Introduction
Every organization aims at maximizing the revenue realized while minimizing costs. Marketing strategies aim at helping the firm increase its market share, its revenue and competitiveness in an industry.
According to Best (2005, p. 229), B2B marketing is marketing that is related to firms marketing their products to other firms in the industry as compared to B2C marketing that markets products to consumers. Firms employ various marketing strategies that help them gain customer satisfaction and loyalty.
For an organization to market its products, it must have a good brand name, reputation, high product value and proper positioning in the industry. Kent Spice Man seeks to venture into the UK market. However, the company does not have any of these strategies. Kent Spice Man is a newly established firm that lacks market knowledge and expertise.
In order to successfully venture into the market, the company needs to first gain enough information about the operations of the food industry in UK. The information would be helpful in helping the company position its products. Moreover, it will help it properly price the spicy sauces from Asia. This study examines the various B2b marketing strategies that are to be employed by Kent Spice Man in the UK market.
Spice Man Company Profile
This newly established company is yet to begin operating in the UK food industry. The organization aims at selling Spicy sauces from Asia to the UK market. The company is basing on the changing cultural factors in favor of Asian traditional food. In spite of the existing opportunity in the UK market, the company has no strengths since it has no brand name, reputation yet it is suffering from inadequate funding. As the company ventures into the UK food industry, it faces the threat of increased competition in the industry.
External Business Environment: PESTLE Analysis
Political and Legal Factors
Kent Spice man is an organization that is seeking to establish itself as a multinational corporation operating in different countries such as Middle East and in UK. The company operates in the food industry. As the company seeks to venture into multinational markets, the need to comply with various political and legal factors in different countries is necessary. For instance, there are different legal regulations in the countries that the company operates.
The country has various compliance requirements that the company products must meet for continued operation of the company in such a country. The utilization of porter’s five forces in this analysis indicates that competitiveness in the food industry is very with many organizations and brands having been already established.
Economic Factors
The economic environment is vital for the success of Kent Spice man. The global economy is recovering from the effects of the global financial crisis and it has been predicted that it is not until 2012 and beyond the sales in the industry will reach a high level that they were in immediately before the crisis. New entrants in the food industry have led to increased competition in the industry in UK.
Socio-Cultural Factors
The consumption of Asian products has increased amongst UK residents. The changes can be attributed to the younger generation that does not stick to the old cultural values. It is estimated that a large portion of the UK population would be consuming more Asian Spicy sauces in future and therefore, there is need for organizations to begin focusing on the market opportunity.
Technological Factors
Technologically, the food industry is characterized by rapid changes that involve innovations. Companies operating in the industry increase their competitiveness through productivity of high quality food products using latest technology with frequently reviewed product cycles.
Companies have managed to remain competitive in the industry through a significant research and development program and low production costs. Moreover, the companies in the industry have managed to enter into various acquisition and joint venture contracts that have enabled them maintenance cost leadership in the industry.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors are very important in the modern society. It is required that all companies should consider environmental factors such as environmental conservation in their productivity. Firms operating in the food industry in UK have considered environmental sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
Most companies are considering utilizing renewable sources of energy while manufacturing products that are environmental friendly. Regulations have been put in place to care for the environment (Best, 2005, p. 245). Moreover, recycling is highly encouraged.
Literature Review
B2B Business
The aim of every organization in business is to maximize the sales revenue while minimizing the costs incurred in production. In order to maximize sales, marketing among other strategies are utilized.
According to Kothandaraman & Wilson (2001, p. 382), marketing is the ability of an organization to sell its products to its clients. It represents a process employed by management of firms in which goods and services exchange ownership from the producer (firm) to the consumer. Companies market their produce or products they deal in to other organizations.
There are various forms of marketing. An organization can market its product to consumers in what is called business to consumer marketing. It can also market its products to other organizations in what is called business-to-business marketing. This study is interested in the application of business to business marketing in Kent Spice Man Corporation, a newly established organization that intends to sell spicy Asian products to UK.
