Physical geography
According to the report of Library of Congress (4), this country occupies about 647500 square km; however, the following table gives more information about physical geography –
Table 1: physical geography. Source: Self generated from Library of Congress (5).
Demography
Birth Rates, Death Rates and Natural Population Growth Rate
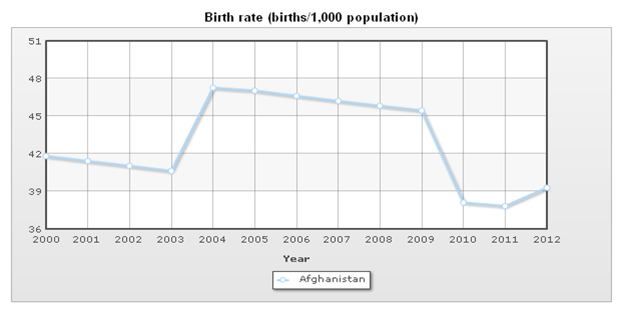
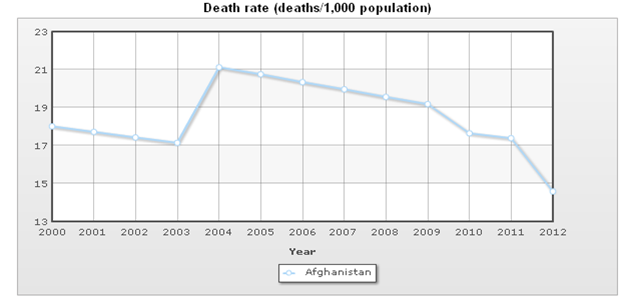
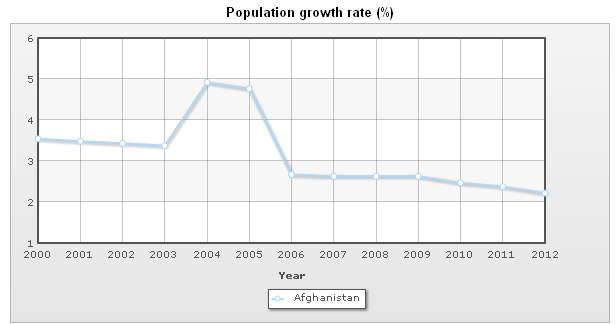
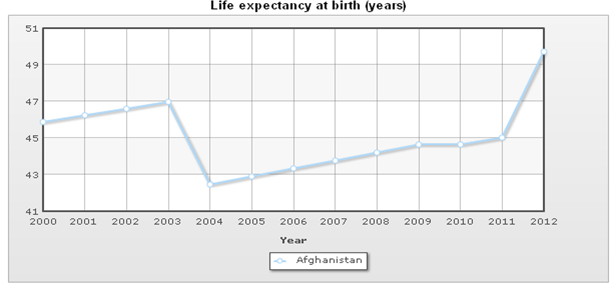
Population pyramid dynamics
Table 2: Population pyramid dynamics. Source: Self generated from Indexmundi (1).
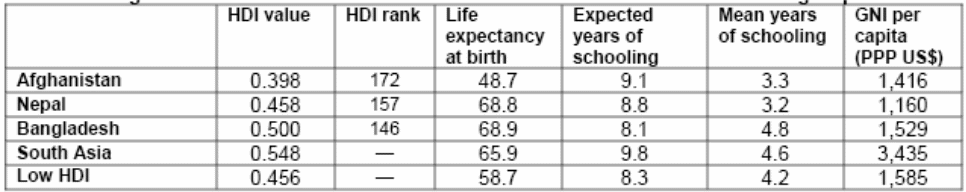
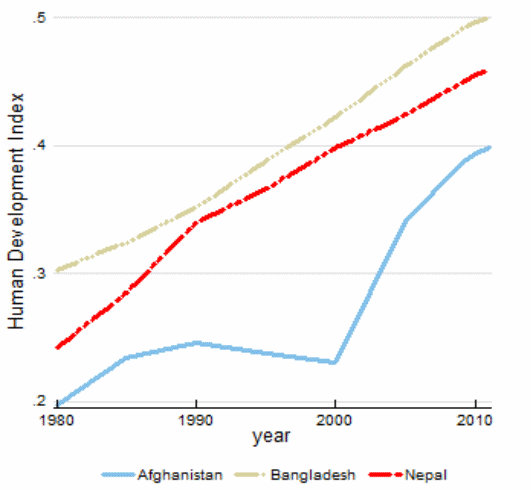
Human Development Index
Health risks
According to the report of Library of Congress (7), health system of this country collapsed from the beginning of 1980s because of military conflict however, health risk is too high because there are only 11 doctors and 18 nurses per 100,000 populations; in addition, malnutrition is pervasive and 800,000 Afghans are disabled.
