Introduction
The marketing function is a very critical requirement for any business setup. Some of its importance arises from the fact that it enables businesses to increase their customer base and to differentiate their products from those of their competitors. Therefore, it is one of the most fundamental activities of any commercial organization and an essential discipline even in non commercial organizations. As a result of the intense competition in the business environment, it is imperative for entrepreneurs to be creative in order to ensure that their enterprises survive in the long term. One of the ways through which they can achieve this is by incorporating effective marketing strategies. Some of the strategies that entrepreneurs can consider in order to increase their customer base include product differentiation and cost leadership. Marketing is a widely used term that is often very misused and misunderstood.
Definition of Marketing
There are different definitions of marketing which have been formulated. For example, some individuals assert that marketing is an all-embracing function which is aimed at linking businesses with the needs and wants of the customers. Marketing can also be defined as the process of through which businesses ensure that their corporate goals are attained by meeting the customers’ needs in a more effective and efficient manner compared to their competitors.
According to Chartered Institute of Marketing in the United Kingdom, marketing can also be defined as a management process which is aimed at identifying, anticipating and supplying the customer’s product requirements in an efficient and profitable manner. This definition of marketing is similar to that advanced by the Business Institute of Marketing (BIM). Leader and Kyritsis (1990, p.21) defines marketing as a set of human activities which are directed towards facilitating and consummating exchanges. Figure 1 shows the marketing exchange process that lies at the heart of modern marketing.
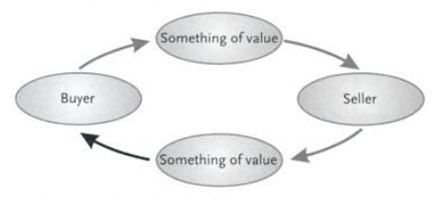
On the other hand, the American Marketing Association (AMA) defines marketing to include the performance of various business activities that are directed towards ensuring effective and efficient flow of products from the manufacturer to the consumer.
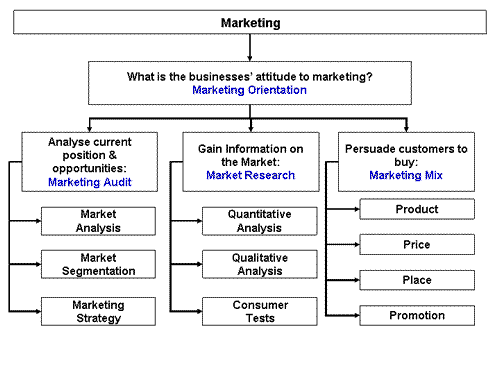
In summary, meaning of marketing varies across different parties. To some people, marketing is the human activity that is meant to satisfy the needs and wants of customers. Marketing is considered to be a business-wide function which means that it cannot be undertaken by its own away from various business activities. It is also be defined as the social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others. Additionally, marketing can be defined as the process of understanding the customer needs and wants and ensuring that the product and services developed match the existing and potential needs of customers. It is also about looking at ways of influencing the behavior of customers. The chart below illustrates the various elements that constitute marketing.
The Marketing Concept
Marketing refers to what an organization must do to create and exchange value with customers. It plays a big role is setting a firm’s strategic direction. To succeed in marketing, an organization must have a deep understanding of customers, competitors and collaborators. The organization’s capabilities must be well deployed so as to effectively meet customer demands. It is therefore very important for any person with the responsibility to spearhead the growth of an organization to not only be insightful but also equipped with marketing skills. Studies have shown that the competitive advantage one firm may gain over another often results from its superior understanding of its customers and how it handles information it has about these customers.
Marketing management is the application of marketing related strategies and tactics to meet an organization’s stated goals. According to this view, every single resource, whether human or otherwise, has a part to play in the marketing process. There are two major objectives of marketing. The first is to attract new customers by highlighting the potential value of a good or service. It is often the case that one gets easily attracted to something when he or she can clearly see its value. This is a strategy that marketers usually employ to get new customers. There are instances where firms have failed to attract customers because the products or services being offered to the customers were not well defined. It is important for business enterprises to realize that getting customers is an active process that requires aggressiveness and innovation. It is very rare that customers will come to a business out of their own initiative.
The second aim of marketing is to retain customers by continually meeting and surpassing the customers’ satisfaction with quality products. One of the ways through which they can achieve this is by ensuring effective customer service. Researchers have discovered that as much as 80 per cent of a company’s revenue comes from as few as 20 per cent of a company’s repeat customers. Satisfied customers often find it easy to recommend the company’s products or services to others and this greatly increases the total number of customers the company has.
On the other hand, an unhappy customer can be very destructive and can quickly spread bad reports about the company far and wide. In an effort to evaluate the level of customer service amongst firms in different industries, MSN Money established a survey known as ‘Customer Service Hall of Shame’. In 2010, Wells Fargo was rated amongst companies in the Hall of Shame due to its inefficiency with regard to customer service. Wells Fargo has adopted the motto ‘The Next Stage in Banking’ to show its commitment towards customer service. Additionally, the firm spends millions of dollars in its advertising campaign. However, the firm does not adhere to motto.
Therefore, it is very important for companies to take good care of their customers. Companies that take existing clients for granted often pay dearly when they start losing them one by one. Firms within the United Kingdom telephone industry are amongst the firms which have experienced a high rate of customer loss as a result of poor customer service (Customer Service Manager, 2012, para. 3).According to a study conducted by Natterbox on the UK voice services companies, 62% of the customers interviewed said that they had cancelled purchasing services from some companies due to poor services.
It does not matter how much influence advertisers claim to have over customers; a personalized service plays a major role in a purchasing decision than any form of marketing campaign. If one was to take a moment and look at Google for example, there is proof that with no formal advertising whatsoever, other than encouraging users to “spread the word”, the company has grown from being a very tiny start up to be a market leader in Internet search. Today, Google stands out as the most popular search engine among many users of the Internet.