Business-to-Business Marketing (B2B)
According to Biemans (2010, p. 80), B2B marketing differs from B2C marketing in various ways that include differences in the marketing structure, the nature of buying units and decisions made and the processes used to make decisions. Firms that utilize B2B marketing are known to have many clients that are handled individually. The success of individual handling of the customers depends on the establishment of a good relationship between the organization and the customers.
Thus, good customer relationship management skills are necessary. On the contrary, consumer marketing is based on availability of many individual customers and the development of a brand as the pillars of success for this form of marketing. According to Fletcher and Hart (1990, p. 59), B2B marketing tends not to employ marketing directors or senior people with the responsibility of marketing the firm brand.
B2C marketing is involved in much marketing and senior management employees are employed to market the company brand. In spite of the differences, the marketing practices employed in the two forms of marketing utilize common marketing principles. For instance, there is no differentiation of consumer buyer behavior between different industrial sectors (Garling, WET & CTH, 2000, p. 13).
Critical Issues in B2B marketing
Customer and Relationships: the relationship between an organization and its clients is very important. According to Best (2005, p. 246), an organization using any type of marketing should seek to establish a long-term relationship with its customers. As Kent Spice man seeks to venture into UK, there is need for the company to establish long lasting relationships with its customers in UK.
A good relationship could be created through proper market orientation. The firm needs to conduct orient itself with the UK food industry with specific interest in the consumption of Asian spicy food products. This could be established through a comprehensive market survey.
Market Research
As indicated above, market research is important and necessary for understanding the marketing and consumption trends in the UK food industry. Internal marketing is an issue in most B2B oriented firms especially regarding gathering resources for B2B marketing. After a successful marketing survey, comprehensive planning should follow.
Resource Allocation to Business winning process
This is an issue when it comes to B2B marketing among different organizations. An organization is expected to allocate enough resources to market its products and brand.
When an organization is entering a large industry dominated by many organizations that have invested heavily in the industry, the resources required are many. Internal marketing is necessary for allocation of enough resources to a given project. Failure to market the project internally, internal weaknesses of an organization may undermine the resources allocated for the venture.
Other issues affect a newly established organization that seeks to venture into a new market. A B2B oriented firm may encounter product development and branding issues that may affect the selling of its products in the market. After the venture, planning and product positioning too may prove to be an issue. Lack of enough information concerning the market trends and consumption trends may affect market segmentation and product positioning in the market.
The issues could however be solved through a thorough market survey in the intended market. According to Biemans (2010, p. 92), pricing could also be an issues affecting establishment of an organization in a given market. A new entrant in the industry is expected to sell its product at a lower price than its competitors charge in order to gain customer loyalty. In addition, the low price should be accompanied by high product quality.
Marketing Mix
According to Biemans (2010, p. 105), some organizations employ various strategies in their marketing in what is called the marketing mix. The main components of the marketing mix of many firms comprise of the product, the price, place and promotion. The elements are vital for any new entrant and existing firms in an industry.
Product
The product is the good or service provided by an organization in a given market for its clients. Groucutt, Leadley & Forsyth (2004, p. 154) note that there are other non-physical elements of the products of an organization that the company customers may be interested in. they may include factors such as packaging, quality, features and the brand name.
A new organization offering new products in an industry must think of these features as elements that sell the product. The product being sold should meet the specific needs of the target market. Biemans (2010, p. 125) adds that the appearance of the product make up what the customer is buying.
In order to provide the products and services with desirable features to the customers, a comprehensive market survey is necessary. In addition, during the establishment of a new product, the firm should ensure that the new product bundle meets the business strengths and weaknesses. Before any venture is undertaken, long term though in the line of broadening the product bundle should be undertaken. This would reduce the chances of product maturity and exit from the industry.
Price
The price represents the money that the company charges for its products or service. According to Dean & Patrick (1993, p. 135), price determination is a tricky and frightening exercise for a new organization. In spite of the need to set the prices of the company product lower than competitors in a new market, the low price can send different signals.