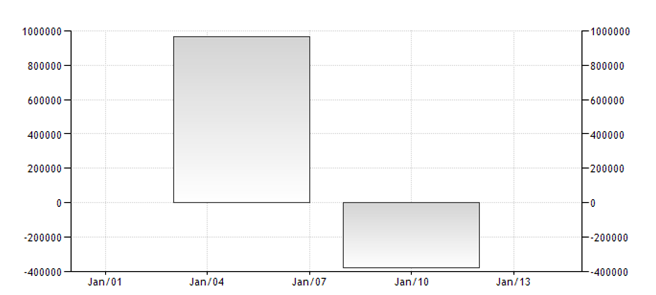
Net migration in Afghanistan
Historical and cultural geography
The country has a long history of feudal monarchy, Soviet backed socialism, and US backed democracy along with struggle against terrorism that is destroying the civilization of the country where the administrative unites correspond to the geographic boundaries, strategic topography, natural borders along with the landmarks that encompass overall resource sharing of the state.
From the terrorist attack in the WTC in September 2001 brought a number of unfortunate events for Afghanistan, in the name of fight against terrorism and to finding Osama Bin Laden, the multinational force destroyed its sovereignty, human rights, while the terrorist groups like Taliban and Al-Qaeda have been increasing from the suppressed civilians Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Table 3: Ethnic Group and Religion. Source: Self generated from Indexmundi (1).
- Language: It has about 30 languages (Dari and Pashtu are the official languages);
- Buzkashi is a vital element of the culture
- Eid Al-Fitr and Eid Al-Adha are the holy days of Afghans
- Food: Afghanistani cuisine
Political Geography of Afghanistan
Duncan, Johnson and Schein (501) pointed out that the contemporary theories of international relations defined political geography as a sub-discipline of human geography that dealt the social interaction, space of physical implication, political identity and the extent of power in the scale of geography and such area of political geography has identified as a vital geopolitics.
The interaction of political geography is not the direct concern of the state, but a small network of major actors of the elite class like foreign diplomats and local bureaucrats who perform in favor of the state would like to recognize their functional values and power in context of geographical identity and it makes geographical reality easy knowledgeable to the people.
On the other hand, under the present unipolar power practice of the United States made it difficult to uphold the local political and economic interest in the international relations of developing countries, rather the geopolitical interest of the USA for natural resource exploitation or strategic location of future securities define the boundaries of political geography in third world countries.
Miakhel (17) explored that provinces are the fundamental unite of administrative function and there are 36 provinces and 364 districts along with 217 provincial and rural municipalities and all of them are divided into geographical locations based on the tribal structures inherited from the ancient socioeconomic culture of this region.
Each province consists of several districts, a provincial municipality while the districts are established with several village council, and at least one rural municipality are represented by the local tribal leaders and to some extents, there are very conscious initiatives to put into practice of democracy at this root level.
Economic geography
Library of Congress (9) reported that the economic position of this country was in unstable position while it faces numerous severe financial challenges, such as, require to replace the earnings generated by opium production, smuggling mainly across the Pakistan border, provincial disparity of wealth, disproportionate monetary growth in Heart, and the threat of social unrest could endanger the present government.
