Background
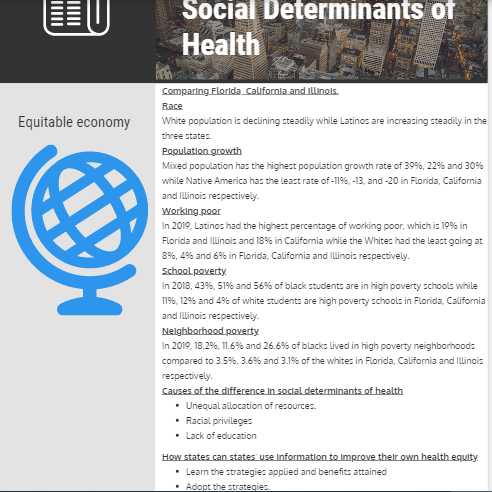
The social inequalities existing in the three states result from decades of systemic racism and historically biased resource allocation. The way a government distributes its resources can result in the inequalities experienced (Donkin et al., 2018). Some of the indicators of inequality are race, population growth, working poor, school poverty, and neighborhood poverty. Based on the information from National Equity Atlas, states such as Florida, California, and Illinois have different data regarding the indicators. For example, the racial makeup in Florida, California, and Illinois has some similarities and differences (National Equity Atlas, 2021). All three states have Asians, Blacks, Whites, Mixed, Native Americans, and Latinos. In all the states, the population of Whites continues to decline while Latinos continue to rise steadily. The following table shows the similarities and differences of data involving the five indicators in the three states.
Insight and Analysis of Each Indicator
The indicators being investigated are race, population growth, working poor, school poverty, and neighborhood poverty. First, starting with race, the population of Latinos has grown tremendously, from 9% in 1980 to 26% in 2020, while the population of whites has declined steadily, from 77% in 1980 to 53% in 2020 in Florida (National Equity Atlas, 2021). Second, the mixed population had a 39% growth rate of 39% while Native America had a growth rate of -11% between 2010 to 2019 in Florida. Third, Latinos had the highest percentage of working poor while the whites had the lowest percentage in all the three states (National Equity Atlas, 2021). Fourth, most black students are in high-poverty schools compared to white students in the three states. Finally, the blacks were the majority of people living in high neighborhood poverty.
The Indicators as Drivers of Inequity
Race, population growth, working poor, school poverty, and neighborhood poverty can drive inequality in the US. First, race as an indicator results in population differences (National Equity Atlas, 2021). Based on the data source, it is projected that the population of minority groups will be more than the whites by 2050. Second, the population growth rate is linked to economic inequality. For example, millennials choose to have fewer children because of economic hardships. Third, working poor are often associated with unequal pay in the workplace and illiteracy. When there is unequal pay, some people will work and still earn less compared to others (Lohmann & Marx, 2018). Fourth, school poverty can be linked with unequal distribution of resources in public schools. Finally, neighborhood poverty can also be linked with an unequal allocation of state resources. For example, the neighborhoods where blacks live have been deprived of resources. Therefore, these indicators can be used as drivers of inequality in the US.
Strategies to Help Grow an Equitable Economy
There are various strategies that can be applied to help foster an equitable economy by addressing inequality. First, racial inclusion in governance will aid in eliminating poverty in all races in the US. The strategy will ensure that the interest of everyone is included regardless of their race. Second, increasing the minimum wage is a strategy aimed at reducing the number of working poor among Latinos and other minority groups in the US. Third, raising the standards of all public schools and providing social support services will ensure that they have appropriate resources to support learning (Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, LLP, 2019). Finally, the implementation of equitable economic development will aid improve the status of poverty-stricken areas. For instance, change the black people’s neighborhoods in the three states. Thus, these strategies can be implemented to create an equitable economy.
Infographic
References
Donkin, A., Goldblatt, P., Allen, J., Nathanson, V., & Marmot, M. (2018). Global action on the social determinants of health. BMJ global health, 3(Suppl 1), e000603.
Lohmann, H., & Marx, I. (Eds.). (2018). Handbook on in-work poverty. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, LLP. (2019). Medicaid’s Role in Addressing Social Determinants of Health. Health Policy in Brief.
National Equity Atlas. (2021). National Equity Atlas.