For instance, consumers may perceive low prices as an indicator of low quality. The pricing approach adopted by an organization should reflect appropriate positioning of the product in the market hence the need to use a price that covers the incurred costs and the profit margin.
Thus, the outcome price should be neither timid nor greedy because a greedy price would drive the firm out of the market while a timid price would reduce the chances of growth for the firm. Various pricing strategies can be applied by an organization in various markets as explained below:
- Cost-plus strategy: this strategy adds a standard percentage of profit above the incurred production cost. The cost can be effectively arrived at after comparison of costs incurred in production.
- Value-Based strategy: this strategy is based on the valuation perceptions of consumers of the product. The perceptions of consumers are based on various product related factors such as quality, prestige and healthy issues.
- Competitive pricing strategy: this strategy is based on the evaluation of the competitor prices and charging the price that are related to competitors. The strategy is simple to apply because what is required is the comparison of competitor’s prices. Market surveys and gathering of information is vital for the strategy.
- Going rate: The strategy charges prices based on the prices that the good is going in the market. It is applied in markets that the firm lacks control of the price in the market.
- Skimming strategy: the strategy targets high consumers. Thus, it introduces a product in the market at a high price with the intention of targeting affluent consumers.
- Discount pricing: the strategy is based on the reduction of the advertised price by a given percentage.
- Loss Leader: the strategy aims at selling the product at a price that is lower than the cost incurred in producing the product. The goal of the strategy is to attract customers to the firm. New entrants mostly apply it.
- Psychological: this strategy sets the prices of products at a psychologically better price such as $9.99 instead of $10.00.
The decision on the strategy to be employed in pricing is accompanied by determination of payment periods, product bundling, discounts and allowances (Dean & Patrick, 1993, p. 137).
Place
After a careful selection of the target market, the product needs to be distributed to the consumers. The place refers to the distribution channels used to distribute the product. The nature of the product is usually considered in the choice of the distribution channels. According to Kotler et al. (2001, p. 156), the type of firm being established determines the section of the supply chain that the firm would be. A retailer would occupy the lower end of the channel of distribution.
A firm can decide whether to supply its products directly to the consumers or sales through an intermediary (Reseller sales). Whichever strategy adopted by the firm, the management needs to decide the market coverage of the product. In order to cover the market, the firm can use intensive distribution where it places its products to as many places as possible within the market. This strategy is often accompanied by low pricing (Kotler, et al. 2001, p. 156).
The company can perform selective distribution where it narrows the distribution of its products to only a few businesses. This strategy enables the firm to establish a good relationship with its customers because high quality product selling retailers are provided with the opportunity to sell the products of the company.
The organization can also be involved in exclusive distribution in which it restricts distribution to a single reseller. The sales volumes will dictate the inventories to hold and the best means of transportation of the products to the market. All kinds of logistics including acquisition of raw materials should be applied in order to realize the cost minimization objective.
Promotion
Product promotion refers to all means that a firm is involved advertising and selling of the product. Through promotions, the firm lets its customers and potential customers know about the features of the products being offered. According to Slack, Chambers & Johnston (2010, p. 98), promotion aims at revealing the specific good features of the product being offered with the goal of convincing the consumers to purchase it.
The promotion of company products should contain a clear message conveyed through an appropriate channel. The targeted audience should be people with the ability to purchase the product. After a successful market survey, the firm should identify the target for its product hence the promotion. Various promotional channels include the radio, television and the print media. Others include the electronic media and use of word of mouth.
An organization can also rely on public relations to create a good image and reputation hence enhancing the marketability of its products. Personal selling could be utilized with sales persons being employed to sell the products of the firm.
Customer Satisfaction and Business Success
Delivering complete customer satisfaction should be the key goal of all organizations including Kent Spice Man. It has been proved that customer satisfaction is directly proportionate to loyalty of the customer with the organization, leading to subsequent profits for the organization (Andersen, Jacobsen & Mittal, 2000, p. 265).
