Introduction
Hospitality industry is a very competitive industry. However, some successful firms have ventured and succeeded in this industry such as McDonalds. These companies have succeeded because of offering high quality service. Whereas production companies compete on manufacturing high quality products, hospitality firms contend on the quality of services offered by the staffs (Boella & Goss-Turner, 2005).
Employees in hospitality industry play a significant part in ensuring that they provide high quality services in order to satisfy customers, irrespective of the nature of the hospitality facility. Therefore, employees who work in a motel or a multi-million dollar resort facility should ensure to provide high quality services to guarantee customers’ satisfaction (Borkowski, 2009).
Motivated employees have low turnover and high job satisfaction. Job satisfaction is important, as employees tend to devote all their efforts and time in offering high quality services to their customers, which result to satisfied clients who respond through repeat business and referrals. The human resource department plays a great role in motivating employees to promote job satisfaction and increase quality of service delivery (McClelland, 1987).
Various factors influence human behavior. Some are psychological, while others are managerial principles. Motivational theories are instrumental in arousing employees’ performances and especially in the hospitality industry, where the employees play a pivotal role in determining the success or failure of the business entity.
This is because customers are always in close contact with the employees and the services they receive from those serving them determines whether they will use the facility services or refer prospective customers in future (Buttle, 2004).
A fast food restaurant is very a complex entity to run and manage. Restaurant managers should therefore, make sure that they are cautious on how they run the restaurants to enhance profit realization, as well as ensure sustainability. It is important for the management to make sure that employees are consistent in offering high quality services to avoid disappointing royal customers or potential customers.
It is not a surprise for a highly successful restaurant to collapse within a short time span, if not well managed. Although good financial management is important in a restaurant industry, efficient human resource management is imperative for the success and sustainability in hospitality industry (Griffin, 2008; Moynihan & Pandey, 2007).
Effective leadership plays an important part for the success of hospitality industry. Most effective managers in hospitality industry are aware that the success of the facility is mainly dependent on their ability in successfully handling the human resource (Gummesson, 2002). Therefore, managers should be well knowledgeable on the various strategies that are effective in managing human resource.
In addition, hotel managers who are not skilled in human resource management should hire competent human resource staffs to assists them in managing the employees, as well as introducing appropriate incentives for motivating employees accordingly. Introducing appropriate incentives in the workplace is important in ensuring that employees are highly motivated and satisfied with their jobs to enhance the quality of services they offer to the customers.
Human resource managers should be aware of the various scientific principles that they can employ to motivate employees in their workplace and use them appropriately to enhance the quality of services offered (Hougaard & Bjerre, 2004).This is important in ensuring employees offer high quality services to enhance profit realization (Jackson, Schuler, & Werner, 2009).
Review of Literature
It can be argued that the ability to motivate employees is one of the central goals of hotel managers. In the pursuit of this goal, the scientific community collaborated with other sectors of society to develop a framework that is both effective and practical when it comes to managing human resources.
As a result a number of theories were developed to understand the nature of motivation and how it can be applied to a workforce. An example of these theories are listed as follows: a) Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory; b) Herzberg’s Two- Theory; and c) Vroom’s Expectancy Theory. It can be argued that motivation is a basic psychological process that can be readily observable in a real-world setting (Moynihan & Pandey, 2007).
As a psychological phenomenon, motivation is used to explain the basis for human behavior. Scientists refer to an internal motive to explain personal drive, feelings and instincts. The source of motivation can also come from external motive and may involve a mental representation (Tucker, McCarthy & Benton, 2003). An example is the knowledge and beliefs attributed to as the reason behind a particular action.
Researchers point to motivation as a force that compels an individual to behave in a certain way. At the same time motivation can be used to explain the differences in the intensity of behavior. In the same way, motivation can be used to explain the direction of behavior. A manager motivating an employee to perform a particular task is made possible through a process of influencing behavior (Werner &DeSimone, 2009).
