Human Threats
There are three main types of human threats:
- Intention:
- Occurs as a results of human activities;
- Accidental:
- Occurs due to inevitable causes;
- Negligent:
- Occurs as a result of failure to do what is expected. Negligent of responsibilities.
Human beings are constantly exposed to many different types of threats. These threats can be classified into three categories (intentional, accidental, and negligent). Intentional threats are intended by human beings on other human beings. The most commonly known intentional threat is terrorism where terrorists attack nations which they are exposed to. Intentional threats normally causes a lot of harm because they are aimed at specific points where the population is believed to be concentrated
Accidental threats occurs due to causes that are beyond human control. Examples of such threats are floods, earthquakes and fires. Just like the intentional threats, the accidental threats causes a lot of harm to both property and living things including human beings and animals.
Negligent threats results from failure of human beings to carry out their responsibility in a professional manner.

Intentional human threats
- Occurs due to human activities.
- Aimed at causing fear on a nations capital.
- Normally occurs between different nations or among citizens of the same nation.
- Enhanced by technology.
- Leads to destructing of both human and property.
- Reasons for causing intentional threats include
- Anger;
- Revenge;
- Injustices;
- Political ambitions.
Intentional human threats results from intended human activities. They are normally caused by one nation over another or may occur between members of the same community. Within a country, intentional threat may result from regional disputes or irregularities in election procedures. The main objective behind intentional threats to attract attention of the general public and to dominant in the news. The common example of intentional threats is terrorism. This occurs when one nation attacks another nation that is believed to a certain aspect that the terrorist are interested in. People who are injured in such an attack are just victims of the circumstances but are not usually the point of interest.
People who cause intentional threat normally use advanced technologies and equipments for instance the use of nuclear power weapons by terrorist.
Anger can be one of the reasons that can influence people into causing threats. Anger may result of land dispossessions, murder, or even exploitation. This is quite evidence among communities normally faced with land disputes and dispossessions which may at times results into use of violence causing death. Another major cause is revenge, for instance if a country is terrorized by another it may choose to fight back by using even more advanced weapons. This results into more threats between the two countries which can only be solved through mutual agreements. Intentional threats also occurs when a specific group of people feel that they are being exploited and are not treated fairly. When this happens, they may choose to use violence as a way of driving their point home. Other reasons include political ambitions.


Example of intentional threats
- The major examples of intentional threats include:
- Worker’s strike aimed at causing damage to property;
- Terrorism;
- Fire.
As seen earlier, intentional threats are aimed at attracting attention is case of anger, exploitation, or injustices. One major example is employees threatening to strike because of poor working condition, or for salary increase. If such behavior results into mass damage, then employee strike becomes an intentional threat. Another very common type is terrorism, this occurs between nations that are not in agreement with each other or can be caused by a specific group of people, for example, the AL Qaeda. Fire can fall under the category of intentional threat, accidental, or can results from negligent. In the next slide, I will explore more on one example of intentional threat, that is terrorism.

Terrorism
- The use of power on people or property.
- A political tactic used by terrorist.
- Terrorists are agents of terrorism.
- The major goal is to exploit the media and gain control over the news cycle.
- Victims are just objects of exploitation used to transmit information to the target group (Crenshaw, 1995).
- Presently, there is the threat of use of nuclear weapons by terrorists.
Criminologists’ define terrorism broadly as the use of violence on people or property for political reasons. It’s the act of causing terror or fear upon the citizens of a particular nation. It’s a political tactic used by terrorist when they believe that there is no other better way to accomplish their desire. Terrorists are the individuals who practice terrorism, they can also be referred to as the agents of terrorism since they attack nations they are opposed. Terrorist targets specific group of people whom to their belief have a connection to a certain view of the world that they posses. The terrorists’ major goal is to exploit the media and get control of the news cycle. They do not necessary aim at destroying the victims, but to make them objects of exploitation to send a message to the third party which in most cases is the government or head of state. The victims are used as the first step of transmitting information to the target group (Crenshaw, 1995).
Currently, many nations are living with fear of terrorists using nuclear weapons which has become common among many terrorist organizations.

