negative affect), those who are high in negative affectivity likely have the proclivity to feel bad more often. If a transitory negative affective state is related to aggression, then those with a more permanent negative disposition may also experience state negative affect more often. Therefore, we would expect negative affectivity to be positively related to aggression.
McFarlin et al (2001) shown in their studies that men are more antagonistic than women. Douglas et al (2003) have shown no important relationship between aggression and sex. On the other hand, Namie & Namie (2000) show that woman is more aggressive than man. Although Bettencourt & Miller (1996) mentioned that man is more destructive about sex. There are situations in which this dissimilarity dissipates, such as the tendency to aggress beneath provocation.
Situational Factors
In contrast to individual differences, as suggested earlier, situational predictors trigger target-specific aggression, and we now discuss the theoretical relationships between each predictor and its hypothesized target (see Figure 1). Distributive injustice. Distributive injustice reflects the perceived unfairness of outcomes. Adams (1965) argued that when individuals perceive their outcomes to be unfair in comparison to referent others, they attempt to restore justice. One method of restoring justice is to reduce inputs (organisation-targeted aggression) or act in a counterproductive manner to rebalance the input-output ratio (Cohen-Charash & Spector, 2001). In contrast, Aquino et al (1999) found that those who feel that their distributions are inequitable are likely to respond to the source of the decision and target the person responsible for the unjust distribution.
Interpersonal conflict
As a workplace stressor, interpersonal conflict refers to discrepant views or perceived incompatibilities between two or more individuals (Boulding, 1963). Aggression is one way of coping with stressors, and research has shown that people are likely to respond to aggression with aggression.
Discussion of the Use of Methodology in Practice
Morgan (1986) and Flood & Jackson (1991) have identified that people raise systems by the metaphor that makes people distinguish the diverse systemic features of an organization. Generally used five metaphors are machine, organic, cultural, neuro-cybernetic and political metaphors. Furthermore, the political metaphor has more sections as team, coalition and prison metaphors.
Our present principal systems methodologies have followed by System Engineering (SE), Systems Dynamics (SD), Systems Analysis (SA), Operational Research (OR), Viable Systems Diagnosis (VSD), Social Systems Design (SSD), Socio-technical Systems Thinking, General System Theory (GST) Strategic Assumption Surfacing and Testing (SAST), Contingency theory, Interactive Planning (IP), and Critical Systems Heuristics (CSH).
To solve the problem, the foremost complexity people always face to use systems methodology is that they cannot choose the proper methodology. In practice, different methodologies communicate with different system metaphors. So proper selection of methodologies can solve a particular problem situation.
The physical measurement and participants’ dimension of the problem situation create SOSM. The SE subsystem is relevant to the simple and unitary problem situation and is parallel to the machine & team metaphor. SOSM is measured having nature of hierarchy with the top stage of it includes SE, SSM, VSD, CSH, etc. On the other hand, SE and SSM etc. comprise their methodologies of inferior levels. That resources the system of SE is just a sub-system of SOSM.
Flood and Jackson (1991) have presented their TSI as based on system metaphors and SOSM. In 1995 Flood further enhanced it. The circular illustration of logical steps of TSI comprises three phases, i.e., creativity, choice and implementation.
The task of the creativity phase is to use systems metaphors as put in order structures to help managers think imaginatively about their enterprise. The task of the “choice” phase is to choose the main and subordinate methodologies that correspond to the system metaphors. During the implementation phase, the assignment is to use the chosen methodologies to interfere with the problem situations and create the proposals of organization reforms.
Problem situations of SSC of City University, London may include problems of Human Activity System (HAS), especially of soft HAS [2] as well as man-made system and viable system. So” total systems intervention” should be used to the SSC of enterprises. Using the extended SOSM, the authors of this paper make practical guidance to the implementation of an SSC project in City University, London.
