Organizational Culture: Essay Introduction
Culture in an organization refers to the values, beliefs, history and attitudes of a particular organization. Culture also refers to the ideals of an organization that dictate the way members of the organization relate to each other and to the outside environment.
An organization’s culture defines its values; the values of an organization refer to the ideology that the members of an organization have as pertains their goals and the mechanisms to be used to achieve these goals. The organization’s values map out the way employees are required to behave and relate to each other in the workplace (Allan, 2004).
There is a very important need to develop healthy cultures in all organizations whether they are religious, commercial or institutional. The culture of an organization determines how it is perceived both by its own employees and its stakeholders. The managers of an organization are said to be able to influence the culture of the organization. This can be done by the implementation of various policies that lead to a culture change.
Many organizations have two types of cultures, the culture that management wants to enforce and a culture that dictates the relationships of the employees among each other. Many institutions have been found to have a persistent and hidden culture among the employees. This is the biggest task to organizational management; how to replace the employee culture with the desired culture (Young, 2007).
There are two types of culture; namely strong culture and weak culture. Strong culture is whereby the actions and beliefs of the employees are guided by the values of the company. Such a culture ensures smooth and efficient flow of an organization’s activities. Strong cultures result in successful and united organizations.
Weak culture on the other hand refers to instances where the activities of the employees are not guided by the values of the company. A weak culture results in the need for a strict administration that is bureaucratic so as to ensure that the company’s activities flow well. Weak cultures result in increased overheads and under motivated employees.
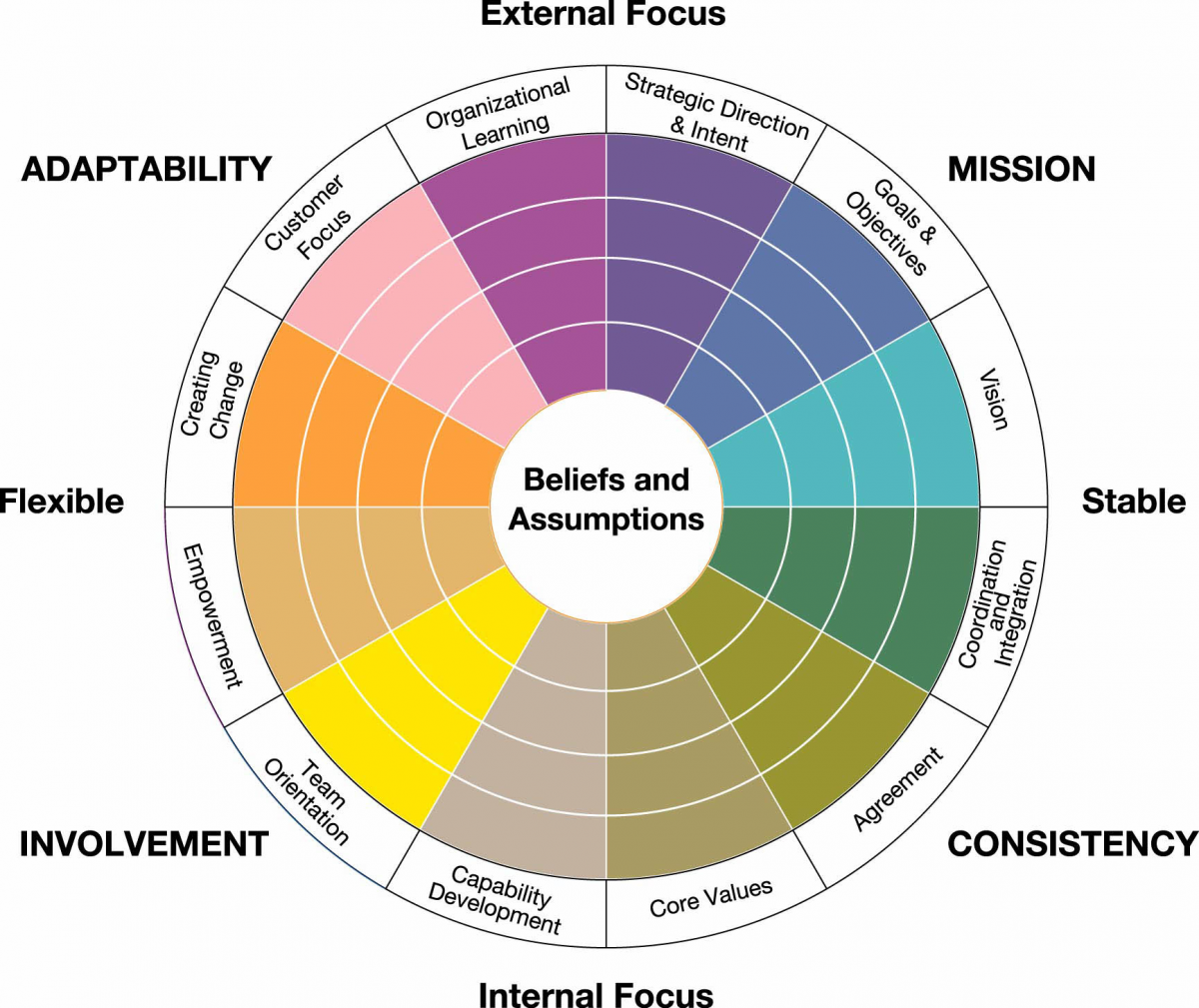
Fig. 1: Organization culture (Burke, 1999).
