Introduction
A successful organisation embodies more than just execution and observance of an array of models of management strategies. It requires developing mechanisms and instruments of business excellence that allow an enterprise to offer quality products and services, reduce operations costs and meet customer expectations. Contemporary economy which is characterised by globalisation and stiff competition calls for organisations to embrace quality management principles to enable them to realise sustainable growth (Patel, 2016). It underscores the reason modern version of the European Foundation of Quality Management (EFQM) model emphasises the significance of building business capabilities and managing with dexterity.
It also advocates promoting ingenuity and innovation to guarantee that customers get value for their money. Dinu (2019, p. 5) posits, “The new model for quality management dubbed ISO 9000 standards champions process-based approach, incorporating the cycle of “Plan – Do- Check – Act” (PDCA) and risk-based thinking and focusing on organisational change and innovation to ensure sustainable performance”. There are efforts to create universal business management principles that integrate environment, quality, social responsibility and safety. Today, quality and environmental accreditation standards have proved to be critical to the realisation of business excellence both locally and internationally because they outline managerial best practices that organisations ought to adopt to improve their performance. This paper will discuss the contribution of accreditation standards to the success of local and multinational companies.
Total Quality Management
Rapid technological development, a demanding customer base, and global competition are some of the features that represent contemporary business environment. Nowadays, for companies to remain productive, they require adjusting their policies, systems, and structures. Kudtarkar (2015) identifies total quality management (TQM) as one of the strategies that modern enterprises use to achieve and sustain excellent performance. This technique constitutes constant procedures that bring together all stakeholders in an effort to improve business activities at all levels. As per Kudtarkar (2015), TQM assembles essential management practices, technical instruments, and existing development efforts under a closely controlled approach aimed at achieving long-term process enhancement. TQM regards clients as the sole determiners of the quality of products and services. Additionally, it underlines the importance of including value in the developmental stages of goods and services instead of having them assessed for quality after their completion.
TQM comprises four essential components which are people, planning, performance, and processes. Planning involves creation and implementation of strategies and policies that are vital to business operations. It also entails identifying requisite resources like human capital, raw materials, suppliers, and establishing alliances. Performance involves creating models for assessing business activities (Kudtarkar, 2015). It also includes formulating guidelines for audits, benchmarking, and balanced scorecards. These measures help to assess if a company is working towards realising its target goals. People refer to all human capital that an organisation requires to discharge its activities. They include employees, customers, suppliers, management team, and shareholders. Promoting cooperation and encouraging innovation are vital for business excellence. Processes refer to a collection of tasks, actions, and their intended results. They aid in ensuring that a company offers products and services that meet consumer specifications. Procedures are also essential in promoting organisational efficiency and minimising wastage. Below is a diagram that represents the framework for total quality management.
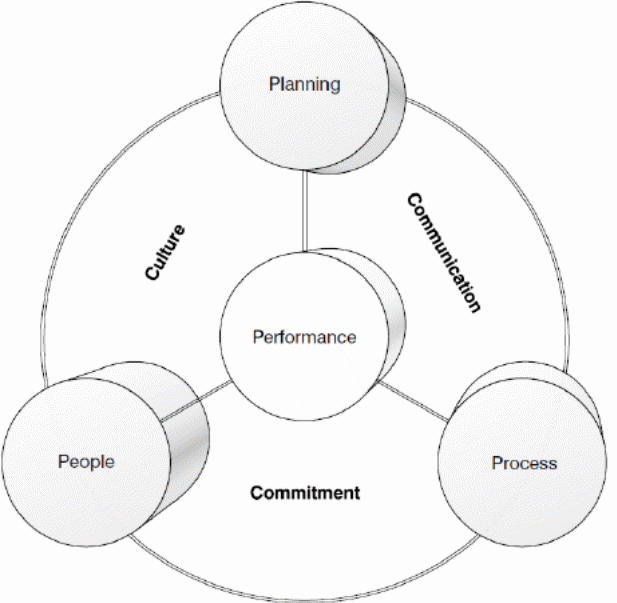
Quality and environmental accreditation awards like Deming Prize, European Organisation for Quality (EOQ) and Malcolm Baldrige award are critical to the realisation of business excellence. The three awards have criteria frameworks that are essential in assisting businesses to implement TQM which is helpful in boosting corporate performance. A company has to confirm that it has incorporated TQM in its operations and adopted customer-focused strategies for it to win the Deming Prize (Dinu, 2019). Businesses employ systematic activities and methods of operations that are not only customer-oriented but also sustainable in effort to qualify for these coveted accreditations. In the process, they enhance their performance, cut on managerial costs, and become competitive, thereby attaining excellence. Dinu (2019) posits that it is only businesses which espouse TQM strategies that align with their management beliefs and administration environment that qualify for Deming Prize. This award encourages companies to evaluate their existing conditions, come up with goals and themes, and develop and change themselves organisation-wide. Deming believed that focusing on quality enables businesses to boost productivity and competitiveness, hence becoming successful.
