Introduction
The issue of hunger is a global one that affects many countries, especially those in the developing world, and Brazil is no exception. This discussion explores the Zero Hunger program, an initiative President Lula da Silva introduced in Brazil in 2005. Its goal was to reduce hunger and poverty in Brazil by providing food security for citizens of all ages. This paper will examine the objectives of this program, evaluate its effectiveness in reducing hunger, and explore whether it could have been implemented more effectively or if similar programs should be adopted elsewhere. Finally, the discussion will provide recommendations for improving the Zero Hunger program or creating better alternatives in the future.
Overview of the Zero Hunger Program
The Zero Hunger program has played a vital role in attaining food security in Brazil. President Lula da Silva introduced the program in the country in 2005 (Silva et al., 2020). Its main goals were to reduce hunger and poverty while providing food security for all citizens regardless of age. This ambitious program aimed to provide access to nutritional foods, promote family farming, support small-scale producers, encourage people to save money, and develop sustainable agriculture systems. It also offered microcredit for those who needed financial assistance. The government allocated more than 6 billion euros ($7 billion) over the first four years of the policy and created a portfolio of activities to tackle hunger from different angles across the country (Silva et al., 2020). These included launching the Food Acquisition Program (PAA), which allowed families to purchase food from local farmers eligible for social protection benefits, and creating Bolsa Familia. This conditional cash transfer program provided financial assistance to the most vulnerable people. It also included the Social Protection Program (PSA), which focused on extending social protection to those in poverty (Costa Maia et al., 2019). The Zero Hunger program also sought to strengthen food monitoring systems, reduce malnutrition and increase public awareness of healthy diets.
In addition to the measures outlined above, the Zero Hunger program sought to create a sustainable agricultural system to provide more food security in Brazil. The government implemented several initiatives to achieve this, including establishing agroecological reserves and farms and improving access to credit for small-scale producers. Other initiatives implemented include investing in research, developing new technologies, and creating incentives for agroforestry (Sousa et al., 2019). The program also sought to create an enabling environment for small-scale producers by devolving decision-making power from the central government and allowing them increased autonomy over their land use (Sousa et al., 2019). Lastly, the Brazilian government developed public policies to reduce malnutrition by making school meals available, improving maternal health care and nutrition services, and expanding social programs to reach the most affected families.
Overall, the Zero Hunger program was an ambitious and wide-reaching effort that sought to tackle hunger in Brazil from multiple angles. Its main objectives were to reduce poverty and improve the quality of life for all citizens, with particular emphasis on providing food security for children and small-scale farmers. To evaluate its effectiveness, an assessment of if it achieved these goals needs to be done and whether any improvements can be made.
Causes and Consequences of Hunger in Brazil
Brazil is classified as an upper middle-income country; however, despite its relative wealth and economic growth, hunger remains an issue for many vulnerable populations. This has been linked to various factors, including low wages, rural poverty, and inequality. Furthermore, the rise in food prices has hurt the purchasing power of impoverished families (Costa Maia et al., 2019). To address these issues, the Brazilian government developed the Zero Hunger program to provide access to nutritional foods through initiatives such as the Food Acquisition Program (PAA). Other aspects included promoting family farming and offering microcredit for those in need (Sousa et al., 2019). This policy successfully improved food security and reduced Brazil’s poverty levels. In the future, further work must be done to ensure these gains are sustained. Further improvements can be made to reduce malnutrition among the most affected populations. Through continued investment in initiatives such as these, Brazil has the potential to become a leader in food security.
The causes of hunger in Brazil are multifaceted and rooted in inequalities. These include disparities in income, access to resources, and social opportunities. Poor agricultural policies, a lack of investment in rural areas, and environmental degradation have contributed to poverty and food insecurity (Costa Maia et al., 2019). In addition, social exclusion has led to further marginalization of vulnerable populations such as women, ethnic minorities, and Indigenous peoples. This unequal distribution of resources can be attributed to structural issues within Brazilian society that have created an environment where specific sectors are disadvantaged. As such, addressing the root causes of hunger requires meaningful public policy interventions that seek to reduce inequality and promote more equitable outcomes for all citizens. The Zero Hunger program is a comprehensive attempt by the Brazilian government to address these issues and provide vulnerable populations with the means to achieve greater food security.