There are five dimensions of an organization’s culture namely power distance, risk taking tendencies, gender issues and employee psychology. The power distance aspect refers to the mentality among the employees on who wields more power and how much power they wield.
This will vary among organizations as some have more powerful managers as compared to others. Risk taking tendencies refers to the willingness of the employees and the organization to take risks in an attempt to grow and improve (Jack et al, 2003). Employee psychology on the other hand is an aspect that covers issues such as individualism and collectiveness mentalities in an organization. Companies that have a collective psychology have been found to work and do well as compared to individualistic ones.
The individualistic psychology has been found to cause a lack of coordination and flow of activities in organizations. Lastly the gender dimension refers to the mentality of an organization’s employees towards members of the male and female genders. Companies that view women as weaker and disadvantaged sexes have been found to discriminate among each other and result in a reduction of the employee cooperation levels (Jack et al, 2003).
There are four types of cultures in modern day organizations, role cultures, power cultures, person cultures and task cultures. Role cultures exist in organized and systematic organizations where the amount of power that an employee has is determined by the need that they fulfill in the organization.
Power cultures are those that have a few powerful individuals who are required to drive and direct the rest of the organization. Person cultures are cultures that exist when an organization’s employees feel superior to the company; this is a common culture in most law firms and firms that are formed by individual professionals who merge with others to form organizations. A tasks culture is a culture that is geared towards accomplishing tasks and doing things.
Project Management & Organizational Design
It is very important to understand the culture of an organization so as to enable an organization to map out the type of management that suits it. Culture as mentioned, is the accepted standard in which the employees of an organization relate to each other and to the stakeholders.
There are several factors that affect the culture of an organization. These include technological exposure, environmental conditions, geographical situation, organizational rules and procedures and influence of organizational peers on a subject. Such factors affect the culture of an organization and in the long run its management structure (Johnstone et al, 2002).
Organizational cultures can have both positive and negative effects on the organization. Negative and unwanted cultures are those that oppose change in an organization. These cultures have the tendency of inhibiting the innovation and implementation of change in an organization. Therefore the understanding of an organization’s culture can be used to determine:
- Why certain projects of the organization have failed or are failing
- Aspects of the culture that hinder innovation and change
- What needs to corrected so as to improve how the organization operates
- The origin of certain culture within an organization
- Measures that can be taken so as to introduce new culture or improve on the current culture
An in depth understanding of an organization’s culture is important so as to allow project managers and other managers to affect the mode in which activities are carried out. To influence the performance of the organization an understanding of its cultures is very necessary so as it enables the management to filter its employees and choose performers from non performers (Johnstone et al, 2002).
The proper understanding of organizational culture and its use in deciding a suitable management structure cannot be stressed further. The success of a project depends on how it is managed. There are three major types of project management namely; project, functional and matrix management structures.
Functional management refers to the type of management that focuses on specialty areas and skills. The departments and responsibilities are determined by the skills of the members. There is vertical and horizontal communication between the departments. To allow operation of all arms of the organization bureaucratic means are used so as to ensure smooth flow of the business.
This type of management tends to reduce operational costs and encourage the specialization of labour. Specialization in turn leads to better efficiency and standardization of activities. Disadvantages of the functional approach include the integration of budgets, operational plans and procedures into the project activities making it cumbersome to implement (Kloppenborg, 2009).