Popular targets and security measures
- Popular targets.
- Buildings in busy cities and towns.
- Highly populated areas for example the September 11, 2001 attack at World trade center (Geoffrey, 2005).
- Security measures.
- Provision of tight security.
- Restrictions on terrorists like the one imposed by the United Nation’s security council.
In most cases the target are buildings in busy cities, towns and urban centers. The targets (buildings) are highly crowded, where most people carry out their daily operations. On the other hand highly populated areas are points of attack whether there are existing buildings or not. For example the United States September 11, 2001 bomb ballast in New York City (World trade Center), was an ideal target for causing panic. Terrorists are pleased when they cause mass panic since this is their ultimate goal; the U.S .A is more vulnerable to this attack and has a reason to panic (Geoffrey, 2005). The government has the responsibility of protecting its citizens from the threat of terrorism and this can only be through provision of tight security measures and restrictions. The United Nations’ (UN) Security Council imposed some restriction to democracies as a result of the terrorist acts. The restrictions included; denial of financial assistance to terrorist, refusal to support persons who have been involved in terrorist acts, criminalizing terrorist acts, encouraging states to be cooperative and offering assistance on information regarding terrorists.

Negligent human threats
- Negligent threats may be caused by an individual, a group of people, or even the government.
- Occurs due to failure to pay attention to instructions.
- They may also occur as a result of negligent of duties.
- One person or many may be injured due to another person’s negligent.
- Examples of negligent threats include fires , global warming.
Negligence threat occurs when one person, a group of people or the government fails to pay attention to the instructions given. They also occurs due to failure of employees to pay attention to the training been given. A negligent threat can cause death or destruction of property either to the person involved or a bigger population. Examples of negligent threats include fires (although may also be accidental), global warming, among others. For this paper I will look at global warming as an example of negligent threat.

Global warming
- Increase in temperatures on the earth’s surface.
- Caused by increased human activities that emit greenhouses gases (Union of Concerned Scientists 2009).
- Global warming results in:
- Increase in the earth’s temperature;
- Increase in global air and ocean temperature;
- Increase in water levels;
- Melting of snow.
Global warming is the increase in the temperatures of the earth’s air surface and the subsequent increase in the water levels that is, oceans and sea levels increase. It results from numerous human activities that emit gasses they prevent the radiation of sunlight back to the atmosphere. Generally when sunlight reaches the earth’s surface, there is an amount of it that is reflected back to the atmosphere at a higher wave length; when this happens, the earth’s temperatures are regulated. In cases where the air is polluted by green house emissions then these green house gasses break the reflected sunlight radiations from reflecting back to the atmosphere, leaving them just at the earth’s surface. Thing increases the earth’s surface temperature (Union of Concerned Scientists 2009). This is not only harmful to human beings, but to all living organisms including plants and animals.

Causes of global warming
- Burning of fossil fuels.
- Deforestation.
- Increased agricultural activities.
These activities Releases three types of gases that make up the greenhouse gases:
- Carbon dioxide.
- Methane.
- Nitrous Oxide (Anon. “Cause and effect for global warming” 2007).
The heating and cooling of the earth is caused by greenhouse gases. Global warming occurs when these gases exceeds a certain limit. Some of these gases are released to the atmosphere through natural process although most of them result from increased human activities, some of these activities are consumption of fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum, deforestation, increased agricultural activities, failing sinks in oceans. Greenhouse gas is comprised of carbon dioxide, methane, and Nitrous oxide. Carbon dioxide constitute the biggest percentage of the greenhouse gas (Anon. “Cause and effect for global warming” 2007).