The consequences of hunger in Brazil are dire and poor nutrition has led to many physical and mental health problems. These issues include stunted growth, developmental delays, depression among children, and an increased risk of chronic diseases among adults. Furthermore, hunger and malnutrition are linked to higher school absenteeism and lower educational attainment, which can have long-term implications for individuals’ earning potential (Silva et al., 2020). Finally, hunger can lead to a greater social instability and unrest due to the lack of access to adequate nutrition. Providing resources to support at-risk families, investing in public infrastructure projects that facilitate access to food assistance programs, and working with businesses to ensure food security in Brazil can be attained. Moreover, non-profit organizations can help provide equitable access to nutritious foods, and people can help reduce hunger in Brazil and create a more prosperous future for all citizens.
The Zero Hunger program has been an extremely successful initiative in reducing hunger and poverty in Brazil. It has positively impacted vulnerable populations, provided access to nutritious foods, and improved incomes for family farmers (Petrovska & Cintula, 2023). Therefore, the Brazilian government must continue to invest in this program or similar programs to ensure these gains are sustained over the long term. Building on the success of the Zero Hunger program, further investments should be made into public infrastructure projects and initiatives that help ensure equitable access to food assistance programs and nutritious foods. Ultimately, with continued investment in such programs, a better future can be guaranteed for all citizens of Brazil. This will create a more prosperous society with reduced levels of poverty and inequality – something everyone aspires to achieve. By continuing to invest in the Zero Hunger program or similar initiatives, a better tomorrow for everyone can be established.
The graph below demonstrates the success of the Fome Zero program in Brazil. After implementing the Fome Zero program in Brazil, the percentage of people living in extreme poverty decreased from 35% to 24% between 2014 and 2018 (Silva et al., 2020). More than 7 million households received financial aid to help them buy nutritious food during this period, demonstrating considerable progress in making healthy foods available (U.S. Department of Agriculture, 2020). Additionally, malnutrition among children aged 6 or younger fell from 10.5% to 8%, while stunted growth dropped by 2% (Silva et al., 2020). These figures demonstrate that the Fome Zero program successfully reduced hunger and poverty levels across the country. These results show that investing in initiatives such as providing access to food assistance programs and working with businesses, non-profit organizations, and government bodies can reduce hunger and create a more prosperous future. Thus, Brazil must continue to invest in such initiatives in the future.
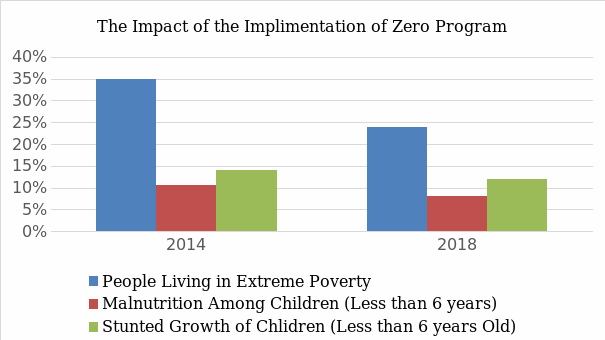
Moreover, the Zero Hunger program in Brazil has been an incredibly successful initiative. It has decreased poverty and hunger levels, improved access to nutritious foods, and provided financial assistance for food purchases (Petrovska & Cintula, 2023). However, there is still work to be done if these gains are to be maintained over the long term. Therefore, the Brazilian government must continue to invest in this program or similar initiatives so that its citizens can enjoy a more prosperous future with reduced levels of poverty and inequality. With continued investment into such initiatives, Brazil will become a leader in food security and create a better tomorrow for all its citizens. The success of the Fome Zero program is proof that investing in food assistance programs and other initiatives can help reduce poverty and hunger levels across the country. Therefore, this program should continue to be supported going forward. With such continued investment, Brazil can create a better future for all.
Solutions to Hunger Challenge in Brazil
In addition to government efforts such as the Fome Zero Hunger program, various other solutions can be employed to combat hunger challenges in Brazil. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and civil society initiatives can play an essential role in providing food aid to poor people while promoting agricultural development projects that empower small-scale farmers (Blesh et al., 2019). Private sector companies can also use their resources to improve nutrition access by promoting healthy eating habits and distributing quality food. International organizations such as the United Nations (UN) have also been working with Brazil’s government to promote sustainable agricultural practices and ensure adequate nutrition for all individuals.
Another way to combat hunger challenges in Brazil is through public-private partnerships. Private companies can partner with local authorities to provide food aid and nutrition education initiatives while investing in agricultural development projects (Blesh et al., 2019). International organizations such as the World Food Programme (WFP) have collaborated with Brazilian partners to introduce innovations that promote sustainable agriculture and facilitate better access to nutritious foods. Furthermore, research initiatives are being launched to identify innovative solutions for improving food security in Brazil. Finally, community-based organizations that advocate for food justice and raise awareness about hunger issues can play a vital role by engaging citizens and advocating for socially responsible policies (Blesh et al., 2019). Together, these efforts aim to create an environment of collaboration between different stakeholders that will ultimately help reduce hunger and food insecurity in Brazil.
