Introduction
Aluminium is comparatively a flexible, tough, and lightweight metal. It is silvery in colour, is non-magnetic and doesn’t catch fire easily. Aluminium is also an excellent reflector of radiance and infrared rays. It belongs to the boron family and its chemical symbol is ‘Al’, with atomic number 13. If we talk about the abundance of aluminium, among the elements of our universe, it comes at the third position and among metals it is at the first position – interestingly, it commands 8% of the total solid portion of the earth.
Information source
The United States Government has patens for the manufacturing processes of various metals. The two patents that I chose for this research are 3853541 (Method for producing aluminium metal directly from ore) and 3856508 (Method for producing aluminium chloride, aluminium metal, and iron directly from ores). Both these patents are authentic and have significant information that is relevant to my research question – How is aluminium ore converted to aluminium metal?
The Process
Aluminium metal is extracted from bauxite. Apart from bauxite, there are several other ores from which aluminium is extracted – until recently, some of these ores were considered to be useless. The processes used are called the Bayer process that is done with ‘sub-halide’ and ‘tri-halide’. The optimum temperature required for these processes is more than 1100 degree centigrade. The following chemical reaction takes place during the heating process:
“Al2O3 + 3C + 3Cl2 2AlCl3 (gas) + 3CO + heat1” (Othmer, 1974, p. 2).
In order to extract more quantities of aluminium from the ore, temperature might be increased up to 1800 degree centigrade – the heating is done in a blast furnace. The amount of heat required in the blast furnace depends mainly on the following factors:
- The type of ore being used – the composition of different ores is different and as such the heat required to break the compounds is also different.
- The quantities of silicon tetrachloride, chlorine gas and aluminium chloride being used for the reaction purpose. The heat generated will depend on the quantities of these three.
- The kind of blast furnace being used – heat loss is a major governing factor for the heat to be generated.
As a result of the heating process, “a hot gas stream containing three moles of mono-halide” (Othmer, 1974, p. 1) is released. Pure aluminium is retrieved by cooling this stream. Care is taken that the cooling process doesn’t take too long (optimum time is one to five seconds).
On cooling, “one mole of tri-halide and two atoms of pure metallic aluminium” (Othmer, 1974, p. 1) are obtained. “The flash cooling uses direct contact with a liquid halide of aluminium or a liquid solution of a halide of aluminium and a volatile or a relatively non-volatile halide of a metal above aluminium in the halide affinity series” (Othmer, 1974, p. 1). This is called the electrolysis process.
In addition to this process, there are certain steps from which aluminium may be extracted such as “clays, feldspars, oil shales, red muds from current aluminium production wastes, slimes from phosphate manufacture, slags from iron and manganese blast furnace operations, etc.” (United States Patent, 1974). Following figure shows the extraction of aluminium through electrolysis process:
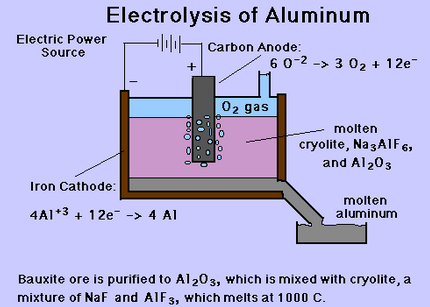
To sum up, aluminium ore is obtained from the earth’s crust in compound form. Using the Bayer process, alumina is obtained. Lastly, after the electrolysis process, pure aluminium is extracted. It is noteworthy that the complete process requires a lot of heat and as such, is a very costly affair.
Textual Analysis
Othmer
United States Patent
Aluminium ore
- Aluminium ore (Bauxite) is obtained from the earth’s crust (p. 1)
- In addition to Bauxite, there are other compounds also that have aluminium (p. 1).
The process
- The ore is processed by a heating process known as Bayer process (p. 2).
- The chlorides that are more explosive are got rid of at the initial stage (p. 2).
- The chlorides that are not much explosive are left behind (p. 2).
- As heat is generated, the following chemical reaction takes place (p. 2):
“Al2O3 + 3C + 3Cl2 2AlCl3 (gas) + 3CO + heat1” (Othmer, 1974, p. 2).
- The optimum temperature for extraction of alumina is 1100 degree centigrade (p. 2).
- For more extraction, temperature may be raised up to 1800 degree centigrade (p. 2).
- The amount of heat required in the melting furnace depends mainly on three factors (p. 3).
- Instant cooling is a critical requirement for attaining maximum output (p. 4).
- Delay in the cooling process might result in loss of precious metal (p. 4).
- A proper coolant liquid may be used in order to expedite the cooling process (p. 4).
Drawbacks
- The process is very time consuming
- The process consumes a lot of energy (especially heat)
- The process is very costly
References
Othmer, D 1974, Method for producing aluminium metal directly from ore, United States Patent 3853541, New York, NY.
United States Patent 1974, Method for producing aluminium chloride, aluminium metal, and iron directly from ores, 3856508, via IP Research & Communities database.