At my work place, one of the things that all employees are encouraged to do is to ensure that customers are pleased with our services. Employees are so passionate about this to the extent that if one is made angry by a customer, he or she would rather not show it in front of the customer. On many occasions, offended employees have tactfully walked away from unhappy clients to evade trouble. The company has grown mostly from the good recommendations of past and existing customers and everyone is convinced that word of mouth is the way to go. The company strongly believes that when a customer is not happy, he or she is likely to spread an unpleasant report about the company to about four potential customers. It therefore pays to ensure that existing customers are well taken care of.
Elements of the Marketing Concept
Marketing concept is concerned with implementation of the marketing mix. Marketing concept assert that determining the consumer’s needs and wants and delivering the products and services to the customer’s level of satisfaction compared to their competitors forms the basis of attaining organizational goals. Marketing concept is characterized by four main elements as outlined below.
- Satisfying needs and wants
- Target market
- Organizational goals
- Coordinated marketing
Satisfaction of needs and wants
Organizations are faced with the challenge of assessing the nature of the consumers’ needs and wants. However, the challenge is relatively high in organizations that deal with services such as libraries. This arises from the varying characteristic of the customer’s specific needs. In order to effectively assess the customers’ needs, organizations should conduct interactive needs. By interacting needs with the customers, organizations are able to understand the customer’s value.
Target market
For organizations to survive in an environment characterized by intense competition, it is imperative that they focus on a specific market. The importance of target marketing in a firms operation arises from scarcity of resources. Most organizations do not have sufficient resources to cater for the entire market. The target market concept enables organizations to be effective and efficient in allocating and utilizing resources.
Achieving organizational goals
This element of marketing concept asserts that organizations should be self-supportive. In order to achieve this, firms should ensure that they make high sales which translate into higher net revenues. However, organizations must appreciate the fact that higher net revenues are as a result of satisfied customer needs. Additionally, this marketing concept asserts that firms’ management teams should have clarity with regard to organizational goals. This will play a critical role in allocating organizational resources.
Coordinated marketing
The marketing function in organizations is conducted by the marketing staff. However, the success of marketing is dependent on all the departments. For example, the production department is required to supply high quality goods in time. According to Jain (1999, p.33), organization should also coordinate with other stakeholders within the external marketing environment. The objective of coordinated marketing is to ensure creation of a program that will contribute towards satisfaction of the customers’ requirements.
Benefits and Costs of a Marketing Approach
Marketing approach forms the basis of understanding the market setup and the target customers. There are a number of benefits and costs associated with marketing approach. Some of the costs of adopting a marketing approach relates to the cost of marketing research. To be effective in their marketing approach, organizations are required to undertake a comprehensive marketing research which requires a substantial amount of money. The marketing research should focus on various market variables such as the customers, competitors amongst others. To survive in the long term, marketing approach requires organizations to undertake continuous product development and new product development which is a cost to the firm. Firms also incur the cost of developing their corporate image. For example, they are required to continuously advertise so as to create sufficient public awareness regarding their existence in the market. Additionally, marketing approach requires organizations to establish a long term relationship with the various stakeholders such as the customers, suppliers and distributors.
Despite the above costs, adapting a marketing approach significantly contributes to the firm’s competitive advantage. This arises from the fact that a firm is able to attain its profit maximization objective, attain a high level of customer loyalty, trust and reputation. The ultimate effect of implementing marketing approach is that the probability of the firm attaining its profit maximization objective is increased.
Considering the fact that the goal of starting a business is to make profit, firms’ management teams should consider integrating marketing approach. Additionally, the costs of implementing marketing approach cannot be avoided if organizations are to succeed in the business environment.
Characteristics of a Market-Oriented Organization
A market oriented organization defines its business in terms of the benefits sought after by the customers. Being market oriented and focusing on customer wants does not necessarily imply that the customers will always receive everything they want. However, becoming market oriented contributes towards organizations attaining overall success. Additionally, being market oriented enhances a firm’s competitiveness. Most of the successful companies such as Nike, Adidas, Apple Incorporation and Amazon.com are market oriented. For example, one of the characteristics which make these companies to be considered as being market oriented arises from their effectiveness with regard to customer knowledge. As a result, they are able to influence the consumers buying decision by ensuring that their products are of high value. For example, Amazon.com has managed to offer its customers personalized shopping experience.
There are a number of characteristics which organizations must possess in order to be considered as being market oriented. Some of these characteristics are discussed below.
- Image building – Market oriented companies invest a substantial amount of money in an effort to develop a corporate image which is aligned to their corporate strategy. One of the ways in which they attain this is by branding.
- Market responsiveness – A market oriented firm is continuously concerned with its ability to adapt to changes in market dynamics. The firm also formulates and implements rules upon which its relationships with various stakeholders are based. Therefore, one can assert that market oriented companies are sensitive to the needs of its stakeholders and market trends (Perret & Jaffeux, 2007, p. 216).
- Long term commitment – Market oriented companies are committed towards long term investments which are aimed at strengthening their market position. One of the ways through which this is attained is by undertaking product, services and process improvement, improving the quality of their products and services, enhancing human resource management, improving interpersonal relationships and their information systems.
- Target focus – In an effort to attain effectiveness and efficiency in their operation, market oriented companies are very effective in targeting their market and customers so as to ensure effective resource allocation.
- Behavior-based segmentation – Developing intelligence with regard to consumer behavior forms the basis upon which market oriented companies segment their market. This is achieved by developing a comprehensive understanding of the consumers’ market related information.
- Internal cooperation – Market oriented companies have implemented organizational structures which are aimed at ensuring cooperation amongst the various departments. The resultant effect is that they develop team spirit which culminates into employee empowerment.