With increased global competition, tight profit margins, several players in the market, and shorter loyalty spans of the customer, getting customer attention through innovative ways. Organizations have now sensed a need to go beyond a previously set baseline expectations of customer satisfaction levels and travel that extra mile towards achieving customer loyalty. Customer Loyalty, for its part, leads to repurchase rate at lower acquisition costs as compared to those required to win new customers.
Consequently, customer satisfaction leads to large turnovers and profits. Through customer referrals, the organizations can grow their prospective database to add new customers in a cost effective manner. The key to customer loyalty is to satisfy the customer completely in all aspects at every level of interaction with the organization. Satisfying the members of the targeted customer group should be a top priority with all organizations (Jones & Sasser, 1995, p. 88).
Behara, Fontenot & Gresham (2002, p. 116), studied the life cycle of using a product or service to gain insight to customer’s evaluation of a product or service with the ultimate goal of increasing customer satisfaction and bringing in additional revenues for the organization.
They argue that customer satisfaction can be achieved through utilization of accurate data on customer’s expectations based on real time experience rather than ideal situation based expectations. This data can be used to develop an enhanced customer service capability for an organization.
Another way of achieving a high level of customer satisfaction is to understand what a customer goes through before, during and after interacting with a company that provides a product and or service. Thus for sake of analysis, we can assume three modes that are pre-sales, sales and after-sales. During a presales mode, the customer is made certain promises towards functionality of a product or excellence and promptness in service.
During the sales mode, the product/service is provided to the customer for a fee with the service coming at a premium and in the after-sales mode, the customer can get a true feeling of the company’s product and service. This stage sets customer loyalty towards the company based on the delivery of promises made by the company. Most problems occur when the customer is promised too much and delivered too less.
Thus, in order to avoid this, organizations should clearly highlight what the customers can expect from them in terms of product, support delivery and hence help the customer to measure the company’s performance based on these parameters. If the company holds ground on its promises, it results in building customer confidence and trust in the organization (Behara, Fontenot & Gresham, 2002, p. 118).
CRM Implementation
According to Raab, et al. (2008, p. 123), CRM technology should be implemented in companies after careful strategic and operational planning. However, sometimes the implementation of CRM technology in falls short of expectations when planning is not properly done.
Poor planning initiative can fail when the implementation process is limited to the choice and deployment of the software without the required accompanying rationale, context and the necessary training/support from the employees. Some organizations implement flawed software without redesigning them to suit their practices.
Though CRM offers many benefits to companies using them, there are many instances that CRM is a failure due to faulty installation and implementation processes. The failures could be attributed to too much functionality, the integrity of data, poor tools of development, poor backend integration, poor selection of application architecture and bad CRM strategy.
CRM Integration issues
It is important that the CRM strategy be well integrated into the system of firms. Many companies usually integrate CRM system by piecemeal initiatives that address a particular need only. Such types of integrations do not offer total solution to the problems of the company.
They offer little or no integration with the overall strategy of the company. They end up offering less complete client view solutions and they may lead to unsatisfactory customers. Moreover, they do not provide customer loyalty as they leave customer unsatisfied (Peelen, 2005, p. 75).
Many issues that face CRM software during their integration lead to their underperformance and therefore affect the growth of the companies. Therefore, though the CRM software offers the promise of improved customer retention, to increase in cross-selling revenues and better customer experience with their clients, failure of its implementation can result to some issues such as poor financial performance, low customer service quality, less effective selling exercises and the cultural impact of derailed company reputation.
Therefore, it is important that firms understand that when implementing the CRM system for their business growth it must be the right and compatible system according to the business needs (Peelen, 2005, p. 89).
Case study: Spice Man
B2B issues facing Kent Spice Man
Having been newly established to supply juicy Asian products in UK, the company faces various marketing issues. Some of the issues facing the company are related to product value, pricing, customers, logistics, pricing and branding.
Product Value Issues
The company has an issue of determining the value of the product to be sold in the UK market. The value of the products is one of the features that customers are interested in and its inadequacy would affect the sale of the products in the market.