Customer Focus and Excellence
An evaluation of companies that have won Deming Prize reveals that they use TQM to improve customer satisfaction. These organisations are recognised for offering quality products that are not only cost-effective but also meet consumer demands. Corporate such as Mahindra & Mahindra and Toyota are renowned for conducting brand equity assessment and leveraging customer satisfaction survey to improve their products (Ghicajanu, Irimie, Marica, & Munteanu, 2015). The mechanisms used to select companies that satisfy the criteria for quality and environmental accreditation check whether organisations involve clients in product development. Consequently, most multinational firms appreciate the importance of conducting consumer analysis to establish existing and future needs. These companies ensure that they work in liaison with customers to transform their desires into product ideas. Indeed, quality and environmental accreditation principles have contributed to the majority of businesses adopting customer-centric practices.
Malcolm Baldrige award is another accreditation standard that encourages companies to assume customer-focused behaviours. A study by European Center for Business Excellence found that organisations that embrace quality models defined by Baldrige award’s criteria for exceptional performance endeavor to serve consumers’ needs. As per Lasrado (2017), the desire to win Baldrige prize leads to companies implementing various customer-centered practices that enable them to improve their performance. They include the application of multiple avenues of gathering customer feedback, customer segmentation depending on their needs, and development of novel products based on consumer demands. Lee and Ooi (2015) argue that one of the features of Baldrige award-winning firms is that they are conscious of their customer relationships. These companies make sure that they generate feasible customer research by following and evaluating definite consumer requirements. Moreover, they gather information regarding the buying behaviours of their customers to aid in the production of goods and services and their shipment to areas where they are urgently required.
Quality and environmental accreditation standards highlight the importance of understanding and grouping customers according to their needs. Lasrado (2017) argues that Baldrige-winning organisations attain excellence because they have adequate knowledge of their clients. Moreover, these businesses tailor their operations to the expectations and preferences of diverse consumer bases. Most multinational corporations that are ISO 9000 accredited have devised measures for gauging customer satisfaction and addressing their complaints. Lasrado (2017) posits that organisations such as Motorola keep record of warranty data, duration taken to repair their products, consumer satisfaction index, and the number of complaints. This information is helpful in understanding consumer preferences and determining if the corporation meets clients’ needs effectively. Moreover, Motorola uses this data, together with its notorious six sigma strategy to develop subsequent products. Understanding the components of mobile gadgets that require frequent replacement has enabled Motorola to minimise the production of faulty devices.
Operations Focus
One of the key ingredients of organisational success is operations management. Today, many companies have procured business process management systems (BPM) aimed at enabling them to streamline operations, cut cost, minimise errors, and boost productivity. It is the goal of every firm to achieve excellence by offering products and services that satisfy consumer demands. Nevertheless, this goal cannot be achieved without ensuring that business processes are geared towards creating value to both stakeholders and clients. The EFQM emphasises the contribution of efficient operations to business excellence. This foundation has devised basic concepts that underpin effective processes. As per Ghicajanu et al. (2015), business activities should work towards adding value to clients. The primary goal of a corporation is to make profit, which cannot be achieved without attracting customers. Conversely, consumers are hesitant to buying products or services if they do not get value for their money. Consequently, a company should make sure that its operations correspond to customer demands and preferences.
The EFQM states that company processes must aid in the realisation of sustainable outcomes. The future of any business is pegged on its capacity to operate without loses and attract return customers. These objectives can only be achieved by building organisational capabilities. It is imperative that a company does not only recruit experienced workers but also conduct on-the-job training to enhance the skills of its workforce. Moreover, encouraging employee empowerment can be helpful in engendering creativity which is vital to the achievement of sustainable results. Below is a diagram that represents the basic concepts of EFQM.