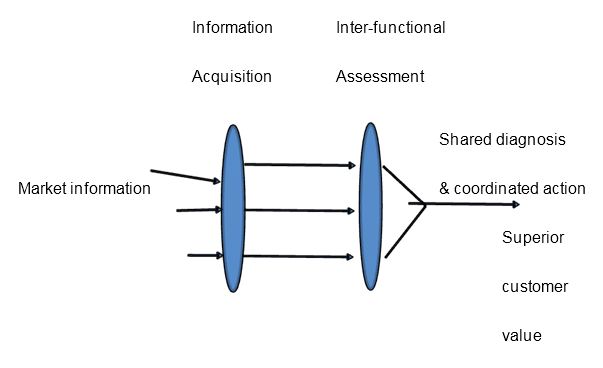
In summary, market oriented companies are able to make profit by taking advantage of customer, competitor and other market information. The resultant effect is creation of customer value, providing customer satisfaction, and building long term relationships with customers.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation can be defined as the process of placing buyers in a product market into sub groups that display similar responsiveness to a particular marketing strategy. This means that it involves identifying a sub group within a larger group. The rationale behind market segmentation is that it enables organizations to leverage scarce resources. Through market segmentation, organizations are able to formulate effective marketing mix. This arises from the fact that marketing mix strategies should be designed to meet needs of specific target market. This means that the concept of market segmentation is similar to the concept of product differentiation.
The concept of market segmentation is built on the premise that customers are different, have different needs and behave in different ways. Segmentation is based upon three propositions: consumers are different, the differences are created by the variation in market demand, and the segments of consumers can be isolated within the whole market. The obvious differences that are seen among customers pose a very big challenge for entrepreneurs and doing business would be probably easier if all customers were the same in every aspect.
It therefore follows that for a firm to succeed, it must understand that proper market segmentation, targeting and positioning provide a very strong foundation for a successful business. An entrepreneur must be able to determine the desired market segments, why these segments are important, how they will be sought after, the cost that will be involved in seeking these segments, and what the return on investments will be. A firm must segment markets so as to effectively respond to the specific needs of the customers and increase the company’s sales volume and profitability. Once the segments have been created, it is important for the company to determine which segments are of interest to the business.
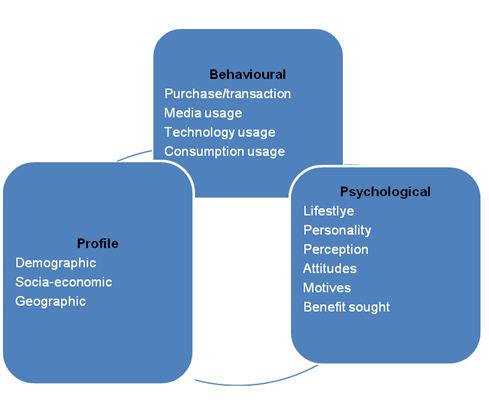
Though quite desirable, segmenting markets effectively is not an easy task. A good working knowledge of the market is required as well as common sense and good judgment. In order to undertake effective market segmentation, organizations must evaluate the prevailing consumer criteria in its target market. There are 3 main consumer criterions that the organization may consider. These include behavioral, psychological and profile. On the basis of these consumer criterions, a firm may adopt various market segmentation approaches. Some of these approaches include; geographic segmentation, demographic segmentation, psychographic segmentation, and behavioral segmentation. The chart below illustrates classification of these market segmentation approaches.
Market Segmentation in the UK by Age
With regard to demographic market segmentation, some of the variables that organizations may consider include age, occupation, religion, consumer income and level of education. Table 1 illustrates demographic segmentation in the UK using age.
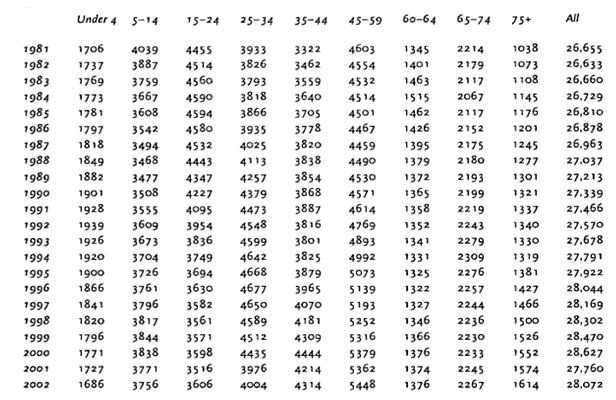
Demographic variables have significant effect on the consumers’ ability to purchase. Life stage market segmentation variable is based on the fact that consumers product needs vary depending on their stage in life. Geographic market segmentation is based on the fact that consumer product needs vary depending on their location. Such differences may arise as a result of variation in climate, tradition or custom. For example, in the US there is a high preference for lighter beers compared to Germany and the UK. On the other hand, Australians have a high preference for carbonated and colder beers compared to consumers in the US and UK.
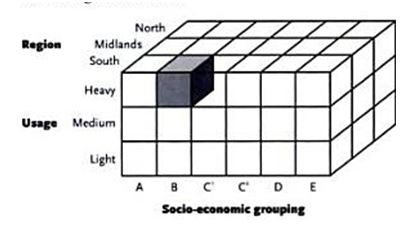
Geographic segmentation allows the company to put customers together based on where they live or work and includes geographic units such as countries and cities or even neighborhoods. Demographic segmentation divides the market based on population characteristics. Demographic segmentation is popular for two main reasons. First, customer needs are often tied to demographic characteristics and secondly, it is easier to locate and measure demographic information on markets than measuring other variables. Segmentation may also be done based on multiple variables as illustrated by figure 5.
