Abstract
Cloud system has become one of the most important business strategies in the current competitive business environment. The increasing need for communication, data analysis, data storage, and dissemination demands for improved information technology infrastructure that may not be available within a given business unit.
This has made it necessary for many firms such as Samsung and Nike, to outsource these services from vendors which offer cloud computing. This strategy not only improves communication within various departments, but also makes it possible for the company to monitor movement of products from the production plants to the market. However, the issue of privacy and security of the data has been cited as its main challenge.
Background
Effective supply chain has become very vital for many firms as the market become increasingly competitive in various industries. According to Gibb (2006, p. 89), firms which operate in the global market have the pressure of delivering their products to the market within the shortest time possible and in the right shape.
The processes in supply chain management must be shortened to ensure that associated costs at every stage are significantly reduced. For instance, products should take the shortest time at storage as a way of reducing costs of storage, and the risk of damage when products take longer than expected in these stores.
It is also important to ensure that goods on transit are effectively monitored to ensure that they arrive at the desired markets within the time that was set (Molen & Brace 2010, p. 25). It is only through this that a firm can ensure that its products are consistently available in various global stores. Reduced costs of product delivery are also an assurance that the cost of delivering products to the market will be reduced.
This will mean that the firm will be able to charge competitive prices in the market. According to Berger (2006, p. 21), cloud computing business models offers these companies a solution in making their supply chain strategies efficient and cost effective. In this research, the focus will be on how Samsung and Nike have used cloud computing models to improve their supply chain in the market.
Cloud Computing Model
According to Carmel and Tija (2006, p. 18), cloud computing has gained popularity as firms around the world try to find ways of improving the quality of products in the market. Many firms around the world have come to realize that to achieve efficiency, they cannot afford to undertake all the activities involved in delivering products to the customers.
For this reason, most firms are specializing in activities they consider most important in maintaining the quality of their products and brands in the market, and outsourcing other activities from other vendors in the market (Jamsa 2013, p. 84). This is the concept under which could computing model in the supply chain come in within a given firm.
Instead of making heavy infrastructural investment to purchase servers, firms have opted for cloud computing models which are considered more reliable and very effective in managing information in supply chain. According to Jae-Nam (2008, p. 570), cloud computing has been very vital in four main areas of operation within a business unit. These areas include planning and forecasting, logistics, sourcing and procurement, and service management processes.
Each of the stages is very important and correct application of cloud computing strategies in the key to achieving success in the market. However, to achieve this, (Dutrénit & Vera-Cruz 2007, p. 326) warns that it is important to identify specific activities that are cloud friendly. The figure below identifies activities that are cloud friendly based on the sensitivity of the data and the network effect.
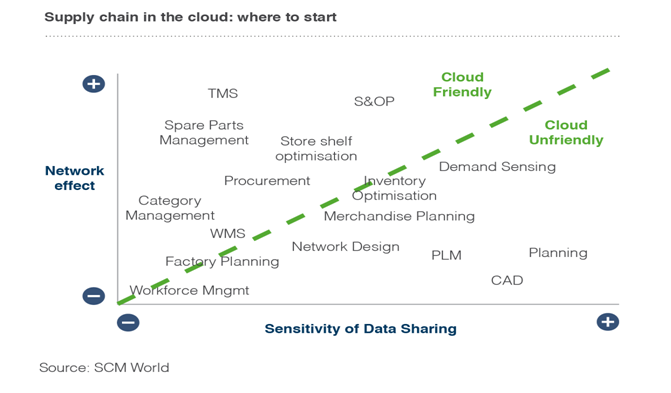
According to Djellal & Gallouj (2013, p. 60), this is the first step towards a successful use of cloud computing model in supply chain management. There are some specific activities that cannot be carried out using cloud computing model because of the sensitivity of data sharing.
Some of the sensitive information may be leaked to competitors if this model is used in some processes, making the firm vulnerable to its competitors (Rhoton 2009, p. 57). This means that not every process would need cloud computing as an appropriate strategy in achieving the desired success in the market.
After identifying the processes that need cloud computing technologies, it is important to understand the business model that will be appropriate for the individual task within the supply chain. The business model can be classified as HaaS (Hardware as a Service), SaaS (Software as a Service), and cloud computing (Kaplan & Norton 2006, p. 109).
Hardware as a Service is increasingly becoming popular among business units around the world. In this business model, a central provider leases computing power to firms upon request.
This model seeks to eliminate the cost of putting up the infrastructure, by enabling a firm to lease these services from the central providers. In this model, the user rents the asset for the specific period when the services are necessary. This model allows a firm to contract a central service provider to maintain and administer hardware system within an organisation through on site services or remotely depending on the needs of the setup.
According to Koontz and Weihrich (2013, p. 50), Software as a Service is another business model where software applications are hosted central service provider or vendor and made available to the users through an internet network.
