Introduction
When expanding into a new environment, a company must ensure that it has a sufficiently developed external framework that will allow it to operate in the target market successfully. Specifically, companies need to consider the essential components of the framework that will help them perform core tasks, such as implementing the core production processes, promoting the end product to the target customer, and maintaining consistent communication it the parties involved.
At EnergyUK, the transition to the Brazilian market simultaneously represents a unique challenge and an opportunity that it cannot miss. For this reason, expansion into the Brazilian market can be done by using the technique of partnering and strategic alliance.
The company is likely to experience significant changes in the Brazilian energy sector. Specifically, the transition to a new framework for service promotion and customer attraction models should be chosen as the main point of difference. Similarly, the current competitive advantage and the relevant communication strategies may have to be altered to reflect the company’s usefulness in the target market setting.
Justification
The choice of partnership and strategic alliance as the core means of advancing in the UK market environment is fully justified for EnergyUK. Specifically, the opportunity to create long-lasting partnerships in the target setting and build a strong network of support for is future performance are vital benefits that the proposed avenue provides. Admittedly, the integration of the strategic partnership and alliance approach entails significant expenses compared to other frameworks for entering a new market (O’Dwyer & Gilmore, 2018).
Indeed, the suggested means of integrating the company into a new setting means spending a substantial number of resources on research and development, as well as the company’s promotion and the relevant financing processes to ensure that the organization is attractive enough for its potential partners. However, the strategic alliance and partnership tool also helps a company construct long-lasting connections s with its new business partners by building trust and encouraging active collaboration.
Given the differences between the economic and sociocultural environments of the UK and Brazil, EnergyUK will have to use all available support to develop a strong market presence and gain traction among its target audiences immediately. In turn, strategic alliance and partnership will pave the way to the firm’s fast integration and quick adjustment to the new setting.
Challenges
At the same time, it is necessary to acknowledge the avoidance challenges that EnergyUK will face in the Brazilian market environment. First, alterations in the internal framework of EnergyUK will have to take place as a response to the changes in its selected market setting. Namely, the firm’s employees are likely to encounter difficulties when navigating an entirely new environment.
Specifically, cross-cultural communication and the relevant issues are likely to become the main impediments. To overcome them, EnergyUK will need to introduce employee training sessions prior to entering the Brazilian market to develop cultural competence in the target audience (Fila et al., 2019).
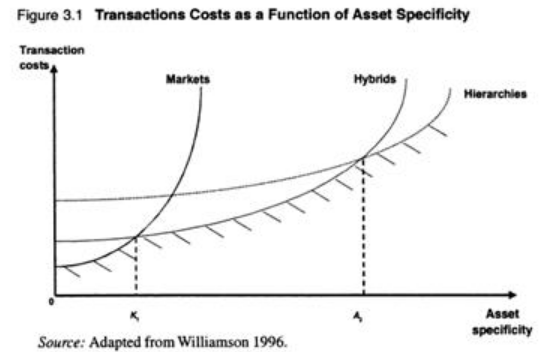
As a result, staff members will gain a more nuanced and intricate understanding of the target population and the specifics of the target market, thus, shaping their performance accordingly. Applying the Transaction Cost theory will show that the increased level of uncertainty caused by the lack of familiarity it the core factors affecting the target market is expected to increase EnergyUK’s costs, which is why the further exploration of the market will be required (see Fig. 1). In turn, the asset specificity (affordable energy) and the recurrence (regular) will help minimize costs.
Furthermore, the unique characteristics of Brazil’s physical environment and its effects on its energy sector performance deserve to be considered. Namely, reports mention that constant drought and the associated issues lead to obstacles in obtaining and delivering energy to the target population (Hoffmann et al., 2018). For this reason, EnergyUK will need to focus on utilizing all available resources to ensure that it has the required amount of water at its disposal (Games & Rendi, 2019). Additionally, cultural specifics of the target region should be mentioned.
Presently, Brazilian culture is geared toward collectivism, which is why incorporating the reference to the specified aspect of their culture will allow EnergyUK to attract customers’ attention and increase the extent of their engagement with the organization (Benitez et al., 2020).
For example, the emphasis on mutual support that is prevalent in Brazilian culture should be addressed by integrating marketing strategies that focus on a collective effort to improve the quality of Brazilian citizens’ lives. Namely, a promotion campaign emphasizing the role that the unanimous transition to the services of EnergyUK will contribute to environmentalism and overall well-being of the community.
Conclusion
By incorporating the framework of partnering and strategic alliance, EnergyUK will be able to enter the Brazilian market effortlessly and maintain a positive competitive advantage in it. Specifically, the proposed technique will entail a change in the company’s approach to risk management, making its foray into the Brazilian market more secure.
Additionally, the offered technique will help EnergyUK to forge crucial friendships and partnerships that will serve as a means of integrating into the target setting quickly. More importantly, the proposed strategy will allow the organization to ensure that the cross-cultural barrier is overcome and that customers are drawn to the organization and its product.
References
Akbar, Y. H., & Tracogna, A. (2018). The sharing economy and the future of the hotel industry: Transaction cost theory and platform economics. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 71, 91-101.
Benitez, G. B., Ayala, N. F., & Frank, A. G. (2020). Industry 4.0 innovation ecosystems: An evolutionary perspective on value cocreation. International Journal of Production Economics, 228, 1-8.
Elia, S., Petruzzelli, A. M., & Piscitello, L. (2019). The impact of cultural diversity on innovation performance of MNC subsidiaries in strategic alliances. Journal of Business Research, 98, 204-213.
Games, D., & Rendi, R. P. (2019). The effects of knowledge management and risk taking on SME financial performance in creative industries in an emerging market: the mediating effect of innovation outcomes. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 9(1), 1-14.
Hoffmann, W., Lavie, D., Reuer, J. J., & Shipilov, A. (2018). The interplay of competition and cooperation. Strategic Management Journal, 39(12), 3033-3052.
O’Dwyer, M., & Gilmore, A. (2018). Value and alliance capability and the formation of strategic alliances in SMEs: The impact of customer orientation and resource optimisation. Journal of Business Research, 87, 58-68.