Psychological market segmentation approach is based on the fact that consumers have varying opinions, activities and interests. Individuals’ behaviors have significant effect on the consumers’ purchasing patterns. This in turn affects the consumers’ decision making process. Organizations can also identify the consumers’ media usage patterns. Similarly, it is possible for organizations to determine the benefits that consumers seek in purchasing a particular product. This increases the effectiveness with which firms design product that meets the intended benefits.
Behavioral market segmentation is based on the fact that consumers have different behaviors in their purchase patterns, product usage and media usage. In order to effectively segment the market on the basis of transaction behavior, organizations should seek information regarding who makes the purchase, what they purchase, their purchasing frequency, the amount they spend and the transaction channel through which they make the purchase. Product usage segmentation may be designed on the basis of usage situations.
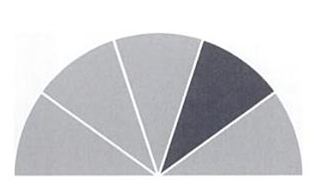
Segmentation, targeting and positioning can be related as follows. Market segmentation subdivides customers into sub groups displaying similar characteristics or marketing responses. Market targeting then evaluates and selects one or more segments that a company chooses to serve. Once segments have been identified, organizations have to select one or more segments with a need that can best be met and these form the targets. An organization can adopt a number of different targeting strategies such as concentration targeting. Figure 6 illustrates the concept of concentration targeting with the shaded part indicated the targeted segment.
Market positioning combines marketing actions to meet the needs and wants for each target group using suitable marketing mix and supporting services.
Macro and Micro Environmental Factors That Influence Marketing Decisions
Businesses are affected by changes in the macro environment and the micro environment. The macro environment relates to the external environment which is beyond the control of the business. On the other hand, the micro environment consists of the internal environment which can be easily controlled by organizational management team. Figure 7 illustrates how they interact with the organization.
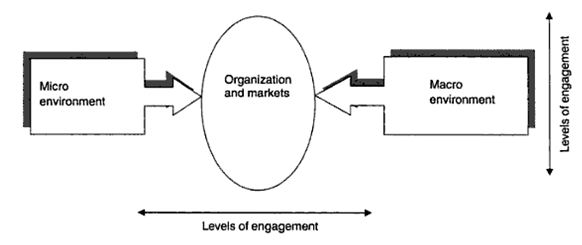
Marketing decisions are significantly affected by macro and micro environmental factors.
Micro Environmental Factors
The micro environment can be described as the organizational environment. This environment defines the forces that an organization has control over. Figure 8 shows the micro environmental forces that engage with the organization.
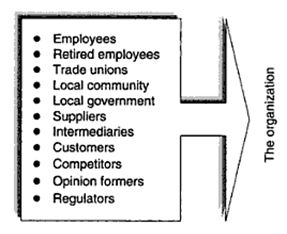
The main micro environmental factors that influence the marketing decision include:
- Suppliers
- The company
- Competitors
- Customers
- The public
- Marketing channel firms (intermediaries).
Company: The marketing decision is affected by a number of parties within the organization. For example, the organizations’ top management teams are charged with the responsibility of ensuring that their organizations mission, vision and objectives, policies and strategies are well implemented formulated and implemented. The marketing decision is also influenced by the marketing managers who work closely with the other departments such as the production, research and development, finance, procurement and accounting departments in an effort to ensure that effective marketing decisions. By cooperating with these departments, the marketing manager ensures that the marketing objectives formulated are aligned to the overall organizational goals.
Suppliers: These include the organizations and individuals who supply various resources that are required to undertake the production of products and services. Suppliers are a very important component in an organization’s value system. This arises from the fact that they affect organizations’ operational efficiency. For example, by increasing the cost of their supply, they affect the organizations pricing strategy.
Marketing intermediaries: These include the various firms that enable organizations to undertake effective marketing through promotion, selling and distribution of the firms’ products to the final consumers. There are different categories of marketing intermediaries who affect the marketing decision. Some of these include the resellers who entail the various distribution channel firms who assist organizations to find customers and to sell products to them. The wholesalers and retailers who purchase products from the manufacturer/producer for resale purpose also affect organizations’ marketing decision. The physical distribution firms which assist organizations to transport goods to their final destinations for example depots and warehouses also affect marketing decision.
Additionally, the marketing decision is also affected by marketing service agencies and financial intermediaries. Examples of the marketing service agencies that influence decision making include the advertising, marketing research and media agencies. These agencies affect the decision making in that they enable organizations to effectively identify and target their customers. F Table 2 shows the relationships that may exist between suppliers and their customers.
Table 2: Relationship between suppliers and customers
Competitors: Unless an organization operates within a monopolistic environment, it will have competition within the market. Competitors are a group of firms that produce products that are a close substitute for each other. It includes both product manufacturers and service providers. Marketing a product for which a competitor already has an advantage may be very difficult.
Public: These include the various groups within the society that have interest in the operation of firms. Examples of these publics include the local publics such as the residents and neighborhoods, the general public, media publics and internal publics.
Macro Environmental Factors
These are environmental factors that directly affect industries as well as individual companies and organizations. They can lead to serious repercussions and must therefore never be underestimated by a company or an organization that wants to succeed. Figure 9 shows micro environmental factors that affect organizations and the markets.
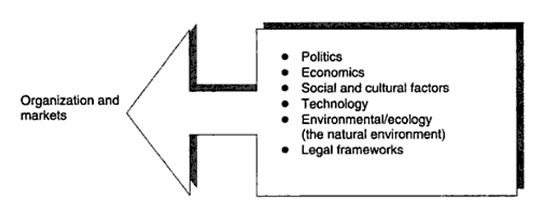
Some of these factors are explained in the following subsections.
