The minimum acceptable remuneration that an employer should pay an employee has been a source of contention among diverse parties with conflicting opinions about the importance and drawbacks of laws on minimum wages. Pursuance of regulation on wages in the 19th century set the stage for the formation of trade unions and other bodies that seek to protect the concept of controlled wages.
Major aspects of focus concerning the minimum wage revolve around the standards of living, socioeconomic status, equality, opportunities, and improvement of business effectiveness. The inexistence of a linear relationship between minimum wages and levels of employment highlights the need for an expansive interpretation of economic factors that influence employment. An analysis of the concept of the minimum wage in the context of economic models and empirical studies illustrates the positive and negative aspects concerning setting wage levels.
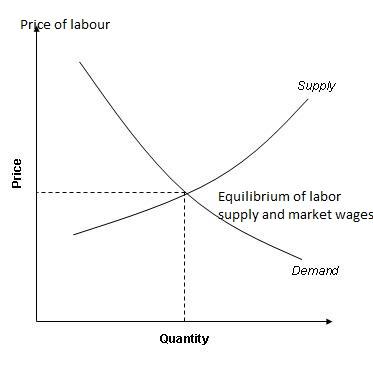
The concept of supply and demand dictates that employment is subject to the equilibrium between labor demand and supply, which incorporates all economic factors. The supply-demand curve is such that as the number of workers increases, the level of wages decreases while as the number of workers decreases, the level of wages increases.
In this regard, the supply and demand for labor determine the level of wages in a natural manner without human interference, and establishing institutions to determine the level of wages is likely to alter the balance between demand and supply (Sherman, Hunt, Nesiba, O’Hara and Wiens-Tuers 377).
Considering that there is a greater supply of low-skilled labor in comparison to high-skilled labor, setting minimum wages will force employers to minimize recruitment within the low-skill labor market, which will affect a significant portion of the population. On the other hand, the high-skilled labor market will remain largely unaffected because of its importance to employers and the fact that the segment constitutes only a limited number of individuals.
Therefore, policies on a minimum wage can only be productive if the focus is on reducing the minimum wage, which would ensure that the low-skilled labor market continues to thrive and prevent the increase in levels of unemployment in a country. The concept of employment as a factor of equilibrium between the demand and supply of labor has come under criticism due to assumptions that fail to consider aspects of market elasticity.
Inelastic demand for certain products creates a scenario whereby the employer transfers the cost of production to the consumer rather than regulation the size of the workforce. In this regard, the increase in wages will lead to increased prices of a product without causing the laying-off of workers because the high inelasticity of the product ensures that the demand for the product continues to thrive.
Furthermore, in the view of the balance of power between employers and employees, setting minimum wages could be productive by ensuring that wages and employment are within the optimal levels of the product of labor. Therefore, laws on a minimum wage would act as a form of regulation that ensures employers benefit from optimum productivity while ensuring that worker gets value for their services.
Proponents of policies on minimum wages claim that ensuring workers do not sell their hourly, weekly, or monthly services for less than the recommended value, safeguards them from exploitation in the workplace. In this regard, laws on the minimum wage create a level playing ground for both employers and employees and enable an environment that nurtures workers’ motivation and commitment towards organizational goals.
Another advantage of setting minimum wages is the promotion of appropriate distribution of income, which is crucial to the stimulation of consumption in a country. Consumption depends on the level of purchasing power, which is attainable by placing the low-skilled workers, who constitute the majority of the population, under a reasonable payroll.
Furthermore, the increase in purchasing power would allow the government to reduce its spending on social welfare programs and direct the funds to other projects. Setting minimum wages encourages people to enroll in education and training programs in the pursuit of jobs with higher pay and facilitates an increase in productivity as employers can adopt diverse technologies and systems to enhance efficiency.
Opponents of laws on minimum wages assert that creating policies that seem to coerce employers adversely affects the employer-worker relationship and contributes to unemployment. Setting up institutions that recommend particular wages forces employers to focus on having a productive but small workforce and introduces hurdles in the sustenance of productivity through the reduction of wages as a cost of production (Taylor and Akila 355).
Therefore, minimum wage laws minimize chances of employment, especially among low skilled workers, and adversely affect the employer-worker relationship as employers seek to get the maximum value for their money. Considering that the criteria for minimum wages focus on the level of education and training, the poor would have limited means of earning an income because their financial situation limits their access to education and training. In this regard, minimum wages are likely to lead to a widening of the gap between the rich and the poor, promote inequality in society, and contribute to social conflicts.