On the other hand, Indexmundi (1) stated that until last quarter of 2001, the Taliban ruled more than 90% of Afghanistan, but after falling of Taliban, the national economy of Afghanistan has recovered and developed significantly after a long conflict due to infusion of international assistance though it is still landlocked, and extremely reliant on foreign aid.
At the same time, Department of Immigration (2) disagreed with such statement arguing that Afghanistan is the poorest country in the world because its infrastructure and agricultural segment have damaged due to conflict, which reduced gross domestic product per capita; therefore, more than six million Afghan refugees failed to recover their financial position after returning to Afghanistan.
Purchase Power Parity (PPP) analysis
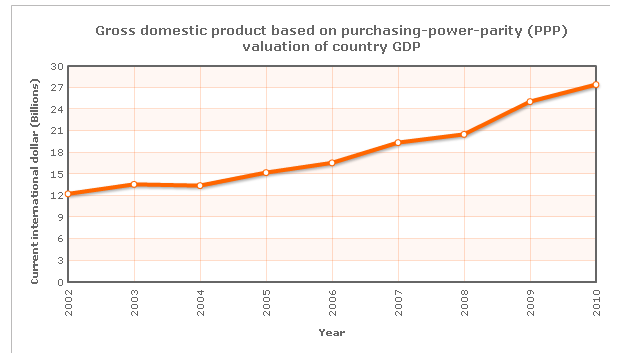
Table 4: Gross domestic product of Afghanistan. Source: Indexmundi (1).
Economic Diversification
Agricultural Sector: The World Bank (1) addressed that this sector is the foundation of Afghanistan’s economy while more than 70% of total population live in rural areas; therefore, the national economy based on the agricultural sector and approximately 50% of total national GDP (80% of the workforce employed for the development of this segment).
At the same time, the World Bank (1) reported that agricultural production growth rate is too slow due to the poor quality of most agricultural land (merely 7.8 million hectares of land is arable and merely 40% of total agricultural land is irrigated); however, Library of Congress (10) stated that agricultural production amplified due to foreign aid along with increased rainfall in 2003, which influenced the farmers to cultivate more areas.
In addition, Library of Congress (10) further stated that this sector incurred a number of problems, such as, limited water supplies, delays in the restoration of irrigation systems, severe grain shortage, import reduction, and intensified violence.
Industrial Sector: Griffin (1) stated that industrial sector of this country was in infant stage though the government provided high priority on industry; at the same time, Library of Congress (11) argued that all productions had stopped from 2004 as a consequence of war damage and lack of raw materials; however, only carpet industry experienced success in 2007.
Library of Congress (11) estimated that about 1 million people engaged in carpet industry; however, some small textiles, leather goods, and processed industry become successful in spite of substantial corruption in this segment.
Services Sector: Library of Congress (11) further stated that banking system collapsed during the civil war; therefore, many farmers had relied on opium for credit, which influenced the government to take initiatives to pass new laws to rebuild banking system though these initiatives failed for inadequate security conditions, smuggling and other illegal economic activity.
Works Cited
Department of Immigration. Country Profile 2012 of Afghanistan. 2012. Web.
Duncan, James. Johnson Nuala and Schein Richard. A Companion to Cultural Geography, Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2004. Print.
Griffin, Luke. Industry. 2012. Web.
Indexmundi. Country Profile 2008 of Afghanistan. 2012. Web.
Library of Congress. Country Profile 2008 of Afghanistan. 2008. Web.
Miakhel, Shahmahmood. Understanding Afghanistan: The Importance of Tribal Culture and Structure in Security and Governance. 2009. Web.
The World Bank. Afghanistan: Priorities for Agriculture and Rural Development. 2012. Web.
Trading Economics. Net migration in Afghanistan. 2012. Web.
UNDP. Afghanistan: HDI values and rank changes in the 2011 Human Development 2011. Web.