NEC3 ECC Design
The NEC3 ECC contract structure encompasses different secondary options, main options, and the appropriate Z clauses. These elements play a cardinal role in the achievement of the project goals and objectives. The selection of appropriate options will enable the principal to overcome various risks associated with the project (NEC Panel 2005).
The ECC contract in this case will entail key options for dispute resolution, additional secondary options that will be used to expand the scope of the contract, one major option for payment methods, and a major clause required for the location-based option. The composition of the design is as shown in the diagram below (NEC Panel 2005).
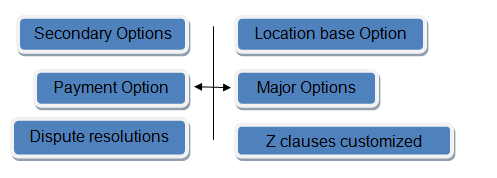
After the principal has chosen the appropriate payment method, which will enable the parties in the contract to develop a proper schedule for the activities, the clauses will be selected based on the features of the contract. For example, in this case, the contract will be pursued in Malaysia, which is outside the UK. Therefore, the university will adopt a sectional option that comes with advantages of early completion.
The element of liability in this contract will be limited to the university and the contractor of the contract (Hudges 2012). The other important element is the selection of appropriate performance indicators that are deemed important for the performance evaluation. The Z score element in the contract will ensure that the needs of the university are accommodated during the construction (Brook 2004).
The construction within the ECC contracts will require the parties to adhere to a set of clauses, which not only govern their relationship, but also ensure that the contract requirements are attained in time. The clauses govern issues such as payment, termination of the contract, time, and responsibilities of the parties.
The clauses will also affect the title of the contract, insurance against risk factors, defects, and testing methods. The justification behind the choice of these clauses is to ensure that the parties involved in the contract adhere to the requirements and pursue their responsibilities (Chappel 2012).
The method of payment in the contract will play an important role in determining how the university and the contractor will share the risks involved. The two parties in the contract will be exposed to the risks depending on the methods of payment in the contract.
For example, the university may decide to pay the contractor in advance to increase the contractor’s incentives. However, this payment method increases the risks on the employer’s side. The two parties should choose a payment option that is beneficial to all of them (Broome & Hayes 1997).
Moreover, the selection of the above options will enable both parties to effectively manage the procurement aspects associated with the NECC3 ECC contracts. For instance, in the tendering process, the contractor will work with the employer to procure materials that meet the requirements of the project.
The contractor in this case will work with the employer to identify various materials for the construction of the accommodation center. This collaboration is also important in reducing the inefficiencies that are associated with traditional methods of procurement.
Collaboration between the contractor and the employer is also essential in forecasting price changes and market conditions as it enables both parties to rely on the early warning measures to identify risk factors, which may interfere with the contracts (NEC 2008).
Particular features of the contract may require the contractor to expand the scope of the project or revise the original scope in order to accommodate some changes. In such a case, the parties in the contract should be guided by the Z clauses of the contract (Brook 2004).
For example, in this case, the principal may be compelled to embrace the regulations of compensation according to the laws of the country. Z clauses may also be used to provide clear guidelines on how additional risks will be shared between the parties (Hudges 2012).
Conditions of Payment in the NEC3 ECC Contracts
Payment under construction projects is a complex issue that requires proper guidelines. Primarily, the parties to the contract should be guided by the value of the project and the processes involved during the construction. Construction projects must have proper conditions, which guide cost allocation and payment of for various services.
The focal point of the agreement between the employer and the contractor in the contract is the definition of the works involved. The concept is also known as a contract sum. Under this agreement, the parties in the contract are required to define the total sum of the contract. The terms of the payment under this concept are used to determine the exact payments in the contract.
However, in scenarios where the parties have failed to honor the terms of the concept, the contractor will be paid according to the quantum method, which is based on the performance objectives and must conform to the rates of pay in the market (Broome & Hayes 1997).
Contract sum may regulate the payment methods used in construction projects. For example, the constructor can be paid using the interim payment method of evaluating the progress of the project. However, under this method the employer may be forced to review the contract sum.
For example, an employer may be compelled to calculate the value of the project on a regular basis to determine the amount of payment. Should the university adopt this approach, the principal and the project coordinators will be required to visit the site on a regular basis. This will also require the employer to divide the project in phases (Hudges 2012).
However, it is cardinal to note that the interim payment method does not have a reliable precedent in the law of contracts or under the common law. Therefore, in construction projects, the employer is required to adhere to the agreements while the constructor must deliver the project within the stated time period for payment.
In a situation, where the employer is not satisfied or has experienced damage during the construction, the principle of abatement may be applied.
Under common law the principle gives the employer absolute privileges to withhold payment regardless of the payment method. Notification to hold the payment must be communicated through appropriate channels to the contractor. The amount involved should also be communicated (Chappel 2012).
Retention is another legal factor that influences interim payment in construction projects. Under this principle, the employer enjoys the privileges to withhold a certain amount of payment that is to be paid to contractor until the project is fully completed.
The legal and commercial reasoning behind retention is to enable the employer to have enough time and funds that can be used for to hire another contractor. It should be stated that contractor’s rights must also be fulfilled regardless of the payment method used.