The company has failed to establish products that have different value from those products offered by competitors. There is no perceived product value with only exhibitions being provided hence short term oriented. In addition, the product value issues are affecting the firm because the company will launch new products without a clear long-term objectives and goals.
The organization is an inside out firm that is able to work across different cultures both from Asian countries to UK cultures. This quality will positively affect the way the organization will deal with cross-cultural issues in the course of its operations in UK. An open to event attitude will help the firm overcome product value issues because the firm will be able to learn of the customer requirements ad expectations. Other
Pricing Issues
Kent Spice Man has issues related to pricing of its products. The retail price offered by the company is higher than the retail price of similar products offered by competitors. The pricing strategy used is targeted rate of return, which has increased the mark up by 100%. This is unrealistic because the cost included may turn out to be irrelevant. The effect high pricing to the company is that it may discourage consumers from purchasing the company products. The overall effect is losses that may lead to early exit from the industry.
Customers
Kent spice Man only knows that UK is a potential market for its products due to changing cultural aspects. However, the company has no specific target customers. The retailers too have not been identified. The senior management lacks experience in marketing hence the overall lack of knowledge in the organization concerning the target market.
The problems of the company regarding customers are worsened by its lack of reputation. Due to this, it is difficult to convince the customers because the products of the company lack value. Lastly, the company has inadequate human and financial resources to successfully venture into the UK food market. The customer issue could affect the company’s launch of new products hence low sales revenue.
Market segmentation
Segmentation divides a company’s target market into different sectors. Segmentation is important to the company to improve its profits and market strategies by understanding its customers’ needs that attract and maintain them from the company’s competitors. The company’s establishment and progress has majored on behavioral and geographic segmentation. Kent Spice Man Corporation should segment the market for its Asian products based on various factors including:
Measurability: the company should divide the target market into segments based on the number of customers that would use the products of the company. The customers could include both individual consumers and organizational consumers that could act as distributors to the company products.
Accessibility: Under this criterion, an organization segments its market based on the ability of the firm to access the market hence consumers. Kent Spice Man has established that the UK market is lucrative and could form a good destination for its products. It is important that the corporation segment the UK market based on accessibility.
This could include grouping regions that could easily accessed together while others that are not easily accessed by the firm in another group. Market segmentation basing on this strategy accompanied by a good distribution network could turn out to be the best for the company because it could enable the organization to maximize its opportunities.
Unique needs: the segments selected by the firm under this criterion have different unique needs. The needs of the segments are based on various factors such as cultural factors, income, tastes and preferences among others. For instance, the cultural factors affecting the consumption of Spicy sauces from Asia in the UK are different from those of consumers in Asia. The firm should make these considerations as it ventures in UK.
Purpose: this strategy enables an organization to manufacture a product that fits individual consumers and organizational consumers based on the purpose of the product. Individual consumers purchase the product in small quantities and for personal use while organizations purchase the product for resale and profit motive an in bulk.
Therefore, consumers can be provided products in small quantities at higher prices while organizations can purchase the product in bulk and at lower prices. Kent Spice Man could also segment the target UK market based on the purpose of the Spicy Asian products sold in the UK market.
Logistics and Packaging Issues
According to Kotler et al. (2001), logistics is “a business planning framework for the management of material, service, information and capital flows.” The warehouses of Kent Spice Man are located in Canterbury, a location that is far from the targeted selling points in UK.
The sauce cannot be properly stored because of inappropriate and limited storage. The stored product in Asia cannot be sold in UK because they may end up being spoilt. Lastly, the company is likely to incur high repackaging costs in order to fit into the UK standards for food labelling.
According to Solomon & Stuart (2008, p. 231), products obtained from Asia involve high transportation costs that lead to high pricing of the products. This causes customer dissatisfaction. The Asian storage facilities require protective packaging. In addition, overseas food import is not favorable since it could lead to many legal issues. The costs are further raised taxes that the company must incur on imports.