Thus, motivation is the process that “arouses, energizes, directs and sustains behavior and performance. That is, it is the process of stimulating people to action and to achieve a desired task” (Rutherford & O’Fallon, 2007, p.14). It is therefore imperative that managers have a clear understanding of how they can direct their human resource management department to develop of strategies that will lead to the creation of a motivated workforce (Schuler & Jackson, 2007).
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
The ‘hierarchy of needs’ theory was first developed by Maslow to show that motivation is driven by needs and drives of an individual. It is one of the most popular theories regarding motivation and the reason perhaps is because it is easy to understand and apply. Maslow made the argument that unmet needs compel an individual to satisfy that need and therefore an action is initiated.
In this regard, Maslow said that there is a five-needs system comprised of the following needs: a) survival; b) safety/security; c) sense of belonging to a particular group; d) ego-status; and e) self-actualization. According to this theory there must be a ladder-like approach to understanding the driving force behind motivation. In other words the needs of a person changes from one stage to the next.
The basic principle that can be gleaned from this framework is that an employee will not be able to reach the self-actualization stage if the other needs are not met. Another important insight that can be learned from this framework is that when a need is met, it ceases to influence the behavior of the person or at least its effect on the decision-making process is less critical.
Herzberg’s Motivation Theory
Herzberg’s two factor theory is an important part of this discussion because it can be argued that this framework was created to understand how to motivate employees. According to Herzberg himself, workers are motivated based on the influence of the leaders and how they perceive job satisfaction. Herzberg also said that when all the necessary components are present, the factors that he call “motivators” , then, the motivation of employees is possible.
On the other hand the absence of motivators can lead to dissatisfaction and frustration. Obviously these feelings are the opposite of motivation. Another important insight that can be gleaned from this framework is the assertion that there is a weak correlation between financial rewards and job satisfaction. It is an important consideration because prior to the introduction of this theoretical framework, managers all over the world developed their strategy based on monetary rewards.
Although, the wrong compensation package can lead to dissatisfaction, it was also determined that an increase in pay does not guarantee better performance from workers. Herzberg also highlighted another important insight when it comes to the need to motivate the workforce and he said that motivation is dependent on recognition of achievement, responsibility, the sense of achievement and personal growth.
Herzberg therefore made the recommendation that managers must empower their workers to experience more self-regulation, they must have the freedom to communicate and they must be given authority to communicate, as well as the ability to have control over resource and accountability.
Vroom’s expectancy theory
Vroom’s expectancy theory was developed in the 1960s. Nevertheless, it is considered as an important addition to the literature when it comes to motivation. The following illustration helps explain this theory.
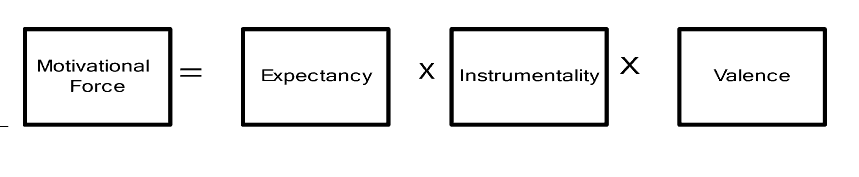
Figure 1. Vroom’s expectancy theory.
Based on the figure given above, one can see that motivation is dependent on expectation. It is based on a belief and then an outcome. If the employee is made to believe in one thing and then experience an unexpected outcome then motivation is negatively affected. Valence on the other hand is the orientation towards a particular outcome and simply means that employees are prepared to move to particular direction.
Instrumentality, as the last component of this framework refers to the perception of the employee when it comes to the probability that a particular action can lead to a specific outcome. Vroom said that workers can be motivated to do a particular task if three areas are dealt with. First of all, the workers must have value the outcome of a particular action.
Secondly, the workers must believe that they can achieve a particular goal given to them by management. Finally, they have to know what to do in order to achieve a particular goal. The theoretical frameworks discussed earlier provided guidance to hotel managers. It is important to reiterate that motivation is a deliberate act and a byproduct of purposeful action.