Increased access to digital technology is another solution that has the potential to reduce hunger challenges in Brazil. Digital technologies such as mobile technology, big data, and artificial intelligence can improve the effectiveness of food aid programs, promote better nutrition practices and reduce food waste (Blesh et al., 2019). Additionally, increased access to digital learning platforms can enable citizens to acquire knowledge about healthy eating habits and agricultural techniques, thus empowering them with the skills necessary for better nutritional outcomes. Finally, digital services allow individuals living in food-insecure communities to access vital information on resources, such as government assistance programs or local NGO initiatives. With increased access to these resources, Brazilians will be better equipped with the tools needed for improved nutrition security.
A final solution that can help address hunger challenges in Brazil is the promotion of sustainable livelihoods. This involves providing individuals access to economic opportunities and resources, such as agricultural training or business development initiatives (Blesh et al., 2019). These initiatives enable people to become economically independent, promote sustainable farming practices, and reduce poverty. Additionally, promoting sustainable livelihoods helps communities build resilience against food insecurity and malnutrition by improving their ability to cope with shocks caused by extreme weather events or other disruptions. Ultimately, investing in these projects can provide individuals with a pathway out of poverty and ensure long-term food security for everyone in Brazil.
These solutions and efforts demonstrate that hunger challenges in Brazil can and are being addressed from a range of angles – from governmental policies to private sector initiatives. Together, these strategies can potentially reduce food insecurity and malnutrition levels among vulnerable populations across Brazil. With concerted efforts from stakeholders across all sectors, it is possible to find practical solutions to hunger challenges in Brazil. By working together and using the available resources to their fullest potential, those at risk of hunger can receive the assistance they need for a brighter future. This could help create sustainable food systems that protect vulnerable populations and guarantee adequate nutrition access to all individuals in Brazil. Only through collective action, both within and outside Brazil, can people hope to address the country’s hunger challenges. As a result, stakeholders must continue working together to develop innovative approaches to ensure access to nutritious food throughout Brazil.
Conclusion
Hunger challenges in Brazil are a multifaceted issue that can only be addressed through concerted efforts from all stakeholders. By utilizing digital technology, promoting sustainable livelihoods, and engaging citizens to advocate for socially responsible policies, it is possible to reduce food insecurity and malnutrition among vulnerable populations in Brazil. However, much work still needs to be done to guarantee adequate nutrition access for all individuals across the country. By continuing to collaborate and explore innovative approaches, researchers and policymakers can help create sustainable solutions for food security in Brazil. In doing so, future generations will have the opportunity to thrive without fear of hunger or lack of nutritional resources. Ultimately, people must continue researching better ways of addressing hunger issues in Brazil and develop sustainable, inclusive solutions for the benefit of all citizens and the world. By doing so, people and governments can work towards ensuring a future where no one has to worry about going hungry.
References
Silva, N. de J., Ribeiro-Silva, R. de C., Rasella, D., Alves, F. J. O., Campello, T., Fiaccone, R. L., & Barreto, M. L. (2020). Shifts towards overweight and double burden of malnutrition among socio-economically vulnerable children: A longitudinal ecological analysis of Brazilian municipalities. Public Health Nutrition. 24(15), 4908-4917. Web.
Sousa, L. R., Segall-Corrêa, A. M., Ville, A. S., & Melgar-Quiñonez, H. (2019). Food security status in times of financial and political crisis in Brazil. Cadernos De Saúde Pública, 35(7). Web.
Costa Maia, N. J., Mourão, G. D., Águas, T. D., Martins, J. A., Gonçalves, L. M., & Monteiro, P. H. (2019). Price of basic food basket in Brazil and the world (2003-2017): Causes and consequences. Journal of Experimental Agriculture International, 1–10. Web.
Blesh, J., Hoey, L., Jones, A. D., Friedmann, H., & Perfecto, I. (2019). Development pathways toward “Zero hunger.”World Development, 118, 1–14. Web.
Petrovska, O., & Cintula, T. (2023). Inflation in Brazil: Addressing food insecurity in Brazil. The Borgen Project. Web.
U.S. Department of Agriculture (2020). SNAP & Other Nutrition Programs. Web.