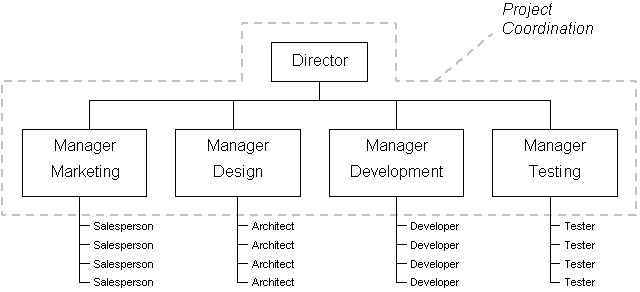
Fig.1: Functional project management (Young, 2007).
Project based organization on the other hand is whereby the activities of a company are organized according to its ongoing projects. This type of management is based on the objectivity principle that emphasizes the importance of solid objectives in improving the efficiency of an organization’s processes.
This principle is used in scenarios that require the efficient management of projects that involve activities from different disciplines e.g. medicine, engineering, law.
The advantages of such management techniques include the fact that power and responsibility is decentralized and is carried out by managers of different teams. Such a management technique also allows for the proper utilization of time, leads to reduced cost and enhanced quality levels. Such a management technique is suitable for certain company profiles and cultures, for example:
- Management of large projects and organizations that require the delegation of responsibilities
- Situations with restricted cost and specification parameters
- Situations that require the coordination and completion of projects from different but interrelated disciplines
- In cultures that value responsibility and accountability of ones actions / decisions
- Cultures that encourage communication among all management levels
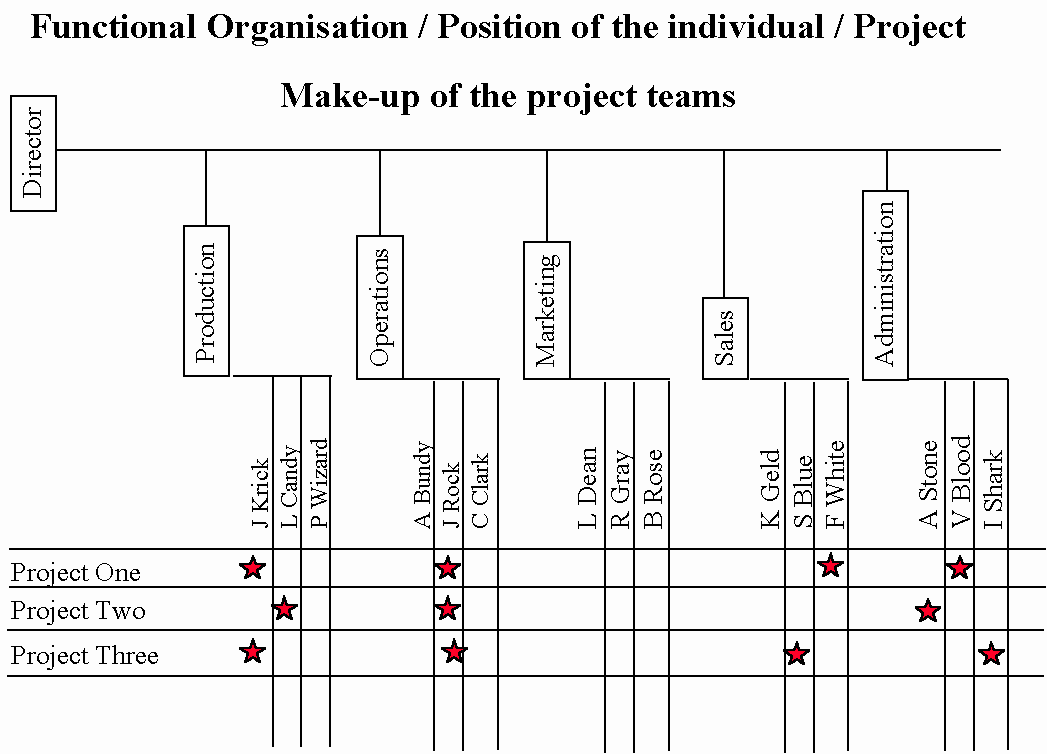
Fig. 2: Example of a project based management (Allan, 2004).