It is the outcome when knowledge, experience and skills are combined to develop a strategy that will lead to a particular outcome (Wick, Pollock, & Jefferson, 2010). A motivated worker is someone prepared to behave that way, in other words, this mindset is already a part of the worker before he performed an action (Brock & Green, 2005, p.9). It is therefore imperative to point out that information plays a key role in motivation (Laird, Naquin, & Holton, 2003).
The corporation must direct the human resource manager to train workers in such a way that they do not only learn the necessary skills but to inculcate in them the necessary mindset to help them tackle their job (Laird, Naquin, & Holton, 2003). Behaviorists pointed out that motivation is not a solitary element of human behavior but a part of a whole: “it is the fusion of elements that includes: inclination; awareness; and ability” (Ritchhart & Perkins, 2002, p.5).
Thus, hotel managers must invest in tools and people that will help workers learn the way to excellent service. It is therefore crucial for leaders to show the way (Wilson, 2005). They can jumpstart the process by learning how to communicate and treat their employees. Managers must make the workers feel that they are part of a team.
Motivation and the Workforce
The claim made by Herzberg should be a foundational framework for the strategy that will be developed by managers. A significant amount of resources can be wasted by spending money on payroll without a clear basis that this particular strategy translates to better performance. They key ingredient that must be highlighted is the need to increase job satisfaction. Hotel managers must be on the lookout when it comes to the factors that will lead to job satisfaction.
According to a commentary made on this issue, employees will stay put and love their work and not ask for a significant amount of compensation if the following condition is met: “the elimination of a small but disproportionately powerful amount of office inanity” (Kreitner & Kinicki, 2009, p.12). This assertion must be treated as good news by managers.
They will come to realize that increasing the salary will not solve the problem of job satisfaction. Thus, they must pay attention to this need. There are different aspects of the workplace that increase the dissatisfaction of the workers. Managers must study the workplace and determine if it is cost-efficient to eliminate these types of office inanities. If they can afford to deal with these problem then it will be beneficial for the whole organization.
In the case of a hotel resort there are facilities given to the workers to help them increase their efficiency. An example of this type of facility is the place where they eat their meals. There may also be lounge given to the workers for them to rest. A locker area may also be provided to help them secure their belongings. It can also be a staging area that will help them prepare for the work ahead.
It is important that managers study these facilities in order to remove cause of disturbance or annoyance. By doing so they can effectively decrease the level of dissatisfaction in the workplace and the reverse can happen. It will then lead to a happier work environment.
The expected outcome is the ability to boost the morale of the workers. A morale booster in the form of dealing with office inanities can help reduce employee turnover. It is a well-known fact that employee turnover is a financial burden to the hotel because they spend money to train workers and when they are already an important part of the workforce the hotel can no longer afford to lose them.
One way to improve the working environment is to develop a culture that promotes positive attitudes such as a heightened level of respect that will lead to a friendlier atmosphere. Team work can also benefit from this strategy. A heightened awareness to work together can lead to the creation of an efficient workforce. The hotel manager must not stop at the superficial level. The hotel manager must continue to find ways to improve the system.
The hotel manager must be sensitive to the need for part-time and full-time workers. As a result, the general manager must direct the human resource manager to devise flexible work schedules. The hotel management must realize that the hotel resort is open 24 hours a day and seven days a week. Thus, the careful management of the workforce in relation to job rotation and increase in the number of workers can lessen the load.
In the case of the hotel resort the maids cleaning the room find it a tedious job to do the same task over and over again. The wisdom of job rotation can benefit them. If job rotation is not possible, another solution is job flexibility. A flexible work schedule can help reduce the tediousness of the work requirement. They are given the freedom to chose what to do even if it is limited to choosing what time to work. All of these things are geared towards the reduction of negative feelings.
If the maids continue to have this negative feeling then they will feel that their job is a heavy burden to carry. The managers must not make the maids feel that they belong to the lowest level of the organizational pyramid. The managers must develop a policy that will help them change their perspective. They have to understand that they are part of a team. Their absence can significantly affect the performance of the hotel resort.