Distribution Issues
The company is venturing into an unknown market. It has no established links on the functioning of the market. In addition, Spice Man does not know of any supplier in the market. This could cause challenges of dealing with new suppliers. Dealing with new channel of retailers could cause distribution issues such as lack of coordination.
The company has established that the products can sold in London, Birmingham, Manchester and Bradford. For the products to reach the market, they have to be delivered at a high cost. Moreover, some slight mismanagement could result in late delivery of the products hence costing the company reputation and revenue. Given that the company imports the products, delivery of the sauces in the cities will cause extra charges (Slack, Chambers & Johnston, 2010, p. 103).
One of the problems facing Kent Spice Man is to decide whether to have direct/indirect distribution channels. In B2B, vendors most commonly use direct methods. However, a large distance exists between the product destination centres chosen by Kent Spice Man.
This can cause problems concerned with the cost of staffing, personal selling is the most effective method as it allows sales messages to be customised to meet the customers’ needs. The sales person is also able to directly answer any questions and communicate information about the product. This will aid in building a long-term relationship with customers (Groucutt, Leadley & Forsyth, 2004, p. 159).
However, this is an expensive method, especially as areas are so sparse. It raises not only transportation cost, but also the cost of other factors such as the salary of the sales person. Another problem is that these costs are incurred whether a sale is made or not.
The distance between destinations may also cause problems when transporting good from the warehouses to the customer, especially as Spice Man products have a sell by date.
Spice man will need to decide the method of transportation (Water, air, road, rail) is most cost effective and the most efficient in getting the product to the consumer in the shortest time.
A future problem for Spice Man to consider when deciding upon his distribution channels is the logistics of the service: For instance, he must access how he can insure delivery is on time and that it remains reliable. He must also insure the order is accurate and how to deal with any damaged goods.
Branding
Spice Man has no brand identity because it is a new organization venturing into the market. The products being offered have no reputation while distribution delays could damage the brand image being created. In spite of lack of a brand, the products are priced at a high price against competitors causing reduced revenue. Many issues affect brand awareness of Kent Spice man.
The company is not even at the awareness stage. The AIDA model postulates that the firm should base its branding on the model. The initials stand for A-awareness (Attention), I- Interest, D- desire (Need) and A- Action (Mudambi, 2002, p. 528).
The attention (Awareness) stage involves initiating efforts that will increase the brand knowledge among the target market. The stage is similar to promotion stage, which involves promoting the products through adverts. Kent Spice has not even reached the awareness stage because it has not yet begun promoting its products to its target market.
The interest phase is a continuation of the awareness phase. Under this phase, the firm should focus on exploiting the customers’ interest created by the awareness phase. The company should support what the customers know about its brand and products offered. Moreover, all efforts should be made to avoid any error that could affect the customers’ interest hence building their interest and triggering the emotions of the customers (Hatch & Schultz, 2003, p. 1047).
The desire phase is characterized by the desire to purchase the company products expressed by the customers. The phase is characterized by more promotions and motivation of customers to purchase the products of the firm. The customers are open to all kinds of information.
The organization should struggle to pump up the customers and increase their desire in the products offered by the firm. During the action phase, the company should motivate and encourage the customers to take action to purchase the products. The customers have all information and what is required is to action. The processes described above should be followed in the creation of the brand of the company (Hatch & Schultz, 2003, p. 1049).
Other issues affecting branding of the products include product differentiation, lack of brand strength, lack of visual representation and limited budget. The factors have negatively affected the firm because there are no propositions for product differentiation.