Political Factors: This is a concern because those who hold power influence both political decisions and consumer issues. It is therefore important for a company to be aware of the political environment.
Technological Factors: In marketing goods and services, organizations must become aware of new materials as well as developments in manufacturing and business processes. The technological environment includes the level of advancement in technical knowledge and equipment in society and the rate of their development and application. We live in an age of rapid technological change and understanding these changes is essential for any organization that wants to explore new opportunities. Marketers need to scan the environments in which the organization operates to understand the important changes that currently face them. It is important for organizations to consider how technological development impacts upon and supports its marketing objectives both now and in the future.
Economic environment: The economy can have an effect on virtually all aspects of a business and marketing is not spared. It is therefore crucial for the marketer to have some level of understanding of how the economy works. In the period of economic recession when consumers have falling incomes for example, it may be difficult to market a luxury product.
Social and Cultural Factors: For an organization to understand the social and cultural environment it must closely analyze the society. Demographic changes such as population growth, movements and age distribution are important, as are changes in cultural values and social trends such as family size and social behavior. Social and cultural factors are very important in influencing marketing decisions and it pays for an organization to stay abreast with social trends.
Environmental/Ecological Factors: Research has shown that ecological awareness is having a major impact on marketing. Environmental conservation has become a very important political issue and is being embraced by governments of different countries globally. In the present world, it is typical of consumers to make environmental concern an important factor in purchasing decisions when buying all manner of goods. Shortage of raw materials as a result of environmental degradation may affect an organizations ability to operate.
Legal Framework: There may be a number of laws constraining the activities of a business and these may work against the success of the business. A market focused firm will fully research all the constraints and try to find solutions that enable it to turn weaknesses into strengths and threats into opportunities.
Segmentation Criteria for two Products in Different Markets
As clearly explained earlier, segmentation involves dividing the market into groups that have similar requirements. The groups may be defined by age, geographical location or any other relevant classification. This may be explained by looking at the following two cases.
The first case regards a company that wants to market a new brand of cooking oil to an urban population. Although various marketing strategies may be adopted to market the new product, it will be important for the marketer to determine what his or her target group is. The majority of people who fancy cooking are women and considering that most women also enjoy watching specific television programs, the marketer could liaise with broadcasters to find out the times when programs widely watched by women are televised. With this information, the marketer can then ensure that his or her advertisements are run when the said programs are shown.
The second case is one that involves marketing a washing detergent to a rural population that lives in an area that is less develop and watching television is a luxury. A marketing approach for the washing detergent requires the marketing team to find a way to reach the identified target group. The marketers could probably move around with a mobile cinema and making stops at nearby markets, the team could show videos of the product and how it is used so as to spread news about the product.
In both cases, the marketer has to figure out the target group and come up with the best strategy to reach the customers.
Factors that Influence the Choice of Targeting Strategy
Among the factors that may influence the choice of targeting strategy include:
- Competition: As pointed out earlier, it is only in a monopoly where a firm will face no competition. The success of the targeting strategy will thus be affected by the strength of the completion.
- Desired Sales Volume: Based on how much the company needs to sell, it may be necessary to target only a particular market group to ensure that the expected sales volumes are realized. In most cases, this also determines the profit levels.
- Consumer Demands: It is important for the marketer to establish what the customers really want. It makes no sense to try and target a group that is not interested in the product being sold.
- The Strength and Maturity Level of the Market: In a mature market, it is almost clear to the marketer what the customers require where and when. Very little effort will thus be spent to know the right products or services to offer various groups and places.
Q&A on Marketing Activities
How buyer behaviour affects marketing activities
Understanding the buyer behavior is very important in an effort to understand the customers. There are various strategies that organizations can integrate in an effort to attain this. One of these tools relates to conducting a market research using questionnaires. This increases the entrepreneurs’ understanding of the customers’ needs and wants. Additionally, the entrepreneur is also able to determine how the customers respond to various issues and how they affect the firms marketing activities.
There are a number of ways through which the consumers purchasing behavior influences an organization’s marketing activities. For example, over the past decade, there has been a rampant growth in social media. In an effort to align with the changes in consumer behavior, organizations are integrating social media such as Facebook, Twitter and You Tube in their marketing strategies. As a result, they have been able to interact effectively with the customers.
Additionally, the consumers’ behavior also affects the organization’s pricing strategy. For example, through a market research, entrepreneurs may identify that consumers tend to purchase from stores that offer price discounts. In order to attract these customers, the organization will be forced to incorporate discount in its pricing strategy. In summary, buyer behavior affects marketing activities for example with regard to promotion activities and pricing strategy.
How products are developed to sustain competitive advantage
Developing a high competitive advantage compared to their competitors is one of the most effective defensive mechanisms that firms’ management teams should consider. Attaining sustainable competitive advantage enhances the success of firms in the dynamic business environment. In order to develop sustainable competitive advantage, there are a number of strategies that firms’ management teams should consider. Some of these strategies are evaluated below.
Product differentiation and positioning
Currently, consumers are faced with a wide range of products to select from. This has arisen from the fact that numerous investors have ventured into various business sectors thus resulting into development of a wide range of substitute products. In order to survive in such a competitive environment, business organizations should incorporate the concept of product differentiation. There are various product differentiation strategies that firms can consider integrating. For example, organizations must consider customizing products in order to distinguish them from those of the competitors. Additionally, a firm may differentiate its products by ensuring that it is of high customer value. However, the pricing of such products should be relatively lower compared to competing products in order to attract customers. Through effective product differentiation, an organization is able to significantly enhance its competitive advantage. The ultimate result is that the firms’ market position is improved.
Staged release of new or improved product version
An organization can also attain a high competitive advantage by ensuring that it controls its product improvement. This can be achieved by releasing a new product or an improved version periodically instead of introducing the product at irregular intervals. Periodic introduction of new products or improved versions into the product plays a significant role in ensuring that the customers maintain their positive perception towards the products compared to competing products.