The maids must be made to understand that in the greater scheme of things they play an important part. Employee turnover can be felt when the maids decide to leave for better employment opportunities. The hotel manager must realize that even low-level employees form the backbone of the business. In a service-oriented business like the hospitality industry the maids play this role.
The hotel resort can have expensive beds and world-class amenities, but if the rooms are dirty or even if there is a piece of garbage left on the floor this will be a major disappointment to the guests. It is important to enhance their value in their own estimation. The maids must not only be told about their importance they must be trained to further increase their value to the organization.
The hotel manager must invest in training their workforce. The manager must coordinate with the owners of the hotel and if there are sister companies that can benefit from a training program. This is one way to reduce the cost of training by allowing other hotels to run the same training program.
The hotel manager must realize that the need to motivate his workforce is important due to the seasonal nature of the business. There are times when the hotel has fewer guests and there are also months in a year when the hotel is in full capacity. Thus, during peak season, the commitment of the workers will be tested. It is during the sudden influx of guests that can create a high degree of stress among he workforce. Nevertheless, it is during this period when the workers are supposed to be working at their highest levels.
It has been pointed out that hotel managers must be proactive when it comes to developing strategies to motivate the workforce. But his job can be made easier if the training process starts at the recruitment stage. There is a big difference in training employees and training them after a rigorous selection process.
They must develop a system that will enable them to choose the right person for the right job. The rigorous process of selection must be balanced with a compensation package that is attractive for applicants. Hotel managers must make the job an attractive one for potential employees, the applicants must be convinced that they have a future in this company.
On the other hand the human resource department must make it clear to them that they have to be teachable and willing to learn the necessary skill sets to help them become an important member of the team. The hotel manager also needs to understand the difference in perception and expectations when it comes to full-time employees and part-time employees. In most cases, part-time employees do not have the same commitment as full-time workers.
It is therefore expected that the quality of their work can be affected. At the same time, part-time workers believe that they do not have a future in the company. As a consequence it is easier for them to leave the workforce and join another team.
It is an impractical system and must be rectified. However, the hotel cannot afford not to hire part-time workers. It is a challenge to maintain high-quality service with part-time workers but it is important to continually develop strategies to improve their system.
The hotel manager can reward the employees with a flexible work schedule. This is a practical step during off-peak season. The need to reduce the work week from six days to five days is a ploy to attract quality workers. The hotel industry generates a negative perception when it comes to applicants. Most job seekers tend to believe that hotel managers require the employees to work on Saturdays and in some occasions, even on Sundays.
By reducing the work week to five days, then it is easier for the hotel to attract workers under the age of 30. It is important to attract this age group because the hotel requires younger workers to handle the load. It is only after hiring qualified and young workers that the process of motivating workers begins. It is a good starting point because hotel managers are assured that their program works more effectively with this type of workers as compared to a group that is comprised of people not willing to commit to a more stringent requirement.
It is also important to point out that one way to increase the number of motivated workers is to deal with the work schedule. The hotel manager must work hard to understand the job requirements and find out if there are overlapping responsibilities. A conflict between workers can easily create dissatisfaction in the workplace and can affect the degree of motivation in the said group.
The Role of Leadership
It is imperative to learn how to balance between the need for transactional and transformational leadership styles. In the beginning of the beginning of the training process, the hotel manager must learn to use the transactional leadership method. In this particular system, the manager must educate the maids and therefore there is a direct teaching and conveyance of information to educate them on their expected duties and responsibilities.
In this stage, the hotel manager informs them not only about the work load but also the rewards for working in the said hotel. The hotel manager provides them the vision for the hotel and he will set clear goals for them to accomplish. After using the transactional leadership method, the hotel manager must shift to the transformational leadership model. In this method the hotel manager leads by example.
He will model the correct attitude. He must set a good example for the workers to follow. A major part of this leadership method is to persuade the workers that they will have an opportunity to advance if they are willing to give their best and stay loyal to the company. In this method, the hotel manager inspires the workers to go beyond what is expected of them.