The project based management structure also faces a few limitations like any other structure. Limitations include the inability of a project manager to mobilize all the resources of a company as he has direct control of only what falls under his area of specialty. Employees and managers of such projects have been found to become slack towards the termination of projects due to the fear of losing their jobs once their projects have been completed (Kloppenborg, 2009).
Due to the limitations of both the operational and functional management structures the matrix was developed. This structure combines both structures to form a hybrid structure. In this type of structure there are two types of managers, namely functional and operational who work together in the same system.
The functional managers are responsible for the distribution of resources in their specialty departments and the operational managers coordinate and manage the activities of their departments. The functional managers are also responsible for overseeing all the technical decisions that fall under their departments.
This method of management has its advantages such as: the project manager oversees all activities that fall under his department. He has all authority and power and thus this eliminates the wastage of time as a result of quarrels and conflicts among the top levels of an organization.
Secondly the manager is able to use organization resources in facilitating the execution of the intended goals and objectives of the company. Disadvantages include the conflicts and coercion between project managers and functional managers that is bound to occur in such a setting. This kind of relationship has an eventual effect on employee motivation as it often results in the demoralization of employees (Young, 2007).
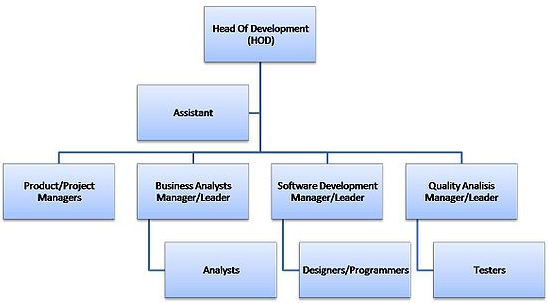
Fig. 3: Matrix management structure (Burke, 1999)
There are various factors that are considered when choosing the management structure of a project. These include the type of activities to be carried out, their importance / order of priority, the human skill required, the amount of time needed and the resources that are required to accomplish the set targets.
Situations that require extensive cooperation and interaction of the functions of an organization require matrix types of management. However there is no optimum type of organization and the organization must strive to come up with solutions to its unique needs and situations.
For a project to be well managed a healthy culture of communication must be developed. Communication theories propose that the project manager should always be like the hub of a bicycle. This means that the project manager acts as a focal point through which suggestions and results are received from various stakeholders.
The project manager also acts as the supporting point for the communication wheel. It is therefore very important for project managers to assist in maintaining a good communicative culture within the organization (Burke, 1999).
Factors such as nature of businesses in which the organization is in, size of projects and type of projects will also have a strong impact on the type of management structure that an organization may use.
The Importance of Culture in an Organization: Formal Management vs Parent Company
Formal management has an overall effect on the operations of an organization. The type of management that an organization has ultimately affects how its activities are carried out. Formal management is important in an organization as it serves as a foundation on which an organization’s goals and principles are guided. There are various guidelines that dictate the behavior and characters of managers in formal systems.
Managers in formal managements are required to have high integrity / moral standards, should be an effective communicators and listeners of others. Managers serve as the basis through which a formal management system is enforced. The project manager should also relate well with people.
He should have the ability to motivate and influence his workers positively. The project manager is also bestowed with the responsibility of ensuring that all aspects and stakeholders of a project work together for the common good of the organization. The manager is also responsible for setting time frames and ensuring that the project adheres to the set schedules.
This serves the purpose of ensuring that there is timely flow of an organization’s activities. Project managers are also required to make assessment of risks that could affect a project and try to manage the risks. In summary, project managers make up the backbone of any formal project management system and the performance of any project depends on the managers themselves (Burke, 1999).
There are three distinct characteristics that define a formal management structure; formality, the presence of groupings and the implementation of various systems. There exist rules and regulations that govern the relationships of the members of the organization. These rules also guide the reporting mechanisms of the members and the responsibilities / power which each member holds. These rules and regulations form the basis of all relationships and activities within the organization.
Formal organizations also group their members into teams and taskforces that are designed to suit various needs within the organization. For example accountants will usually be grouped together, designers with fellow designers and so forth. The groupings form departments and many departments form the organization.
However formal management has been said to be a very rigid mechanism by which an organization / project should be kept in check. This is because failure on the part of the managers would result in the total collapse of the organization. This is because managers are expected to provide guidance, direction and ensure that all members perform their duties.
