Introduction and Overview
Organisational effectiveness is one of the key measures of the success of a business. It entails examining the business in terms of its profitability, productivity, efficiency, adaptive-ness, growth, morale, stability, and ethical conditions. For these conditions to be achieved, it is necessary that the organisation architecture, decision making process leadership and team building activities be carried out effectively.
This research work evaluates the different managerial functions that must be carried out to ensure that the organisation is effectiveness. A detailed analysis of these factors is carried out to determine their importance and what managers should do to ensure that their company is effective.
Organisational Architecture
Organisational architecture refers to the process through which organisations guide and control the business so as to realize their principle qualities such as customer satisfaction. Figure 1 below shows the main elements of the organisation architecture.
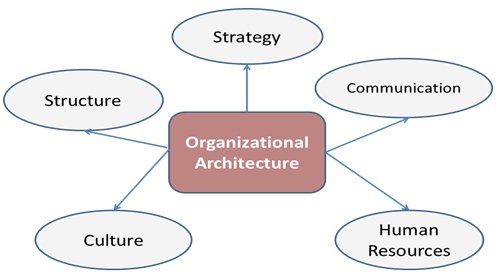
Figure 3 elements of organisational architecture
Organisational Society
An organisation is operated under strict guidelines and fixed rules. Furthermore, organisations have a hierarchical rank. This is referred to as bureaucracy. The main characteristics of a bureaucratic organisation are division of labour, technical competence, hierarchy to the authority, meritocracy, rules, formalization and rights of the position. For the organisation to be effective the following factors must be taken into consideration:
- operations should revolve around the process
- power must be dispersed
- the organisation must focus on the customer
- the organisation must combine both managerial and non managerial functions
- the company must invest in training and developing employees
- the company must reward employees
Organisational structure
The organisational structure is the hierarchical arrangement of an organisation. This structure enables effective communication and sharing of duties within the organisation. Organisation structure results to differentiation and integration. Differentiation entails the subdivision of an activity into smaller parts while integration entails to combination of many task to produce a product or service.
Decision making within the organisation
Decision making in an organisation is one of the key elements. Managers make crosscutting decisions that affect the company performance. Management science developed the need for appropriate decision making in an organisation. In 1950 the bounded rationality theory was introduced as alternative to the classical theory. In 1953, the Herbert Simon formalized the behavioural theory (Simon, 1979).
Decision making theories
Ethical decision making process will entail the use of several principles such as reality principle, value creation, justice, honesty, rational self interest and long term profit (Woiceshyn, 315).
Rational decision making process
In this category, there are two main theories, these are; the classical and the behavioural theory. The classical theory asserts that the predictive power is got from environment shape while the behavioural theory relies on the knowledge and computational abilities of the human agent (Ibrahim, 631). Rational decision making process is a systematic process that aids in the formulation of a decision (Williams, 89; Ibrahim, 631). This process is sequential and has several steps as outlined below (Lunenburg 3):
- Problem identification
- Identifying alternatives
- Evaluating the different alternatives
- Selecting the best alternative
- Implementing the selected alternative
- Monitoring the decision effectiveness
Limitations of the decision making process
The main limitation that affect the decision making process are
- Limited mental capacities and know how
- Limited resources
- Complexities in the organisational environment and emotions (Good & Yeganeh,15).
Management power
For the management to be effective, they must wield some power on their employees. There are several sources of power which managers rely on. These sources of power include: expert power, legitimate power, referent power, reward power and coercive power.
Roles of power in an organisation
The main purposes of managers excising power in an organisation are
- Motivation: managers use power to motivate their employees
- Reward and punish employees: authority allows managers to reward hard working workers and reprimand errant employees
- Compelling vision: the managers can develop a compelling vision
Types of managers
The main types of managers are (McClelland, 128):
- Affiliative managers: these managers aspire to be liked that getting the job done
- Personal power manager: this group focus on getting the job done and don’t care how employees perceive them.