The hotel manager must realize that their workers are not really interested in what they say during meetings. The workers are mindful if the manager really cares for the well-being of the workers. There are limits to what hotel manager can do to show his concern for the workers but at least the managers demonstrates his willingness to help them increase their value in the eyes of the corporate leaders and their co-workers.
The hotel managers must learn to focus on what they say in front of the workers. At the same time they must focus on their actions. The hotel manager must also be very careful when it comes to the use of stereotypes because this can influence the way they treat their workers. The hotel manager must be mindful of the way he acts in front of the workers.
According to behaviorists, a stereotype is defined as, “an individual’s set of beliefs about the characteristics or attributes of a group” (Kreitner & Kinicki, 2009, p.14). The hotel manager may underestimate the intellectual capability of the maids and the other workers in the hotel and treat them as such. But the workers can react based on the way they are treated.
If the manager treats them as intelligent and competent individuals then there is a greater chance that they behave in accordance to that perspective. The main goal of the hotel manager is to develop workers who are already committed to work in that particular hotel.
They will make a commitment and they will be motivated to work because they can clearly see the goals before them and they are convinced that they have the necessary training to accomplish the goals set before them.
There is a temptation to increase workers pay but hotel managers must realize that it is only part of the package. There must be non-monetary rewards to be given to the workers. Thus, they are motivated to work even if there is no signifiant increase in wages. The non-monetary rewards can come in the way of job appreciation. This can also come in the form of acknowledgment that the workers did a great job.
Since the hotel manager has found a way to set clear goals then it also means that the manager will have a way to find out that a goal has been completed. Thus, every time a milestone was reached, then, the team must celebrate the victory. It will help boost the morale of the workers. This is just an example how the hotel manager can help communicate to the workers that they are valuable team members in the said workforce.
Conclusion
Highly motivated employees play a great role in ensuring that customers receive high quality services leading to customers’ satisfaction. Managers in hospitality industry should be aware of the importance of motivating their employees to enhance the quality of services offered for their restaurants/hotels to have a healthy competition with rival brands.
Therefore, managers should know the models/theories of motivation that they can embrace to motivate their employees accordingly. An effective human resource department is imperative in a hospitality industry in ensuring competent workforce.
Therefore, managers and human resource staffs should work in collaboration and make sure that they recruit highly competent staffs, train them, as well as motivate them accordingly to enhance service delivery.
References
Boella, M. & Goss-Turner, S. (2005). Human resource management. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Borkowski, N. (2009). Organizational behavior, theory and design in health care. MA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Brock, T. & M. Green. (2005). Persuasion: psychological insights and perspectives. CA: Sage Publications.
Buttle, F. (2004). Customer relationship management. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Cummings, T., & Worley, C. (2009). Organization development and change. OH: Cengage Learning.
Griffin. R. (2008). Fundamentals of management. Houghton Mifflin Company.
Gummesson, E. (2002). Total relationship marketing. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Hougaard, S. & M. Bjerre. (2004). Strategic relationship marketing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Jackson, S., Schuler, R., & Werner, S. (2009). Managing human resources. OH: Cengage Learning.
Kreitner, R., & Kinicki, A. (2009). Organizational behavior. New York: McGraw-Hil.
Laird, D., Naquin, S., & Holton, E. (2003). Approaches to training and development. New York: Perseus Books LLC.
McClelland, D. (1987). Human motivation. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Moynihan, D., & Pandey, S. (2007). Finding workable levers over work motivation: comparing satisfaction, job involvement, and organizational commitment. Administration and Society, 39(7), 803-832.
Ritchhart, R., & Perkins, D. (2002). Intellectual character. CA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Rutherford, D. & M. O’Fallon. (2007). Hotel Management and Operations. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Schuler, R., & Jackson, S. (2007). Strategic human resource management. MA: Blackwell Publishing.
Tucker, M., McCarthy, A., & Benton, D. (2003). The human challenge. NJ: Prentice Hall.
Werner, J., & DeSimone, R. (2009). Human resource development. OH: Cengage Learning.