Recommended Strategies
Pricing strategies
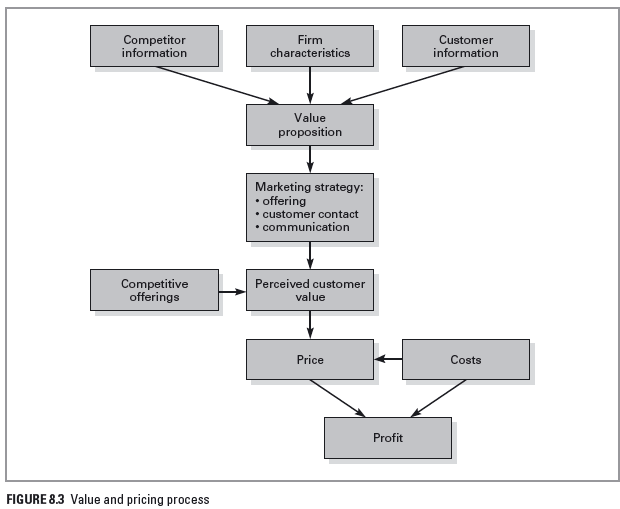
Kent Spice Man should adopt a cost based pricing strategy. The customers of the company are interested in purchasing products that have a high value compared to the price being offered.
Market communication strategies
Communication in a market is very important in conveying the qualities of the products of an organization. Various organizations use different communication strategies to convey the required qualities of the products being offered. Spice Man as explained below can apply some of these strategies (Garling, WET & CTH, 2000, p. 14).
Information acceleration: this strategy utilizes web based computerized marketing program that that simulates web based marketing. According to Anderson (1995, p. 346), this strategy is suitable for Spice Man because it is not expensive yet it is easy to access while providing consumers interested in the company products a chance to find the required information regarding the spicy sauces.
Free trials: under this strategy, Spice Man can establish centers in which it provides free samples of spicy sauces to both English and Asian customers in UK. Through this strategy, first product adopters can become marketers of the company products.
Solomon & Stuart (2008, p. 246) note that the first responses from the use of the products must be positive in order for the strategy to turn out to be effective. The word of mouth is a powerful tool especially when communicating the value band qualities of product. However, the tools can turn out to be too destructive to the brand image in case of any challenges.
Relationship Management
Kent Spice Man needs to establish reliable relationships between all participants on its supply chain. This includes the establishment and maintenance of good relationship with suppliers, distributors, retailers and consumers.
CRM Strategy
This strategy involves maintenance of good relationship with customers of the spicy sauces. The strategy utilizes consumer feedback to enhance product quality. Through this strategy, Spice Man can maintain the database of its customers and ensure that their specific needs are met by the company product quality (Romano & Fjermestad, 2006, p. 61).
Through customer relationship management strategy, the company would be able to maintain customer its existing customers, attract new customers, and increase satisfaction among customers and customer loyalty that can be easily translated into larger market share.
In addition to the customer relation management strategy, the firm should maintain an active supply chain with all participants satisfied. This calls for measures to satisfy supply chain participants (Stefanou, Sarmaniotis & Stafyla, 2003, p. 622).
Distribution strategy
One of the problems facing Spice Man is to decide whether to have direct/indirect distribution channels. In B2B, vendors most commonly use direct methods. However, there is a large distance between the places, in which Kent Spice Man has selected to distribute his products.
This can cause problems concerned with the cost of staffing, personal selling is the most effective method as it allows sales messages to be customised to meet the customers’ needs. The sales person is also able to directly answer any questions and communicate information about the product. This will aid in building a long-term relationship with customers.
However, this is an expensive method, especially as areas are so sparse. It raises not only transportation cost, but also the cost of other factors such as the salary of the sales person. Another problem is that these costs are incurred whether a sale is made or not.
The distance between destinations may also cause problems when transporting good from the warehouses to the customer, especially as Spice Mans products have a sell by date.
Spice man will need to decide the method of transportation (Water, air, road, rail) is most cost effective and the most efficient in getting the product to the consumer in the least amount of time.
Future problems for Spice Man to consider when deciding upon his distribution channels are the logistics of the service: For example, he must access how he can ensure timely and reliable delivery. He must also insure the order is accurate and how to deal with any damaged goods.
Branding Strategy
The branding issues could be solved if the company begins by identifying the target market. The company is to operate in UK yet the source of the products is in the Asian markets. After target market identification, the company should segment the market. For instance, the target market is all UK consumers. The UK population is comprised of people from different background including residents from Asian countries.