Many companies have found this strategy very useful in cutting the cost and improving efficiency of their operation. This is because this model enables them to access web-based solution without the need to maintain servers or set up IT infrastructure (Sosinsky 2011, p. 48).
In the current business environment where physical space is becoming scarce, this is one of the most important strategies that any firm can use to achieve efficiency in its supply chain management. Other important components of cloud computing include Infrastructure as a Service, Process as a Service, and Platform as a Service.
Application of cloud computing business model can use either of the components or a combination of two or three based on the needs at that particular time. According to Mukherjee (2009, p. 29), firms have the task of identifying the specific needs of the company and finding the model that would be the most appropriate at that particular time.
The next step would be to identify the service provider that would offer the best services within the desired timeframe. At this stage, it would be necessary to discuss how some of the leading firms in the world are using cloud computing in their supply chain to achieve success in their respective industries.
Cloud Computing in Samsung Corporation
Samsung is operating in one of the most competitive industries in the world where success of a firm is hinged on the superiority of the strategies it uses in the market. The electronic industry has become very competitive as many firms, especially those from China, have infiltrated the industry with cheap products.
According to Parker (2012, p. 38), the electronic industry has remained competitive in the world market, and the market environment has numerous challenges that makes it difficult for firms with inferior strategies to survive. Motorola Inc was once one of the leading firms in this industry, but it was forced out of the market because of its inability to adapt to the emerging technologies.
Nokia is currently surviving to remain competitive and it has since been replaced by Samsung as the top manufacturer of mobile phones. The success of Samsung can be directly attributed to its emphasis in using modern technologies in various stages of product delivery.
However, this success was not achieved overnight. It involved a vigorous process of working through various strategies available in the market to achieve specific objectives within changing market environment.
Supply chain was once one of the most challenging management tasks for Samsung. With its main manufacturing plant in South Korea, Samsung was finding it difficult to avail its products in the world market, especially the U.S. market that was considered very lucrative. Some of the main competitors of this firm were actually American firms with their production plants within the United States.
This meant that they did not have to incur the cost transporting products to the market. This gave them a competitive advantage over Samsung which had to move its products miles away to the markets in this country and various other parts of the world. According to Winkler (2011, p. 81), customers prefer buying products that are always reliable in the market.
When a customer plans to purchase a Samsung television, camera, phone, or laptop, he or she would be pleased if he or she finds a variety of this brand to choose from in the stores. In case the brand is not in the store, such a customer would switch loyalty to competing brands in the market. This was one of the biggest challenges that this firm had to address in its supply chain management.
The supply chain and marketing units realized that one of the biggest weaknesses in their supply chain was poor communication system between the marketing unit and various departments, especially those who were in the field. Communication breakdown was a common phenomenon at the firm as the system went down when it was needed the most.
The firm spent a lot in purchasing the infrastructure for the serves and in hiring qualified personnel to ensure that the server was operating optimally. Despite this heavy investment in IT infrastructure, Samsung was not getting the results it expected. Communication between the firm and its agents in the world market remained disruptive and unpredictable.
In some cases where there were agencies, it forced some of the employees to make direct phone calls which were not only very expensive, but also lacked references that are always important when undertaking important business tasks. As the firm was growing, its servers were becoming weak, and this was affecting its supply chain.
To solve this problem, Samsung employed cloud computing business model in its supply chain management. In order to back-up its servers, this firm decided to introduce Hardware as a Service from CharTec Business Solutions as a way of solving the constant problem of constant server breakdown. CharTec was assigned the task of developing and administer hardware assets to help improve communication within the firm.
This firm was to provide Samsung with a strong server and other related hardware services that would help in improving the communication system within the firm. Given the increasing amount of information that needed storage, analysis, and transfer, the firm noted that the best approach would be to rent the services from this firm.
CharTec would be responsible for monitoring the servers to ensure that it was operating optimally and that data flow and data storage within the firm was effective enough to meet the needs of Samsung. The HaaS component of Cloud Computing Business Model offered the solution that Samsung needed to improve is supply chain (Sherman & Zhu 2013, p. 71).
The firm was able to get the right information about the products needed in the market. It would also monitor the movements of various products from various sources to the firm, and from the firm to the market. The serves became strong enough to support the increased need for information flow and storage within the firm. This partly explains why Samsung has been very successful in the market
Cloud Computing in Nike
Nike is one the leading firms in the apparel industry. For a long time, firms in this industry believed in marketing using the mass media as a way of reaching its customers. Bick-and moter stores was the only way of selling products to the customers. This meant that firms had to developed huge stores along busy streets in order to attract as many customers as possible.
The stores had to be strategically arranged in order to appeal to the customers. Supply chain took a simple model where the outlets would make direct phone calls to the production units in case the stocks for the products had gone down. With the increasing customers, this business model started failing (Wejman 2010, p. 24).