Categories of systems and HAS
Prof. Checkland classified systems into categories of natural, man-made, human activity, etc on the basis of their origins. He thought the goal of a human-made system is clear; HAS has its purpose but its goal is not clear. However, from the viewpoint, if there is an interests conflict then the reason for a HAS is not clear either. On this basis, the concept of soft HAS is presented. Different systems methodology should be used to deal with different systems problems, so a new methodology is needed to face the problem of soft HAS.
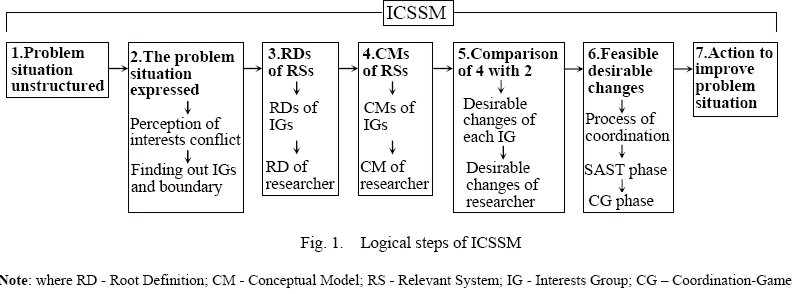
Interests-coordination SSM
ISSM applies to problem situations in which interests conflict exists. In ISSM, the learning process of Checkland’s SSM is replaced by the interests coordination process. Fig1 shows the logical steps of ISSM. The key step of them is the phase of a coordination game, which could be one of the two alternatives, i.e., with power intervention or without power intervention, depending on whether or not there are common top leaders of the game-players.
Furthermore, the phase with power intervention could be one of the two types by the difference of whether or not the top leaders of enterprise themselves are a game-player. And, the phase without power intervention could be that of a cooperative game or non-cooperative game. Game equilibrium is the result all game players have to accept in the situation, it has the coercive character
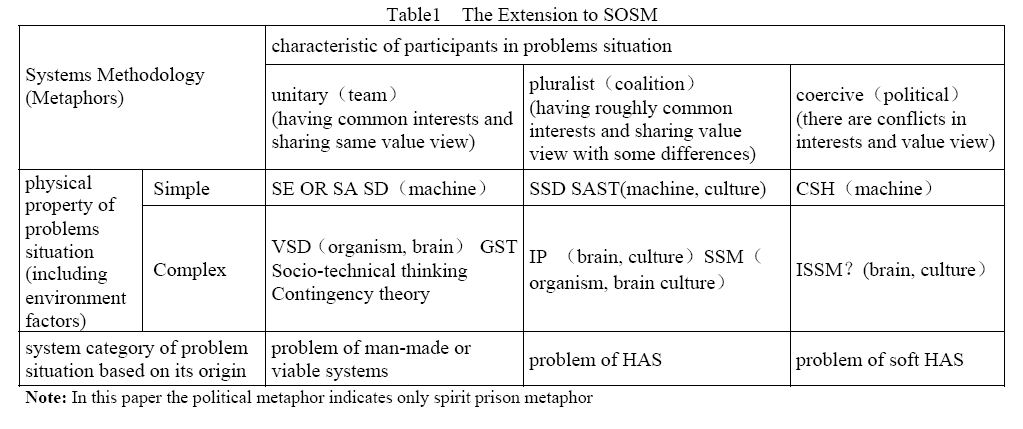
The extension to SOSM
The extended SOSM is shown in Table 1. SOSM is extended through supplementation of ISSM and system category of problems situation based on the origins. In this paper, problem situations are categorized into dimensions of the physical property and of participants’ characteristics. In table 1 listed are system methodologies and their metaphors. ISSM is put into the problem situation grid that corresponds to the complex, coercive, and problem of soft HAS.
References
Flood R.L., & Jackson M.C. (1991), Creative Problem solving: Total Systems Intervention, Chichester: Wiley.
Checkland P. (1981), Systems Thinking, Systems Practice, Chichester: John Wiley & Sons.