Apart from the effects on employment, minimum wages increase the likelihood of inflation as restrictions on businesses force organizations to transfer costs to consumers. Furthermore, minimum wages encourage job movement as people look for relevant occupations, which may interfere with development agendas in particular regions. Another disadvantage of minimum wages concerns the negative effects on small firms, which lack the capacity to offer high wages in comparison to large firms in the same industry. Unfair competition in terms of wages would force small firms out of the market, leaving large organizations to enjoy and exploit their monopolistic existence, which would have a detrimental effect on the economy.
Empirical studies by David Card and Alan Krueger on the relationship between the minimum wage and employment in New Jersey between 1992 and 1993 illustrate that an increase in the minimum wage from 4.25$/hr to 5.05$/hr among workers in restaurants led to an increase in employment (Kosters 56). Economic analysts attribute the increase to the setting of minimum wages at the equilibrium point of labor demand and supply for low-skilled workers, which creates a scenario whereby low-skilled workers would get a similar amount of pay in the absence of laws on minimum wages. Adjustment of the federal minimum wage in 1997 provided an opportunity for David Neumark and William Wascher to analyze the effects of minimum wages in New Jersey and compare the results with previous studies by Card and Krueger. By analyzing payroll records from large restaurants, the researchers identified detrimental effects of the increment in the minimum wage from 4.25$/hr to 5.15$/hr.
The conflicting results from the two studies became a source of contention, which the researchers ended by reaching an agreement that while minimum wages had no detrimental effects in the context of small restaurants, negative effects were evident in large restaurants (Neumark and William 108). Further studies showed that the negative effects of minimum wages on employment were significant, as evident by the incorporation of additional data sets from California. An analysis of the trend of the federal minimum wage in the United States shows that between 1979 and 2003, the real value of minimum wages declined by about 30 percent. In contrast, there has been a significant increase in the level of hourly earnings for the average worker, which economists attribute to diverse factors apart from the equilibrium point of demand and supply.
The composition of a country’s population is a center of focus in the study of the effects of minimum wages with concerns that an increase in minimum wages increase unemployment in countries that constitute mainly of the youth because young people have few skills. Economists cite the case Australia whereby despite the high rate of the minimum wage and employment, the country has had to formulate plans to lower the minimum wage rate for teens. The structuring of the wage rate in Australia is responsible for low teen unemployment in the country, which is about 16 percent as compared to the United States, which has an average teen unemployment rate of 24 percent (Blau and Lawrence 84).
Australia has put in place measures that ensure minimum wages progress with age to include the aspect of increased education and training. A comparison of the minimum wages in Australia and the US shows that adopting policies on minimum wages to reflect levels of training and incorporate economic indicators has positive effects on employment. The role of economic indicators in influencing the effects of minimum wages is evident by statistical analysis on the impacts of increased minimum wages that indicate an increase in minimum wages in Western Australia led to a loss of about 100,000 jobs.
The lack of consensus among economists on the relationship between minimum wages and unemployment calls for further research on the relationship between the two factors. Research shows that unemployment is subject to a variety of factors, which economists must incorporate in their analysis of the impacts of setting minimum wages. The interrelationship between aspects such as purchasing power parity, saving rates, political and institutional intervention determines the influence of minimum wages in a country.
Interventions by financial institutions to control inflation may alter the transfer of income to workers and either render the minimum wages ineffective or increase the overall level of employment and consumption. For example, by increasing interest rates to control price levels, banks discourage investment and lower the demand for labor even with decreased minimum wages. Business entities may create and promote oligopoly so that despite the guarantee of high minimum wages, workers may not enjoy the benefits of increased salaries because of increased prices of goods and services.
While the debate on minimum wages is not about to cease, a consensus on the matter is important to allow the formulation of policies that allow countries to attain optimal productivity and reduce unemployment. The principle of equality and opportunity largely depends on the economic status of an individual, which is subject to employment and remuneration.
Works Cited
Blau, Francine, and Lawrence M. Kahn. At home and abroad: U.S. labor-market performance in international perspective, New York: Russell Sage Foundation, 2002. Print.
Kosters, Marvin H. The effects of the minimum wage on employment. Washington, D.C.: AEI Press, 1996. Print.
Neumark, David, and William L. Wascher. Minimum wages, Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 2008. Print.
Sherman, Howard J., E. K. Hunt, Reynold F. Nesiba, Phillip A. O’Hara, and Barbara A. Wiens-Tuers. Economics: an introduction to traditional and progressive views, 7th ed. 2008. Armonk, N.Y.: M.E. Sharpe. Print.
Taylor, John B, and Akila Weerapana. Principles of microeconomics: global financial crisis edition, 6th ed. 2010. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning. Print.