For example, the contractor has the legal rights under the law of contracts to suspend the construction if interim payments are not settled in time. The contractor is also privileged to charge interest on the payments according to the predetermined rates (Eggleston 2006).
Risk factors also influence the issue of payment in construction projects. For instance, during the procurement process the university may adopt a traditional procurement method where lump sum payments are made to the contractor.
This method will enable the institution to have absolute control over the project design. However, the design may be of low quality or may fail to conform to the construction standards (Gerard 2005).
Contractual Standings and Conditions
Relations in contract agreements are guided by the principles and standard forms, which are derived from the legal paradigms. For example, in construction contracts elements such as clauses, rights, responsibilities, and appendices derived from the legal relationship between the parties in the contract are important in determining the nature of relationship between the parties.
Consequently, these elements constitute the content or forms of contract as implied in the legal jargon. The content of the elements guides the behavior and the activities of the parties in the contract (Chappel 2012).
In the NEC3 contracts the forms of contract are very important in determining the duties of the parties involved in it. The type of work to be performed in the contract will determine its complexity. In such contracts, the contractor is obliged to draw and describe the scope of the project.
The procurement and payment in the project are determined from the scope. Another element is the quality of work to be done. Quality statements in the project play an important role in communicating quality requirements.
Contractual conditions that are properly written and distributed to the parties are also essential in determining the relationship between the contractor and the employer. Such conditions provide clear-cut guidelines on issues such as payments and responsibilities of the various parties.
Project time span and scheduling are also crucial since they determine how the contractor handles different activities and processes involved in the project. Parties in a contract can also rely on various standard forms to define their contractual relationship.
The type of legal connection between the parties is needed to determine the contractual standings. The method of payment and nature of the project is also important in outlining such relationships (Gerard 2005).
Dispute Resolution Methods
Disputes are inherent problems in every contract. As such, construction contracts are not an exemption. The major disputes in the NEC3 contracts mainly emanate from the differences between the employer and the contractor.
Disputes may not only lead to the failure of a project, but may also cause serious legal damages to the parties. It is therefore important to establish effective dispute resolution methods. Negotiation is the most appropriate method that can be used to solve disputes. It entails discussion between the parties to identify solutions to the problems (Cartilege 2011).
Apart from negotiation, mediation is another method of solving disputes in construction contracts. It involves a third party invited by the individuals participating in a dispute. The mediator takes a neutral stance in order to solve the problems affecting the individuals (Chappel 2012).
Conciliation involves a third party who does not establish the solution, but helps the individuals involved in a dispute come up with suggestions that are relevant to the problem. Conciliation can also serve the same purpose as neutral evaluation.
However, the latter requires the third party to give an opinion that has legal support. Individuals involved in a dispute can also rely on the advice of an expert to solve their problems. These methods have no adverse impacts on the parties. However, such methods as arbitration and litigation may come with serious adverse impacts.
Based on the issue of adversity, the best option in the NEC3 ECC contracts is negation. The university should therefore rely on negotiation to solve the disputes in the contract. This method is less complicated and has no legal requirements. Negotiations also establish a good working relationship between the parties (Gerard 2005).
Analysis Section
NEC3 ECC is the latest type of contract in the field of construction. The method embraces cooperation and collaboration between the employer and the contractor. Analytical comparison between the NEC3 ECC method and FIDIC Red Book form reveals that the former is very effective in ensuring the achievement of the project goals (Broome & Hayes 1997).
Unlike FIDIC Red Book form, which focuses on identification of the legal liabilities between the parties, the NEC3 ECC contracts provide clear-cut guidelines, which can be used to prevent disputes and solve other problems related to the contract.
The parties adhere to the requirement of the clauses and options in the contract. The contractual connections between the individuals are guided by the legal provision under the law of contracts. The forms in these contracts are easy to understand and have the main objective of ensuring collaboration between the parties (Eggleston 2006).
The NEC3 ECC forms provide the adequate space and time for the parties to identify various issues that affecting the contract. The contracts have objective modalities of operation. For example, the parties have to design effective time management strategies from the clauses.
They can also establish effective risk management strategies. For example, the use of early warning measures and indicators play an important role in identifying various sources of risks (Broome & Hayes 1997).
References List
Anon, 2005, Procurement and Contract Strategies: An NEC Document, Thomas Telford, London.
Broome, J.C & Hayes, R.W 1997, A comparison of the clarity of traditional construction contracts and of the New Engineering Contract. International Journal of Project Management, vol. 5 no. 19, pp. 56-60.
NEC, 2008, NEC3 Engineering and Construction Contract, Thomas Telford, London
Gerard, R 2005, Relational contracts—NEC in perspective. Lean Construction Journal, vol. 7. no. 3, pp. 120-124.
Brook, M 2004, Estimating and Tendering for Construction Work, Butterworth-Heinemann, London.
Hudges, K 2012, Understanding the NEC3 ECC Contract: A practical handbook, Routledge, London.
Chappel, D 2012, Understanding JCT Standard Building Contracts, Routledge, London.
Cartilege, D 2011, Quantity Surveyor’s Pocket Book, Routledge, London.
Eggleston, B 2006, The NEC3 Engineering and Construction Contract: A commentary, Blackwell Science, London.
NEC Panel, 2005, NEC3 Engineering and Construction Subcontract, Thomas Telford, London.