Culture on the other hand is a better driver as it does not need to be enforced by anyone. Culture is self driven and once the members of an organization have adopted a desirable culture they will conduct themselves in accord to the culture without being supervised by a manager (Johnstone et al 2002).
Culture is also a better means of ensuring that a project is completed as it allows people to go out of the set boundaries and make innovations. Culture driven projects are better as they allow for unified and independent thinking at the same time. Whereas a formal management structure relies on the manager to make decisions a culture driven project accepts all decisions as long as they fall under the culture boundaries of the organization.
Formal management structures are slow and time consuming. This is because all major decisions and control is dependent on the managers. This leads to a very slow decision making process as the managers have to receive reports from members, deliberate on the reports and then give their recommendations. In cases where the manager is slow or is not presence this hinders the further development of the project (Young, 2007).
Many organizations that employ the formal type of management usually group their employees into departments. The departments are usually made up of people with common skills and areas of expertise. However such departmental setups hinder the exchange and sharing of ideas between people of different areas of expertise.
Due to the formal setup members from different departments lack a common factor that would enhance cooperation between the departments. This leads to poor coordination between the departments. In culture driven organizations, the members are unified by the common culture and this enhances the cooperation levels of the employees. Culture driven projects are therefore much more organized and have a better flow of activities as compared to formal projects (Kloppenborg, 2009).
Formal management of projects requires the mapping out and development of clear cut systems that will ensure the smooth flow of the project. These systems are essential in ensuring efficient execution of the project and its activities. Culture driven projects however do not need such a system so as to run smoothly. The culture itself forms a dynamic system through which all the activities are executed effectively.
Strategic management is a major component of formal management systems. It involves the science and methodologies of formulating cross functional parameters that enable an organization to achieve its objectives. Strategic management involves the development of missions and visions, mapping out of objectives and the making of critical decisions for the company (Allan, 2004).
Projects in formal management are stepping stones on which a firm uses to achieve its goals and objectives. The project development processes of a firm are driven by its strategic development goals and objectives. Examples of strategic elements include mission, objective, goals, programs and workable strategies.
Formal management is however beneficial as it promotes proper and sober decision making as compared to culture based management. This is because decision making and planning activities in a formal management are usually done after careful consideration and assessment. Culture based management is however prone to errors and misguided actions due inadequate consideration and thinking.
Organizational Culture: Essay Conclusion
From the study it is evident that culture is an important aspect of any organization. Culture has been found to affect the behavioral attitudes of a company’s employees and the manner through which these attitudes are manifested. The strong impacts of culture have resulted in the need for managers to find ways to affect the culture of their employees and of the work places.
By influencing the culture of an organization the managers are therefore able to influence the way the organization operates. Culture is an unsaid norm which the members of an organization abide to (Jack et al, 2003).
Organizations implement different types of organization structures. The type of organization structure implemented depends on the size and project characteristics. The type of project management has an effect on the eventual delivery of the project. The study has shown that there is no perfect method of management.
Managers of projects are therefore required to assess and identify the appropriate structure for their specific conditions. Project management structures have a great effect on the quality and effectiveness of the organization’s activities (Allan, 2004).
The study has brought to light the importance of proper culture in an organization. Culture has been found to be a better determinant of employee behavior as compared to formal management. Formal management is dependent on the enforcement of those in authority / wield power.
Culture on the other hand is enforced by the members themselves as they are part and pertinent of the culture. Formal management has also been found to be excessively bureaucratic and procedural and thus its implementation is rather cumbersome and expensive. Culture has therefore been found as the most appropriate way of managing a project.
References
Allan, B., 2004. Project Management: tools and techniques for today’s ILS professional. London: Facet Publishing.
Ashish, D., 2010. Project management Module. Hull: University of Hull.
Burke, R., 1999. Project Management, Planning and control Techniques. Chichester: Wiley.
Jack, M. & Mentel, S., 2003. Project Management: A Managerial Approach. New Jersey: Wiley and Sons.
Johnston, R. Chambers, S. & Slack, N., 2002. Operations management. Essex: Pearson Publishers.
Kloppenborg, T., 2009. Project management A Contemporary. Chicago: Xavier University.
Young, T., 2007. The Handbook of Project Management, A practical Guide to Effective Policies and Procedures. Washington: Kogan Page publishers.