- Institutional managers: these are more interested with power more than anything else
Tactics used by managers to influence their employees
Influence can be defined as the ability to change someone behaviour. Managers use different tactics to influence their employees. Managers must master the ability to influence their employees positively for them to deliver better results as compared to the organisation competitors (Rykrsmith, 1). To do these, managers must develop appropriate tactics. The development of these tactics is influenced by the leader traits, behaviour and the current organisation situation (Holmes, 1). Among the major tactics used by managers include: coalition, exchange, consultation, exchange, pressure, inspirational appeal, legitimating, personal appeal and rational persuasion.
Team building within an organisation
Team building entails the process through which members of a given organisation are seen as working as a group and not as individuals. The main essence of a team is shared goals, collective work, mutual accountability and assigning teams different roles (Norman-Culp, 2). In a team, the members are all committed into working for a common goal and this brings out efficiency and effectiveness in product and service delivery (Katzenback, Jon and Douglas, 167)
A manager must choose and build a team effectively, the main strategies followed when choosing and managing a team are
- Select members with skills and potential to handle the assigned task
- The rules and regulation must be clear
- The group should be trained and new information availed to them
- The group and its leader should spend time together
- Hardworking teams should be rewarded (Katzenbach and Smith, 124)
Communications within the organisation
Communication can be defined as passing of information from one person to another. For managers to be effective in their day to day duties, they must have good communication skills. Communication helps a manager to perform his main duties such as planning, controlling and organising.
The main communication documents within the organisation are letters, memos, financial reports and outlines. The main elements of an organisational conversation include intimacy, inclusion, intentionality and interactivity (Stephen et al.,155).
Conclusions and recommendations
Conclusions
In conclusion, there are several factors that affect the effectiveness of a given organisation. These factors include the organisation architecture, leadership, adopted strategies, team building activities, effective communication and appropriate decision making process. The managers must enhance all these skills for them to be effective and for the organisation to grow.
Recommendations
For an organisation to be effective the following must be done
- Ensure that the decision making process within the organisation is adequate and managers can be able to make rational decisions
- Ensure that workers are encouraged to work as a team
- Ensure that there a good communication channels within the organisation
- Ensure the managers and employees are well trained
- Ensure that the company has a good corporate culture which is geared towards employee and customer satisfaction
Works Cited
Simon, H. A. Rational Decision Making in Business Organization. American Economic Review, 69(4), 493-513. (1979).
Good, D. and Yeganeh, B. “Cognitive Agility: Adapting to Real-time Decision Making at Work”. OD Practitioner, 44.2 (2012):13-17. Print.
Woiceshyn, Jaana. “A Model for Ethical Decision Making in Businesss: Reasoning, Intuition, and Rational Moral Principles”. Journal of Business Ethics, 104.3. (2011): 311-323.
Ibrahim, M. “Theory of bounded rationality”. Public Management, 91.5. (2009):3-5.
Lunenburg, Fred. “The Decision Making Process.” National Forum of Educational Administration and Supervision Journal 27.4 (2010): n. pag. Web.
Radner, R. Costly and bounded rationality in individual and team decision-making. Industrial & Corporate Change, 9(4), (2000): 623.
Williams, Chuck. “Chapter 5: Planning and Decision Making.” Mgmt4. Mason, OH: South-Western, 2012. 89-93. Print.
Rykrsmith, E. (2011, November 15). Becoming a Better Influencer: 4 Most Effective Influence Tactics (Part I) | The Fast Track. Web.
McClelland, D. C. (1995). Power Is the Great Motivator. Harvard Business Review, 73(1), p. 125-139.
Holmes, S. (2008, September 16). The 5 Most Important Influence Tactics For Leaders. Web.
Katzenback, Jon and Douglas Smith. The Discipline of Teams. Harvard Business Review, (1993): 162-171.
Katzenbach, Jon and Smith, Douglas. The Wisdom of Teams: Creating the High- Performance Organization, Harper Business, 1993. Print.
Stephen Robbins & Timothy Judge. Chapter 10: communication. In, Essentials of Organizational behaviour (2009): 155-157.