It was common to experience a scenario where by the time products are released from the production plants, the shelves at various outlets would be lacking the products. This meant that customers would not be able to get the products they desired.
Things became worse when firms in this industry started embracing online business. The servers of this firm were too weak to support online business even after the management decided that the firm would go online.
The supply chain and marketing units realized that there was a need to introduce cloud computing business strategies as a way of changing its supply chain from the analogue system to a digital one. The management needed both the HaaS and SaaS components of cloud computing business model.
HaaS was needed because the current infrastructural IT assets at the firm were not able to support the increasing need for information. This was outsourced from Equus Managed Services Solutions. SaaS was needed to improve the software applications that were used by the firm (Yeaple 2006, p. 610). NetSuite was considered the most appropriate firm for this service.
NetSuite was assigned the task of offering software solution that would help the marketing unit to track movement of cargo while on transit. The cloud had to make all relevant information available to different employees of the firm at different locations around the world.
The communication system between different departments also had to be improved. This is one of the business models that have enabled Nike to become the leading firm in this industry.
Challenges of using cloud computing in supply chain
According to Beard (2008, p. 17), many firms have embraced cloud computing business strategy as one of the best ways of improving communication system. However, there are a number of challenges that have hindered its effective usage in the market. One of the main challenges is the issue of security and privacy of the information in the cloud.
Given that the information is managed by a third party, its security is not guaranteed. Halpert (2011, p. 70) also notes that the quality of the service may be compromised because the service provider is serving many companies. This system also poses challenge with the billing system that should be highly secure.
Conclusion
It is clear from the discussion above that cloud computing is gaining popularity in supply chain management. Cloud in supply chains offers a completely new approach of managing supply chain within a firm. It involves integration of the emerging technologies into supply chain system in order to improve speed, reliability, and efficiency of delivering products into the market.
It improves communication in the process of delivering products to the market. Many firms around the world are currently using various models of cloud computing in their supply chain as a way of improving their efficiency in the market.
List of References
Beard, H 2008, Cloud computing: Best practices for managing and measuring processes for on-demand computing, applications and data centers in the cloud with SLAs, Cengage, New York.
Berger, S 2006, How We compete: What companies around the World are doing to make it in today’s global economy, Currency-Doubleday, New York.
Carmel, E & Tija, P 2006, Offshoring information technology: Sourcing and outsourcing to a global workforce, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Djellal, F & Gallouj, F 2013, Measuring and improving productivity in services issues, strategies and challenges, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham.
Dutrénit, G & Vera-Cruz, A 2007, ‘Triggers of the technological capability accumulation in MNCs’ subsidiaries: The maquilas in Mexico’, International Journal of Technology and Globalisation, vol. 3. no. 3, pp. 315-336.
Gibb, F 2006, ‘A framework for business continuity management, International Journal of Information Management, vol. 26. no. 2, pp. 128- 141.
Halpert, B 2011, Auditing Cloud Computing: A Security and Privacy Guide, Wiley, New Jersey.
Jae-Nam, L 2008, ‘Exploring the vendor’s process model in information technology Outsourcing’, Communications of AIS, vol. 22. no. 1, pp. 569-589.
Jamsa, K 2013, Cloud computing: SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, virtualization, business models, mobile, security and more, Jones & Bartlett Learning, Burlington.
Kaplan, R & Norton, D 2006, ‘How to Implement a New Strategy without Disrupting Your Organization’, Harvard Business Review, vol. 4 no. 3, 100-109.
Koontz, H & Weihrich, H 2013, Essentials of management: an international Perspective, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Molen, F & Brace, C 2010, Get ready for cloud computing: A comprehensive guide to virtualization and cloud computing, Van Haren Publishing, Zaltbommel.
Mukherjee, P 2009, Operations management, and productivity Techniques, PHILearning, New Delhi.
Parker, D 2012, Service operations management: the total experience, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham.
Rhoton, J 2009, Cloud computing explained: Handbook for enterprise implementation, Recursive Ltd, London.
Sherman, H & Zhu, J 2013, Service productivity management improving service performance using data envelopment analysis (DEA), Springer, New York.
Sosinsky, B 2011, Cloud computing bible, Wiley, Indianapolis.
Wejman, B 2010, ‘Continental Airlines: Outsourcing IT to Support Business Transformation’, International Journal of Communication, vol. 2. no. 1, pp. 19-25.
Winkler, V 2011, Securing the Cloud: Cloud Computer Security Techniques and Tactics, Elsevier Science, Burlington.
Yeaple, E 2006, ‘Offshoring: Foreign direct investment and the structure of US trade’, Journal of the European Economic Association, vol. 4. no. 2, pp. 602-611.