Research and marketing
In order to be successful in the process of undertaking product improvement and new product development, organizations should conduct a comprehensive market research. Market research enhances the effectiveness with which organizations understand the customers’ needs and wants. Additionally, entrepreneurs are also able to identify gaps with regard to a particular product. As a result, the firms are able to undertake product developments which are in-line with the market demand. For example, in an effort to develop a high competitive advantage with regard to its product offering within the US construction industry, Corus Construction conducted a comprehensive market research by focusing on the external environment. The firm attained this by integrating the PEST model. The firm also intends to introduce new products into an industry that is considered to be very conservative with regard to new product development.
How prices are set to reflect organizations objectives and market conditions
In the process of determining the price point for a particular product, entrepreneurs are influenced by a number of factors. These include the cost of materials, the expected market share, the intensity of competition and the customers’ perceived value. Additionally, the price set also takes into consideration the duration taken to produce a particular product. This is evidenced by the fact that the time taken is factored in the hourly rate. When introducing a new product into the market, the price set must be competitive. There are various pricing strategies that firms can incorporate in the process of setting the price point. These include skimming, cost-plus leadership, penetration and psychological pricing. The pricing strategy adopted serves as an indicator of the firms’ objectives.
How distribution is arranged to provide customers with convenience
Distribution is concerned with ensuring that the customers access products more conveniently from the market. This means that the product must be available at the right place, time and quantity. Place can also be used to refer to the physical or virtual store which is used in displaying a firm’s product. Alternatively, place also entails the distribution channel adopted by a firm. Organizations can either adapt direct or indirect distribution channels. The indirect distribution channels may either consist of the wholesalers, retailers, agents and also distributing through the internet. Considering the growth in Information Communication Technology, most organizations are integrating the concept of e-commerce in order to provide customers with their desired level of convenience. For example, Amazon.com distributes its products virtually through the internet.
How promotional activity is integrated to achieve marketing objectives
The success of every marketing activity is dependent on the effectiveness with which the firm creates market awareness. One of the ways through which an organization can create sufficient market awareness is by undertaking effective promotional activities. Through promotion, an organization creates information to the public regarding what it does and what it offers. Possessing information regarding a product or service plays an important role in the consumers’ decision making process.
For example, through advertising, an organization is able to inform potential consumers the benefits they can acquire by consuming its products or services. Additionally, potential customers become aware of where they can purchase the product from. Considering the fact that one of the objectives of marketing is to enable a firm increase its sales, promotion plays a critical role towards its attainment. This arises from the fact that it influences the consumers’ decision making process through creation of information which is the first step towards making a purchase. The resultant effect is that the firm is able to increase its sales. Promotion activities also contribute towards creation of a good relationship between the organization and the various stakeholders such as the customers and the public. This is attained by integration of strategies such as public relations.
Additional Elements of the Extended Marketing Mix
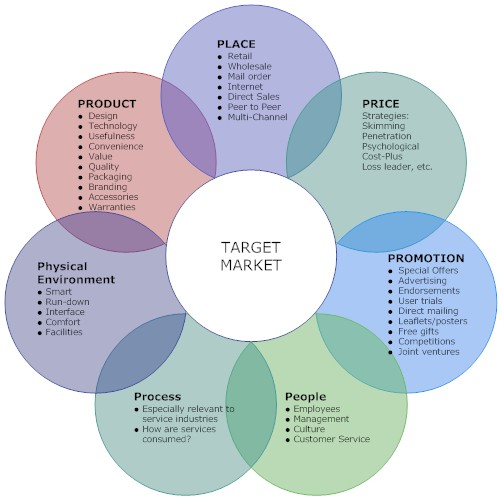
Marketing mix refers to a combination of strategies that are incorporated by businesses in an effort to attain their objectives by marketing the products and services to their target customers. Traditionally, the marketing mix is composed of four main elements which include the price, promotion, place and product. However, marketing of services such as tourism is relatively different to marketing products. As a result, there are 3 more marketing mix elements which are integrated to the 4P’s. These include people, process, people and physical evidence. The seven elements, that is product, price, promotion, place, people, process and physical evidence constitute the extended marketing mix.
People
The delivery of services is unique due to their inseparable nature. This arises from the fact that the service is produced and consumed simultaneously. As a result, successful marketing of services is dependent on the effectiveness of the employees in delivering the service. Therefore, one of the most important elements in providing services is the contact employees. Firms within the service industry should have qualified staff in order to ensure effectiveness and efficiency in the process of service delivery. Additionally, they should ensure that the contact employees make a positive impression to the customers.
To attain this, firms should conduct a comprehensive process of employee recruitment and selection. Additionally, organizations should conduct employee training in order to ensure that they offer high quality services to customers so as to appeal them. Additionally, training the employees keeps them motivated in executing their duties. The training process should be continuous due to the varying characteristic of the employee’s performance. Such variations in employee performance can translate into variation in the quality of the service. In an effort to ensure consistency in its service delivery, Starbucks which is well established within the US hospitality industry trains its employees for 25 hours so that they can understand the recipes and learn about the varieties of food products. Additionally, the training is also aimed at ensuring that the employees have positive behavior and attitude toward the customers (Pride & Ferrell, 2006, p. 368). One of the ways through which they can achieve this is by possessing appropriate interpersonal skills.