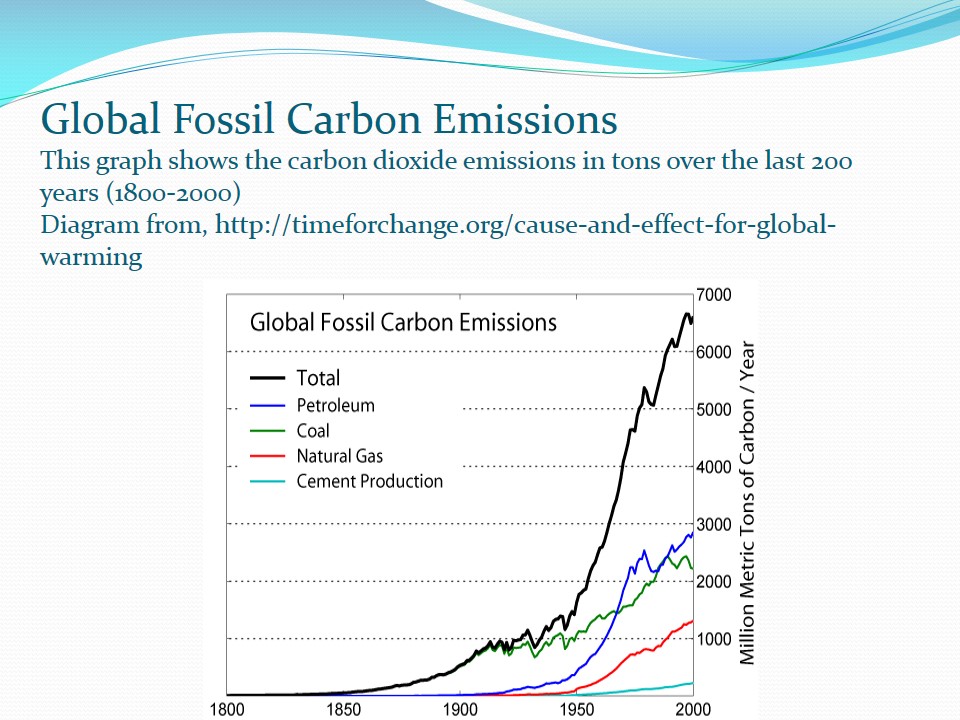
Global Fossil Carbon Emissions
From the above graph, it is clear that, the total amount of carbon dioxide released in the atmosphere has been on the increase since 1800. Petroleum seems to be emitted a lot of carbon than all the other fossil fuels. This is people most people rely on petroleum energy sources since it is believed to be cheaper and easy to use. Cement production releases the lowest level of carbon followed by natural gas.
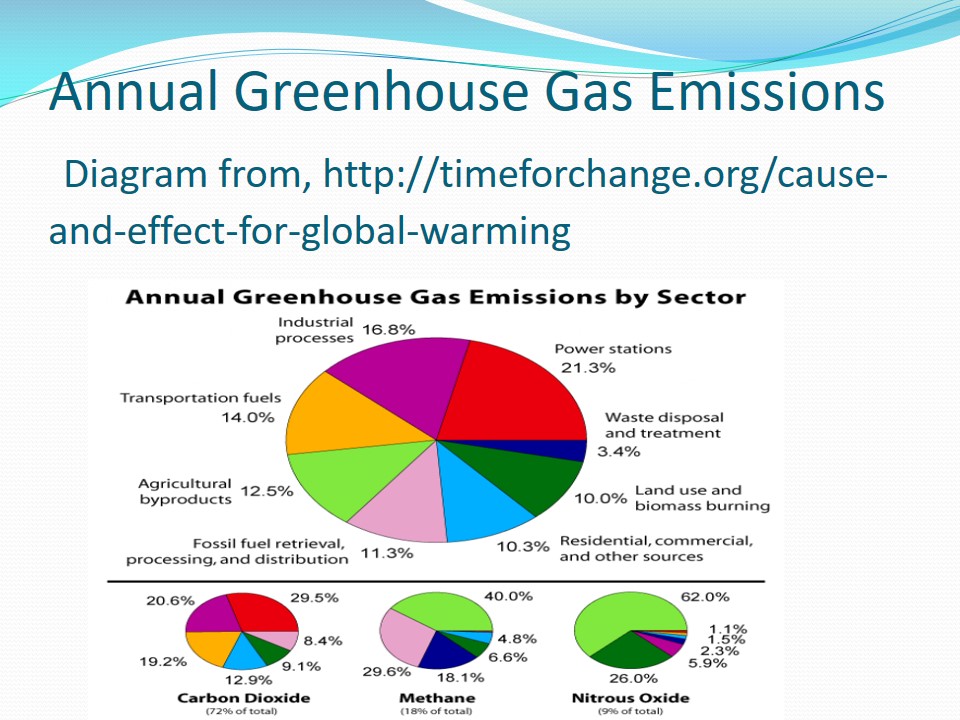
Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The bigger circle shows the total annual greenhouse emission from each sector while the other circles shows the total emissions of carbon dioxide, methane Nitrous oxide respectively from each sector. From the diagram it is clear that, power stations releases the highest percentage of greenhouse gases (21.3%) especially methane and carbon dioxide With the least percentage (3.4%) coming from waste disposal. Agriculture byproducts releases 40% and 62% of methane and nitrous oxide respectively.
Ways of controlling global warming
- In today’s world it is becoming increasingly important to reduce harmful emissions from the production of power, to lessen their environmental impacts.
- The following are some of the methods that can be used to control carbon dioxide emissions:
- cap-and trade;
- baseline-and-credit approach;
- Carbon price;
- Carbon tax (Fischer, 2010).
Emerging technologies are being developed to reduce or eliminate these greenhouse emissions are of the utmost importance and will continue to be in the foreseeable future. The cap-and-trade method is a market based method for controlling carbon dioxide emissions by use of tradeoffs and incentives. Under a rate-based baseline-and-credit plan, firms are prescribed a performance standard spelling out the target industry emission rate (Fischer, 2010). An emission rate represents the emission technology level of a firm and is the amount of pollution that is emitted per unit of output. A rising carbon price is needed to transform consumer and life style choices, to make renewable energy and energy efficiency cheaper than fossil fuels, to spur business investment, innovation and associated economic activity, and to move the nation to the cleaner environment beyond the fossil fuel era. A carbon tax would be an efficient control method because it will discourage companies from releasing gases into the atmosphere. However, in order to achieve the desired results, the tax should increase as the level of gases released increase for it to reduce carbon dioxide emissions (National Greenhouse Gas Inventory Committee 1995).