Therefore, the company should segment the market into mainly the westerners and the Eastern people from Asian countries. The product brands should reflect the target market segment. However, the company should do more than just product labelling in order to convince the customers with Asian origin that the products are original Asian spices and sauces. This may include additional flavouring for the products meant for Western consumers.
Distribution Strategy
As indicated above, Spice Man faces the issue of deciding whether to use direct or indirect forks of distribution. The study proposes an indirect distribution strategy for Kent Spice Man because of the large distance existing between the company stores and the final product destination for retailers. Indirect distribution strategy would happen if the company hires another distributing agent to distribute the spicy sauces from the distribution center.
Moreover, the strategy will enable the firm to increase its profitability since the costs incurred in extra staffing would be avoided. The products sold by the company are to be sold for specified short period. The use of reseller distributor would reduce inefficiencies in transportation hence avoiding expiration of products before their sale.
The alternative distribution strategy is to use air transport to deliver spicy sauces to preferred destinations. The sparsely distributed retail centers are costly being reached by road transport in terms of time spend and employees. However, air transport is fast and convenient. The only issue would be financial constraints affecting air distribution since it is costly.
References
Andersen, H. Jacobsen, P. & Mittal, A. (2000) Implementing CRM: 20 Steps to success. Customer Relationship Management. pp. 267-282
Anderson, J.C. (1995) Relationships in Business Markets: Exchange Episodes, Value Creation, and Their Empirical Assessment, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 23(4), 346-350.
Behara, R., Fontenot, G. & Gresham, A. (2002) Customer Model Process Approach to building loyalty. Total Quality Management, (13)5, 105-121
Best, R. (2005) Market-Based Management: Strategies for Growing Customer Value and Profitability, New Jersey, NJ: PEARSON/Prentice Hall.
Biemans, W. (2010) Business-to-Business Marketing, a value driven approach, new York: Mcgraw-Hill higher education
Dean, K. & Patrick, A. (1993) Perceived value approach to pricing. Industrial Marketing Management 22(2) 133-140.
Fletcher, K. & Hart, S.J. (1990) Marketing strategy and planning in the UK pharmaceutical industry: some preliminary findings, European Journal of Marketing, 24(2), 55-68.
Garling, A., WET & CTH (2000) Market Segmentation Marketing Communication Strategies and Elecctric VEhicel Drive. Web.
Groucutt, J., Leadley, P. & Forsyth, P. (2004) Marketing: essential principles, new realities. London: Kogan Page Publishers.
Hatch, M.J. & Schultz, M. (2003) Bringing the corporation into corporate branding. European Journal of Marketing, 37(7/8), 1041-1064.
Jones, T. & Sasser, E. (1995) Why Satisfied Customers Defect. Harvard Business Review. (73)6, 88.
Kothandaraman, P. & Wilson, D. (2001) The Future of Competition: Value-Creating Networks, Industrial Marketing Management, 30 (4), 379-389.
Kotler, P. et al. (2001) Principles of Marketing, 3 Ed., McGraw Hill, New York, NY.
Mudambi, S. (2002) Branding importance in business-to-business markets: Three buyer clusters, Industrial Marketing Management, 31(6), 525-533.
Peelen, E. (2005) Customer Relationship Management, London, UK: Pearson Education
Raab, G. et al. (2008) Customer Relationship Management: a Global Perspective. New York, NY: Gower Publishing, Ltd.
Romano, N. & Fjermestad, J. (2006) Electronic customer relationship management. London: M.E. Sharpe Publishers.
Slack, N., Chambers, S. & Johnston, R. (2010) Operations Management. 6th ed. Harlow: New Jersey: Pearson education ltd, Prentice hall
Solomon, M. & Stuart, B. (2008) Marketing: Real people, Real decisions. 1st European edition. Harlow: Pearson education ltd, Prentice hall.
Stefanou, C., Sarmaniotis, C. & Stafyla, A. (2003) CRM and customer-centric knowledge management: an empirical research, Business Process Management Journal, 9(5), 617-634