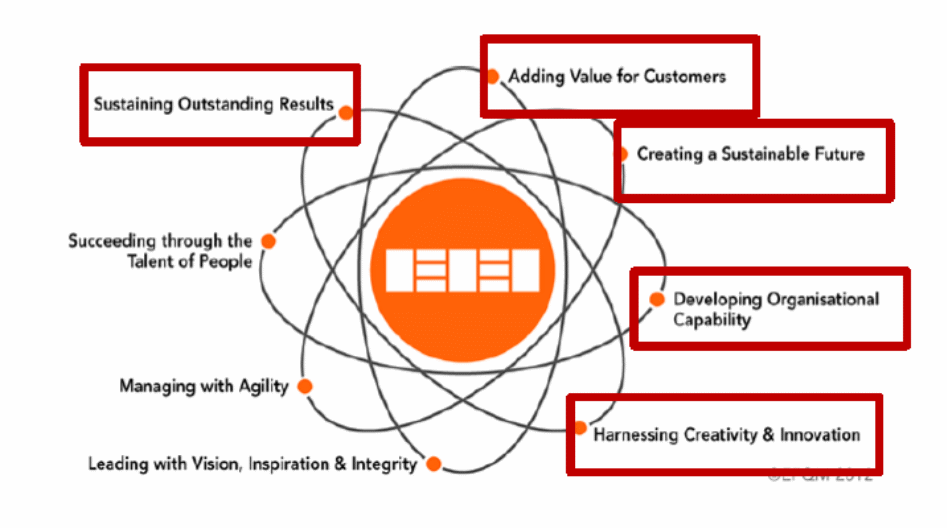
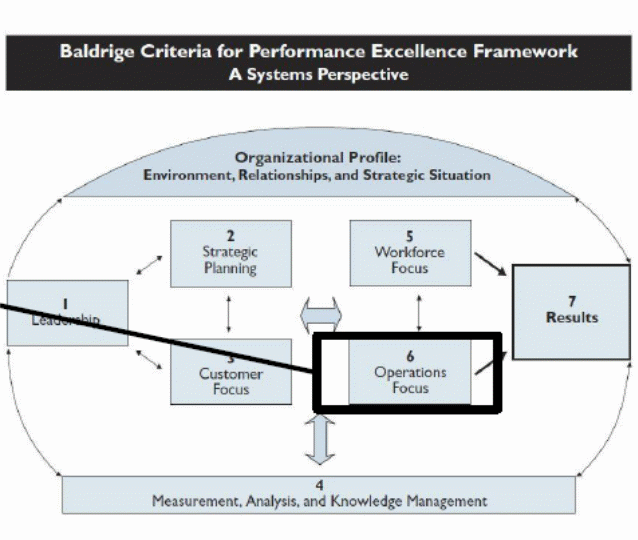
Quality and environmental accreditation standards like Malcolm Baldrige award and Deming Prize assist organisations to implement operations aimed at facilitating the attainment of business excellence. For instance, the Baldrige award has an excellence framework that highlights the principles that organisations should use to engage employees, boost productivity, enhance operations, and meet consumer demands. According to Lee and Ooi (2015), Baldrige is more than just an award, as its framework enables organisational leaders to understand how their companies operate. Moreover, it helps in the identification of processes that require improving and those that are critical to business excellence. Today, Baldrige serves as an essential diagnostic system that assists businesses to discern their capabilities and areas that need improvement, thereby creating value for shareholders, employees, clients, and other stakeholders. This accreditation standard outlines the measures for performance excellence that organisations use to gauge their operations and act appropriately. It is imperative to acknowledge that this framework is non-descriptive, and therefore organisations are at liberty to modify processes according to their needs. For instance, some companies may opt to use six sigma or lean strategies to improve their productivity. Below is a pictorial representation of Baldrige criteria for performance excellence framework.
Fujitsu UK & Ireland
Fujitsu UK & Ireland is one of the companies that display the contribution of quality and environmental accreditation standards to business excellence. This multinational enterprise is renowned for meeting the requirements of various certifications, among them ISO/IE20000, UK government inter-operability framework (E-GIF), Information Systems Examination Board, and UK government accreditation of individual security practice consultants (CLAS). The adoption of these standards has enabled Fujitsu UK & Ireland to enhance the quality of its products and services. Process management is critical to the operations of any business. In the course of adhering to accreditation principles, Fujitsu UK & Ireland has procured business management system (BMS) that aids in streamlining its operations. The leadership of this company understands the significance of process management to its success. Consequently, the BMS is aimed at improving operations by ensuring that all personnel have sufficient knowledge of the organisation’s processes. The implementation of this system has allowed Fujitsu UK & Ireland to collapse its activities and assign them to distinct departments, thereby guaranteeing smooth operations. Below is a diagram that depicts the nature of process management at Fujitsu UK & Ireland.
