Introduction
According to Smith (2002) suggests that “Break even analysis is the point at which cost and expenses equals to revenues” (Smith, p. 3). Forecasting is a statistical model used to calculate and predict future trends using analyzed data.
Break even analysis
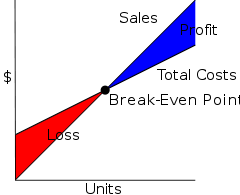
This is a business model used in economics and cost accounting to determine the point at which the revenues are equal to expenditure. At this point there are neither profits nor losses realized but only opportunity costs paid. Businesses use breakeven analysis to determine when all the expenses will be paid and at what point the business would start to realize profitability. It is pointed out that the expenses involved need to be clearly stated and identified.
Expenses involved include fixed and variable costs which are usually used for calculating the breakeven point. Fixed costs are costs that do not vary with sales volume produced hence are always constant.All start up costs are usually considered as fixed expenses and include costs such as rent ,insurance and other expenses usually included in the startup of the business such as administrative salaries. Variable costs on the other hand are not constant and are usually recurring with each extra unit produced and mostly include transportation costs and manufacturing costs for a product.
Breakeven point is usually calculated as:
- Fixed costs/ (selling price per unit- variable costs).
Managers should use this model to determine when they are to break even i.e. point at which they are able to fully cover all their expenses in order to start achieving profitability. It helps the managers to know how many units they need to produce in order to cover costs and start achieving profitability.
Business forecasting
Muller (2005) defines “Business forecasting as a process of estimating future patterns and trends using the compiled data from the field” (Muller p.12). Examples of business forecasting techniques include: services and products demand prediction on fraud and risk, inventory management and reorder level calculation. Forecasting models are usually used by executives, analysts and end users in making decisions using intelligent software and decision support systems. Examples of forecasting models comprise of financial forecasting models, quantitative models and qualitative models.
Qualitative models are considered to be effective in determining short term predictions of products and services of companies and where the scope involved is limited. They are usually considered to be professionally determined in order to make material decision. However it is considered that they are usually subject to certain limitations involved in the market such as measurable data. Qualitative methods commonly used include market research analysis and Delphi method. Market research analysis involves testing a certain product or service on random or a large group to determine whether it will be bought or not when it is launched in the market.
On the other hand Delphi method involves using sales and field experts and using their forecasts and then compiling it to a material opinion to be used in making decisions. Managers should use qualitative methods to determine the short term factors such as weather changes customer tastes and preferences to make decisions on how to price and procure.
Quantitative methods use variables and eliminate the human factor in accomplishing its purpose and examples are such as time series analysis, moderator approach and eccentric modelling.Variables such as sales, product cost and expenses involved are calculated to come up with the required data. Managers should use quantitative methods to analyze the data
References
Muller, B.M (2005). Business Forecasting. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
Smith, C.T (2002). Fundamentals of Economics. Mississauga, Canada: Jones and Berlet Publishers.