Process
This refers to the mechanism or flow of activities through which services are delivered to the customer. According to Richardson and Gosnay (2011, p.125), process has a significant effect on the quality of service offered to the customers and hence the experience attained. For example, firms should formulate effective and efficient processes which are aimed enhancing the customer’s level of satisfaction. Some of these processes may relate to how customer complaints are resolved, process of identifying the customers’ needs and wants and how to handle customer orders. In their purchasing patterns, customers are not concerned with details regarding how a business operates. However, they are interested with the efficiency of the system for example, the average waiting duration before a service is delivered and the effectiveness with which they provide information. Considering the fact that services are perishable, managing the process of delivery is very critical.
For example, a customer may require seeking information about a firm’s services through the phone. In the event that they are required to hold for a long time, they may become disoriented and prefer to purchase from competing firms. Lack of a reply is an indication that the firm has a poor process. The resultant effect is that a negative image is created in the customer’s mind. Replying the customers’ inquiries forms the most important component the process. However, firms which have integrated effective customer service process enhance their customers’ level of confidence and loyalty towards the firm. In order to achieve this, organizations have to ensure that their Call-Center staff is well trained with regard to handling customers. Therefore, the ‘process’ component of the extended marketing mix significantly contributes to firms’ competitive advantage.
Physical evidence
Services are experienced after they are delivered. Therefore, decision to purchase a service is risky due to their intangible nature. This makes marketing of services to be challenging. However, firms within the service industry can overcome such a challenge by developing case studies which can enable potential customers make a purchase decision. The case studies act as testimonials that the firm provides high quality services. The reliability of such testimonials arises from the fact that it does not come from the firm but from customers. Therefore, feedback is an important component of ensuring that customers are aware of the quality of a firm’s services. Alternatively, firms in the service industry can also educate their customers about their operation through representations of services using various mediums such as brochures, business cards, letterheads, reports, digital signage and the internet. The physical evidence provided by a firm must be in-line with the customers’ assumptions. For example, if a firm within the hospitality industry such as the Hotel Industry intends to create a perception that it offers high quality services, one of the ways through which it can attain this is by ensuring that it has an effective design, lighting, decoration, furnishing and layout. This will significantly influence the consumers’ perception towards the quality of its service delivery.
Application of Extended Marketing Mix to Different Marketing Segments and Contexts
Marketing Mixes for Two Different Segments in Consumer Markets
The marketing mix provides a useful way of looking at the marketing of products. Marketing mix is also regarded as a set of controllable variables that a company may use to influence the customers’ response (Dransfield, 2004). Figure 11 illustrates the elements of marketing mix.
In marketing its products and services, it is possible for an organization to use a combination of different elements of the marketing mix to meet its sales objectives. I will use two scenarios to elaborate the concept of marketing mix. The first case refers to a competitive market environment with the same product manufactured by different firms. This segment consists of a wealthy population. The second case will examine a market segment that is made up of middle class customers who are unable to afford a luxurious life.
In the first case, I will propose a marketing mix that focuses more on the product as well as place. Here, the product will be the most important element in the organizations’ marketing mixes. Closely associated with the product is branding. According to Dransfield (2004), people often buy the brand name as much as the product itself. It will therefore be vital for the organizations to tap on the strengths offered by their brand names. The power of branding is seen when consumers walk into a supermarket and purchase a new product just because it has been manufactured by a particular company. Considering that this market has companies offering products that are substitutes of each other, organizations will only reach their expected sales volumes if they bear a brand that is appealing to the customers. It will also be necessary for the organizations to target places in this market where they are sure that their brand is well recognized.
In the second scenario, I will suggest that the organizations include price and promotion in their marketing mix. The population here is not so wealthy and as a result, people only make purchase based on their needs. It is possible for consumers to ignore some products simply because they are in the habit of buying what they are used to. It will therefore take some promotional activities for organizations to create awareness about substitute products that are available. Marketers may need to move from place to place sensitizing buyers about their products. Coming up with affordable prices is also very important and must be at the center of the organizations’ marketing strategies. It may be necessary for a firm to offer cost leadership so as to attract a greater number of consumers.
Marketing Products and Services to Organizations Rather Than Consumers
Organizational markets or industrial markets are those markets that consist of buyers who purchase goods and services to be used in the production of other goods and services (Dransfield, 2004). Some organizations will sell their products in both the consumer and industrial markets. For example, motors manufacturer may produce cars for individuals to buy as well as commercial vehicles for manufacturers to use (Dransfield, 2004). Marketing to organizations is sometimes referred to as Business to Business (B2B) while marketing to consumers is referred to as Business to Consumer (B2C).
When a company is selling its goods and services to other organizations, it still needs to understand the behavior of its customers. The marketing principles that employed when considering individual consumers still need to be taken seriously. However, there are some notable differences. In marketing to organizations, a firm will tend to focus on building lasting relationships and ensuring that it gets the most out of such relationships. Organizational marketing is also characterized by lengthy processes and in most cases targets smaller markets. Organizational marketing also involves educating other organizations about the products or services being offered to them. An organization that seeks to market to other organizations but does not invest in sharpening the skills and knowledge of its employees may not go far with its marketing activities. It is the desire of organizations to know clearly what they are being offered. On the contrary, marketing to consumers is largely driven by the type of products that a firm produces. It is characterized by a simplified buying process and aims to reach a larger market environment. It is also common for organizations to purchase larger quantities unlike individual consumers.
Differences between International Marketing and Domestic Marketing
The concept of international marketing has been reinforced by globalization and advancements in technology. As a universal activity, marketing transcends geographic, cultural and political borders to serve the needs of markets wherever they exist. International marketing usually involves the marketing of products in two or more countries (Dransfield, 2004). Although in some instances, it will involve trade between a business organization and customers in just one country, an organization may sell in many countries and manufacture in many other countries. A number of reasons have led to the growth of international marketing.
Desire to Improve the Standard of Living
Considering that no single country is self sufficient, there is need to depend on others and hence the need to import and export to other countries. Exporting overseas helps to pay for the imports that help to improve the standard of living (Dransfield, 2004).
