Description of the system
Business administrators and computer scientists have long realized that information technologies can greatly assist customer relationship management (CRM). There are various CRM applications; overall, they are aimed at supporting the following activities as marketing and sales activities, technical support, and so forth (Sheth, Parvatiur & Shainesh, 11).
CRM tools can be divided several groups: sales automation software, scheduling applications, order management programs, etc. These applications can function separately although very often they are grouped into a software package. The choice of programs depends upon the size of the company, its structure, and their supply chain, and the kind of product that they offer to their clients. Therefore, the composition of CRM application can vary.
CRM solutions enable the company and its customers to interact through different types of channels such as telephone, e-mail, instant messaging, or chat (Jha, 2). In the majority of cases, they are Internet-powered.
These programs are supposed to provide accurate information about the customers, their needs, their response to the product, or to the marketing campaign of the company (Jha, 6). We need to note that CRM applications draw information from different kind of sources, for example, service personnel, sales managers, marketing departments, call centers, or business developments agents (Picture 1) (Sheth, Parvatiur & Shainesh, 16).
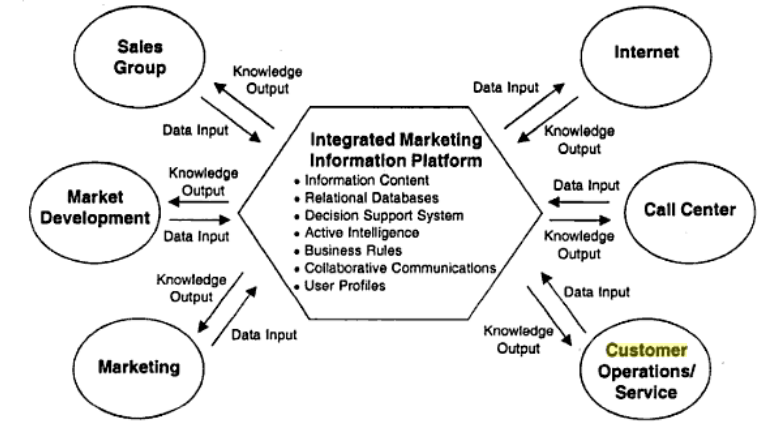
Thus, one can say that CRM systems can be regarded as analytical tools which help the management to understand the behavior of their clients and their buying preferences. Furthermore, these applications are intended for simplifying the interactions between the clients. It is very important when one speaks about ordering or purchasing of goods.
Judging from this description, we can argue that a CRM system can be regarded as a set of multimedia solutions which have to serve a wide range of organizational purposes. They assist the management with the collection and analysis of the information about customers and market trends.
The benefits of the system
A company that has successfully implemented CRM systems can expect a great number of benefits. For instance, they can reduce the time required to respond to the client’s needs and increase customer retention (Kurtz, MacKenzie and Snow, 301). When we are speaking about the customers’ need, we should mention such issues as expectations for the product or service, and the problems which they need to resolve.
The second improvement brought by CRM systems is cost savings, such as reduced capital investment, especially the money required for product development. Secondly, these applications enable the companies to reduce labor costs (Picture 2) (Reynolds, 28). On the whole, the major advantage of these applications is that they allow the company to “hear the customers’ voice” (Grünewälder, 5).
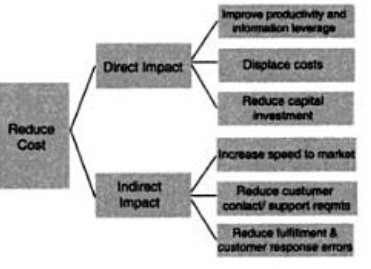
In other words, they can understand why the customers can either loyal to the company or dissatisfied with it. CRM solutions provide the clients with an opportunity to express their views about the company’s product or services and make recommendations for their improvement. By adopting CRM systems, the management can convince the clients that the company is concerned with their problems and needs. This is one of the best ways to increase customer retention rates.
Among other advantages of these applications is that they allow enterprises to better match the supply of their products with the demand. The thing is that they provide historical data about sales rates. They show how whether a specific type of product will be required by the customers in the future.
This information is very important for those enterprises which manufacture a great variety of items. CRM applications help them develop production schedules and avoid such risks as shortage of supplies or overproduction (Kurtz, MacKenzie and Snow, 301). Thus, the benefits of CRM systems are related to the following areas:
- Customer satisfaction and loyalty;
- Internal operations;
- Cost savings.
Its application in business activities
Customer relation management tools can be applied to different business activities. One of them is the monitoring of the employees’ performance.
This function is particularly important when we are speaking about service companies, in which management has to know whether employees are able to respond to the customer’s requests as quickly as possible (Jha 230). Another business activity that we need to mention is product development. CRM applications provide accurate numerical information about the clients’ reaction to new products and services.
The thing is that by using these programs, the management can understand why customers can either like or dislike a product. By using these data, the company can better manage its value chain that includes supply of raw materials, manufacturing, marketing delivery of goods, and post-sale services (Reynolds, 27). Therefore, it is possible to argue that CRM applications can be indirectly related to every business activity of an enterprise.