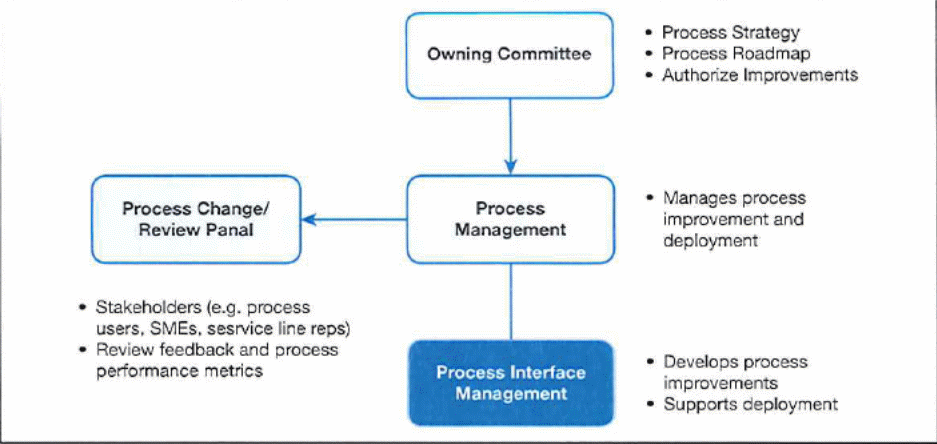
The present level of competition in the global business calls for companies to continually monitor and improve their operations. Fujitsu UK & Ireland understands the importance of having efficient processes. Consequently, its management system assists not only in control but also assessment, communication, and support of varied operations. This company constantly upgrades its processes in an effort to meet the demands of external standards. The company has appointed senior executive members who are in charge of distinct regional business processes. These managers are mandated with implementing necessary changes to business procedures to ensure that Fujitsu UK & Ireland addresses consumer demands.
Leadership and Strategic Planning
Leadership refers to the capability of a company’s official to rally workers behind common goals and persuade them to devote their time and energy to the realisation of these targets. Breja, Banwet, and Iyer (2016) outline six critical aspects that a leader ought to demonstrate which include vision, mission, values, ethics, goals, and philosophy. One should acknowledge that the actualisation of corporate mission, vision and dreams is pegged on a leader’s ability to inspire their workforce. Communication is critical; hence leaders should encourage dialogue amid workers to ensure that they cooperate.
One of the factors that contribute to disruption of business activities is communication breakdown. Breja et al. (2016) hold that most workers require knowing the direction that their leaders have taken before supporting them. Carvalho, Sampaio, Rebentisch, Carvalho, and Saraiva (2019) contend that not understanding the path that a company or leader wishes to take may lead to employees becoming disillusioned. Consequently, organisational managers should offer a sense of direction by setting priorities. An administrator must guarantee that corporate goals are definite, unambiguous, concrete, and understandable to all workers. Moreover, it is necessary to draw correlations between business goals and the established procedures to enable employees to understand the significance of their duties.
An analysis of the criteria used to choose businesses that qualify for Baldrige award reveals that the selection team looks for companies with a keen eye for corporate mission, vision, strategies, systems, values, and structures that promote a tradition of constant growth (Schaefer 2015). The Baldrige framework identifies numerous factors that define successful leadership. Some of these elements are the ability of a manager to create a disciplined work process, formulate and implement effective business policies, and recognise their clients and competitors. Understanding the Baldrige criteria has led to most organisational leaders changing their management strategies. Today, the majority of corporate heads are result- and data-driven, a quality that enables them to raise business profit and boost shareholder value (Schaefer 2015). Baldrige criteria assist leaders to evaluate companies objectively, thereby understanding what they need to achieve their missions. Business acumen is an essential feature of both corporate leaders and employees. Baldrige framework is critical to improving company leadership because it promotes shrewdness by revealing the connection between varied facets of an organisation. The diagram below shows leadership practices that promote effective performance.