Accidental Human threats
- Occurs due to inevitable causes.
- some of these threats occurs in emergency situations for instance fires.
- Others are caused by natural calamities, for example:
- Floods;
- Earthquakes (for example the Haiti earthquakes);
- Drought.
Accidental human threats occurs due to reasons that are beyond human control. Most of them results from emergency situation while others are caused by natural calamities. Examples of these threats include fires, floods, drought, and earthquake. Most of these threats may have adverse effects if they do occur and normally leaves a lot of destructions. An example of an accidental threat that occurred recently is the Haiti earthquake that affected a very large geographical area leaving thousands of people dead and others homeless.

Fires
- A hazard that causes damage to people and property;
- Mostly occurs due to emergency cases;
- Occurs whenever the three elements causing it are present;
- Oxygen;
- Heat;
- Fuel.
Fire is a hazard that causes damage to both people and property. It can occur any where provided the three components that cause it are present. It occurs after the reaction of oxygen, fuel and heat also known as the fire triangle. By understanding the causes of fire, it is possible to prevent it from occurring though most of the time it occurs as an emergency case. Before taking any step to fight a fire, one should have knowledge on how fire functions. The fire triangle is used to explain how it functions.

Types of fire
- There are four main types of fires:
- Class A (caused by paper, wood, etc);
- Class B (caused by inflammable liquids);
- Class C (defects in electrical equipments);
- Class D (caused by metals) (Buzzi, 1992).
There are mainly four types of fires which are referred to as “the ABCDs of fire”. Each type of fire has its unique characteristics which determine the control mechanism to be employed (Buzzi, 1992). Class A fire is mainly caused by sources such as paper, cloth, plastic, or wood. When these materials are burned, they leave ash behind. Class B fire results from liquids which are flammable such as oil, grease, or gasoline. These materials will only cause fire if ignited by heat. The third type of fire is known as class C. It occurs due to defects in electrical equipment which require current. The last type of fire is class D which is caused by metals such as aluminum, potassium, sodium and magnesium.

Fire prevention
- knowledge of the fire triangle.
- Introduction of a fire prevention program.
- Analysis of the work site:
- surveying of fire hazards at factories;
- identifying any combustible material;
- proper installation of fire extinguishers.
- fire control and prevention training.
- Employee training on:
- the use of fire extinguisher;
- Habitual inspection on fire hazard;
- Good housekeeping procedures.
Other measures include;
- Putting fire company’s phone numbers in an accessible place (Buzzi, 1992);
- Providing a detailed map to the fire company of the farm or factory’s location.
Most fires can be prevented by identifying the causes. Fire occurs after the reaction of oxygen, fuel and fuel also known as the fire triangle. Knowledge of the fire triangle is the first step in fire prevention. This can be done through the introduction of a fire prevention program on maintenance, analysis of the work-site, and fire control and prevention training. The fire prevention program has been proven to be one of the most effective methods in prevention of fire. a work-site analysis involves; surveying of fire hazards at factories, companies or farms, identifying any combustible material and storing them in a safe place, and proper installation of fire extinguishers where there are readily available accessible by any employee. Fire extinguishers should be recharged annually and inspected by professionals.
Every employee should be equipped with proper training on fire prevention and control. It is the responsibility of every individual to have adequate knowledge on the procedures for fire prevention and control. He should be trained on how to use a fire extinguisher and the different types of fire extinguishers, how to inspect fire hazards and good housekeeping procedures.


Conclusion
- Human threats fall under three categories (intentional, accidental, and negligent).
- They cause a lot of destruction to both property and people.
- Some of them can be mitigated against while others are caused by inevitable causes.
- The government need to provide security measures to protect its citizens against the intentional threats.
- Proper training on employees and the public at large can help in mitigating some of these risks.
As seen earlier, human threats falls under three categories, that is intentional, accidental, and negligent. Intentional threats are caused by human beings on others resulting in massive destruction of property and even death. A common example of intentional threat is terrorism which has been a contentious issue in many nations. Accidental threats occurs due to inevitable causes, they include fires, floods, or earthquakes. Although it may seem difficult to mitigate against these threats, some of them can be predicted by intellectuals before they occur and the necessary preventive measures taken. Training can also help in reducing the likelihood of such threats occurring for example fires. Negligent threats occur as a result of employee sloppiness in following policies or other human activities. An example of negligent threat is global warming which is caused by increased human activities that release carbon dioxide in the air. This can be controlled by use of government regulation on the amount of carbon to be released in the atmosphere.

Reference list
Anon. (2007). Cause and effect for global warming. Web.
Buzzi, R. A. (1992). Chemical hazards at water and wastewater treatment plants. CRC Press.
Crenshaw, M. (1995) Terrorism in context, Penn State Press.
Fischer, C. (2010). Combining rate-based and cap-based-and-trade emissions policies. Climate Policy 3S2, 89-109.
Geoffrey, L. Z. (2005). Agents of bioterrorism: Pathogens and their weaponization. New York: Columbia university press.
Union of Concerned Scientist (2009). Global warming. Climate 2030: A National Blueprint for a Clean Energy Economy. Web.