Growth and Economies of Scale
Overseas trading may help to achieve growth and this is true especially in a country where the domestic market has stagnated and is not advancing. International trading also allows organizations to reduce their dependency on only a single market. By growing and expanding into an overseas market, an organization gets to benefit from greater economies of scale. This means that over a larger output, costs per unit are drastically reduced and the supplier enjoys a competitive advantage (Dransfield, 2004).
Response to Competition
This is another reason for international trade. Intense competition at home for example, may force a company to seek markets for its products or services overseas. Alternatively, where markets are largely dominated by companies that are involved in international trade, the only way for any company to compete them is to also trade internationally.
Economic Benefits in Developing Countries
Opportunities overseas may arise in developing countries where goods or services produced in more developed countries are in high demand. Sometimes, a number of economic benefits such as cheaper labor costs may exist in some countries and this makes it worthwhile for traders to produce in such countries (Dransfield, 2004). The rules, regulations and economic conditions such as taxation and currency values that are established in another country may provide organizations with very useful opportunities to grow.
In certain areas, organizations have been able to import raw materials cheaply from the developing nations, process tem into finished goods and export them back to the very countries that provided the raw materials. Both countries therefore benefit from each other. It is, however, important for the countries involved to trade based on an agreement that will deprive either party. Without such agreements, one party may easily take advantage of the other.
Globalization
Advances in technology are forcing organizations to change their approach to business. There is an increasing trend for organizations to broaden their perspective and go beyond national boundaries (Dransfield, 2004). Companies that are not able to make the big leap to becoming global will soon discover that they are becoming irrelevant and may be swallowed up by giant companies. Overcrowded and saturated home markets are also encouraging organizations to look for new customers and other opportunities in markets overseas. An effect of increasing globalization of markets is the increasing interdependence among markets and a continued growth in opportunities for businesses desiring to develop an international presence (Dransfield, 2004).
Although quite similar when it comes to the fundamental marketing principles, there are clear differences between international and domestic marketing. Some of these differences are discussed below.
The degree of complexity in international marketing is relatively high compared to that of the domestic marketing. International marketing is also unique due to the fact that firms are faced various uncertainties. Some of these uncertainties arise from the fact that the businesses have to deal with unfamiliar legal environments, unpredictable consumers, competition, weather and government controls.
Environmental Differences
The business environments within which organizations implement their marketing plans are dynamic in nature. Despite the fact that businesses which operate within the domestic and the foreign markets face uncontrollable marketing environments, firms within the domestic market feel more comfortable. As a result, they can rely on their forecast regarding the future business climate in their operation. On the other hand, firms within the foreign market cannot depend on their forecasts with a high degree of certainty.
Difference in the Application of Marketing Techniques, Concepts and Principles
Firms which have ventured into the global market face intense competition arising from the large number of firms within the global market. Additionally, such firms are also faced by unique market problems which firms within the domestic market do not experience. As a result, they are required to develop unique competitive strategies in order to survive in such an environment.
Difference in Relations Between the Businesses and the Government
In their operation, firms which have integrated the concept of internationalization may experience a challenge arising from conflict between the firm and the host government. Some of these conflicts may arise from lack of agreement regarding transferring funds from the foreign to the domestic country. The host government may require the earnings made by the foreign company to be re-invested in its economy. Additionally, the products being marketed y the multinational company may result into a significant social transformation. For example, by venturing into the Chinese market, a company such as Kentucky Fried Chicken and Pepsi may introduce products which may result into change in the Chinese attitude towards materialism and leisure. However, such a transformation may not be desirable for the Chinese government. Therefore, conflicts between the company and the host government may have significant effect on the marketing strategies adopted.
In order to survive in such an environment, international marketers must possess a high level of marketing competence. Some of the core competences that they must possess relate to ability to communicate effectively and to appreciate the cultural differences. However, domestic marketing does not necessary require individuals to possess these competences.
In domestic marketing, the marketing strategies used are geared towards influencing customers within the same country. A company operating in a domestic market only caters for local customers and does not need to bother with takes place in foreign markets. There are, however, possibilities that the company may be competing with other international companies. In international marketing, an organization endeavors to win international customers and competes against foreign companies. Goods and services are often produced to be marketed in overseas markets. Whereas the coverage of a domestic market is very narrow, an international market is quite large and offers a greater number of opportunities. International marketing also has the advantage of generating foreign currency for an organization. The foreign currency may later on become very helpful when the economy begins to decline. Unlike domestic marketing, international marketing is to a great extent affected by political relationships and international laws as well as barriers.
Reference List
Customer Service Manager. 2012. United Kingdom: Natterbox poll finds six in ten customers leave and go elsewhere after a poor telephone experience. 2012. Web.
Dransfield, R., 2004. Business for foundation degrees and higher awards. Oxford: Heinemann.
Groucutt, J., Leadley, P., & Forsyth, P., 2004. Marketing: Essential principles, new realities. New York: Kogan Page.
Hinchcliff, M., 2010. The customer service hall of shame. Sydney: University Of Wollongong.
Jain, A., 1999. Marketing information products and services: A primer for librarians and information professionals. Ottawa: International Development Research Center.
Leader, W., & Kyritsis, N., & Roberts, F., 1990. – 4475 Words | Essay Example of marketing. Cheltenham: Thornes.
Perret, F., & Jaffeux, C., 2007. Essentials of logistics and management. New York. EPFL.
Pride, W., & Ferrell, O., 2006. Marketing: Concepts and strategies. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co.
Richardson, N., & Gosnay, R., 2011. Develop your marketing skills. London: Kogan Page.
Slater, F., & Narver, J., 1994. Market orientation, customer value and superior performance. 2012. Web.
Tutor2u. 2012. What is marketing? 2012. Web.