Additionally, one should not forget that CRM applications can help them management determine whether the company’s internal operations are efficient.
For instance, if the customers are often complaining of the employees’ lack of responsiveness, the necessity to wait for a long time, untimely delivery of goods, and so forth, the management should focus on the structure of the organization, the training of the workers, and the cooperation between different departments.
Customer relation management systems can pinpoint the underlying cause of the problem. More importantly, they can assist front-line managers who organize the employees and evaluate their performance.
Modern companies place companies at the core of their every business activity, including product development and design, production, marketing, assessment of performance, and other areas. The strategy is based on a self-evident fact that clients are the major stakeholders for any organization. Customer relation management applications only help them implement this philosophy. This is why they are so important.
The relevance of the CRM applications to marketing
In the previous sections, we have described several applications of CRM system. At this point, it is necessary to discuss their relevance to the marketing activities of an enterprise. One of the most important applications is sales force automation, which means that this software reduces the time required to order goods or service, make financial transaction, and deliver the products to the client (Chaffey et al, 342).
Additionally, CRM systems enable the management to see which distribution channels are the most effective (Havaldar, 73). For example, the companies need to know whether the clients purchase via Internet or from chain stores. CRM solutions can give them accurate statistical data about the purchases made by the clients. Therefore, the management can determine which distribution channel is more important to them.
Another marketing application of CRM is that it allows the management to understand how clients learn about the products and services. This knowledge is essential for the management because it allows them to develop advertising strategies (Chaffey et al, 342).
For instance, many companies do not know whether they should promote their products through television, radio, newspapers or Internet. CRM systems show how customers search information about new goods and services, and this is major application to marketing activities of an enterprise.
Finally, CRM applications show which products the customer has recently purchased. This data can be used by the developers of online websites (Chaffey et al, 342). So, we can say that CRM applications can support different marketing activities. They main function is to offer the management tools for the analysis of quantitative or qualitative data so that they could understand the future behavior of the clients.
CRM systems help the executive officers understand why people buy certain types of products, why they do, how they learn about them and what appeals to them most. Without answering questions the company can hardly plan any marketing strategies. Customer relation management tools are important for market research and advertising campaign.
The use of this system by Saudi Arabian firms
Statistical data suggest that Saudi Arabian firms are willing to adopt CRM system in order to enhance their performance because the economy of this country is now becoming less oil-based and many industries such as construction, IT, services sectors, and banking institutions require customer relations management tools (CRM Forecast, unpaged). There are numerous examples of how CRM are used by Saudi Arabian firms.
We can refer to such company as Al Alamiah, which is a leading software provider in the country. The company had to find ways of improving support center activities, especially when engineers had to respond to a customer’s problems either with the equipment or software (SAGE, unpaged).
Before the implementation of this system the company had to spend much time in order to spread information from one department to another. As a result, the clients had to wait for hours and many of them were dissatisfied. The CRM applications, which Al Alamiah installed, allowed them to automate this process and monitor the performance of engineers. As a result, this service company managed to reduce the response time and avoid criticism of the clients.
Another example is Al Rajhi Holding Company that consists of more than 100 divisions. The corporations needed to create a single customer database and develop tools of analyzing sales information. They needed to analyze sales data by product, region, salesman, or period (SAGE B, unpaged).
This is why they implemented Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system that included CRM programs. These tools helped them develop marketing strategies and organize their supply chain. Judging from these two examples, we can argue that Saudi Arabian companies adopt CRM solutions in order to improve the cooperation between different departments and speed up the flow of information.
These applications bring them such benefits as increased satisfaction of the customers, opportunities for planning the production, and ability to understand the buying preferences of the clients. These examples suggest that in the future Saudi Arabian firms will make full use of CRM systems to improve their performance.
Works Cited
Chaffey Dave, Ellis-Chadwick Fiona, Mayer Richard, and Kevin Johnston. Internet marketing: strategy, implementation and practice. NY: Pearson Education, 2009.
CRM Forecast. “CRM Software Market Share For The Middle East”. (n. d) Web.
Grünewälder Arend. Implementing CRM Systems: Approaches and Potential Problems. Munich: GRIN Verlag. 2008. Print.
Jha Lakshman. Customer Relationship Management: A Strategic Approach. Dehli: Global India Publications. 2008. Print.
Havaldar Krishna. Business Marketing: Text & Cases. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. 2010. Print.
Kurtz David, MacKenzie H.F. and Snow K. Contemporary Marketing. NY: Cengage Learning. 2009. Print.
Reynolds Janice. A practical guide to CRM: building more profitable customer relationships. London Focal Press, 2002. Print.
SAGE. “Case Study Al-Alamiah implements SalesLOGIX CRM” 2010. Web.
SAGE (B). Case Study Sage connects large Saudi enterprise. Web.
Sheth Jagdish, Parvatiyar Atur, and Shainesh G. Customer relationship management: emerging concepts, tools, and applications. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. 2001. Print.