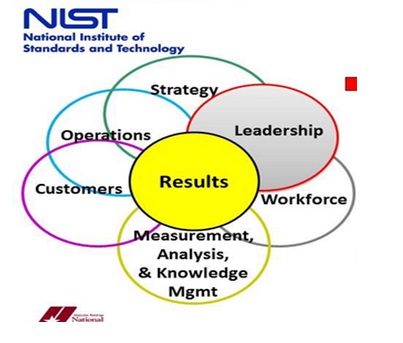
A study of Indian businesses that have won Deming Prize reveals that accreditation standards are critical to building corporate leadership. As per Rajashekharaiah (2014), Deming framework underscores the importance of organisational leaders hiring the right employees. It argues that human capital plays significant role in enhancing the value of products and services. Consequently, it is difficult to attain the objectives of TQM without involving the right personnel. Deming standards are invaluable to human resource managers because they enable them to come up with recruitment strategies which guarantee that a company hires qualified workers.
Strategic planning refers to a company’s process of defining its targets, course of action, and assembling the necessary resources to achieve these goals. Ford and Evans (2018) allege that business plans must correspond to the mission and vision of a company, challenging but feasible, not restrictive, and few in numbers. Communication is paramount to the success of a strategic plan, and all employees must know their responsibilities in the execution of a given procedure. The Baldrige criteria for performance excellence outline essential considerations that guarantee the success of a company’s strategic plan (Ford & Evans, 2018). A business’ action plan should consider factors attributed to employee capabilities, level of competition in the market, and suppliers’ abilities. These criteria assist local and international companies to formulate strategic plans that are not only easy to monitor but also appraise. Therefore, it is easy for an organisation gauge its operations based on the established strategic goals and take the necessary actions.
Conclusion
Quality and environmental accreditation standards outline operations principles that are useful in the realisation of business excellence both locally and internationally. The Deming Prize advocates total quality management which is critical to boosting organisational performance and meeting consumer demands. Moreover, this award has a framework that highlights the importance of involving customers in all stages of product development or service delivery. The Baldrige criteria for performance excellence underscore the need for embracing customer-centered practices. It would be difficult for business to offer competitive products or services if it does not understand market forces like consumer preferences.
Baldrige award has an excellence framework that enables companies to identify operations that require improving. Additionally, its criteria for performance excellence enlighten leaders on how to identify and exploit the strengths of their businesses. Fujitsu UK & Ireland is among the multinational companies that confirm the contribution of accreditations principles to business excellence. This company has leveraged these standards to streamline operations and guarantee customer satisfaction. It has business management system that aids in communication and coordination of processes across various departments. Accreditation standards are helpful in nurturing leadership qualities and formulating strategic plans that are vital for business excellence. Today, corporate heads consider employee skills, business capabilities, and consumer demands when formulating and implementing strategic plans.
References
Breja, S., Banwet, D., & Iyer, K. (2016). Towards sustainable excellence: Strategic analysis of Deming Prize winning companies. The Total Quality Management Journal, 28(3), 14-34.
Carvalho, A. M., Sampaio, P., Rebentisch, E., Carvalho, J. A., & Saraiva, P. (2019). Operational excellence, organisational culture and agility: The missing link? Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 30(13), 1495-1514.
Dinu, V. (2017). Quality management and business excellence. Amfiteatru Economic Journal, 19(44), 5-7.
Ford, M. W., & Evans, J. R. (2018). Conceptual foundations of strategic planning in the Malcolm Baldrige criteria for performance excellence. Quality Management Journal, 7(1), 8-26.
Ghicajanu, M., Irimie, S., Marica, L., & Munteanu, R. (2015). Criteria for excellence in business. Procedia Economics and Finance, 23(1), 445-452.
Kudtarkar, S. G. (2015). Deming award, a journey towards business excellence. Journal of Business and Management, 1(1), 1-9.
Lasrado, F. (2017). Perceived benefits of national quality awards: A study of UAE’s awards winning organizations. Measuring Business Excellence, 21(1), 50-64.
Lee, V., & Ooi, K. (2015). Applying the Malcolm Baldrige national quality award criteria: An approach to strengthen organisational memory and process innovation. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 26(11), 1373-1386.
Patel, S. (2016). Business excellence: Exceeding your customers’ expectations each time, all the time. London, UK: Productivity Press.
Rajashekharaiah, J. (2014). Quality leadership – Learning from the Deming Prize winners in India. International Journal of Quality Research, 8(3), 431-446.
Schaefer, C. (2015). A Baldrige award recipient shares leadership practices that support operational excellence. Web.