Abstract
This report has been demonstrated the planning and resource management capabilities in a real-world project and to proper understanding this paper is selecting Stansted airport expansion project or G2 Project. The objective of the project is to expand its passenger service and within 2030 more than 68 mppa (million passengers per annum) will travel by this airport.
To organise the planning and resource management capabilities of G2 Project, this paper has analysed the objectives of the project, expansion costs of the project, SOW and planning of the project. It has also presented the implementation problems of the projects and the opportunities such as it considers user benefits, economic impact and social costs and advantages. This paper focus the objection of G2 Project that it creates serious environmental problems and to solve these problem it has to expend £8 billion to protect the environmental problem. This report would draw attention on both positive and negative aspects of the expansion project and draw conclusions and recommendations in a logical basis.
Introduction
The top priority of project planning and resource management is to match the stakeholders’ interest and expectations with the project. By using substantial project management mode of practice the project manager is accountable introduce diverse initiatives to get successful execution. After Heathrow and Gatwick airport, Stansted airport is the third busiest airport in the United Kingdom. Among the all-foremost airports of the world Stansted airport now holds its position in the top 60.
Therefore, this paper has been selected Stansted Airport expansion project to argue with project planning and resource management. To discuss the planning and resource management of G2 project, this report will consider the work breakdown structure (WBS), project life cycle Structure, scope of work, Gantt chart of Stansted Airport Expansion Project
Literature Review
Burke, R. (2003) has taken the opportunity to explain Project management as an appliance of knowledge based on the skills, materialised tools and Sharpe techniques to the lead generation of a project to gain the vision statement of the project. Project managers are always dedicated to work hard to work with project planning, resource management as well as implementation phase to congregate stakeholders’ interest and expectations with the project.
Burke, R. (2003) added that project planning and resource management are an efficient and effective line of working with managing projects, where efficiently implies performing the work well, and effectiveness implies performing the right work considering supporting other team members.
Elonen, S & Arttok, A. K., (2002) argued that multi-project planning should have six stage (work breakdown structure), which would be pointed out the sub-projects and this type of planning must include the complicated hypothesis such as critical path analysis (CPM) in the stage 4-6. However, Blisma N G, et al, (2004) stated that it is necessary to include sub-projects in main project to mitigate the dilemma of shortage of resources and high demand of resources by providing the appropriate estimation of resources. Blisma N G, et al, (2004) also added that sub-projects are completely independent projects so the planning would not be same for all projects. In this context, risk of the project would be high if the master project fails to find out the loophole of activating planning and allocating resource methods.
Branconi C V and Loch C H, (2004) argued that in order to develop the planning and resource strategy, project manager should modify the development activities as well as contractual agreement for the master project then the sub project will automatically remove the barriers from contracts and strategies.
Vargas, R. V., (2009) addressed that management tests show that teams repeatedly make better decisions than the team members would make individually with the same information. This has been attributed to the personnel’s wider range of skills and experiences than any one individual would have.
Ballard, G. et al (2003) mentioned that the project process steps are outlined here as a sequence of discrete operations and the factors may influence the sequence and there will almost certainly be a number of iterations, compromises and trade-offs before achieving an optimum plan. Steps of project process included project charter, feasibility study, meet the stated objectives, work breakdown structure, organisation breakdown structure and execution strategy.
Kupakuwana, P. S. & VanderBerg, G. J. H. (2009) stated that the successful project manager must also be competent in a wide range of general management skills in addition to the nine knowledge areas. These would include:
- Recruiting and personnel
- Economics
- Computer system
- Legal contracts
- Personnel and human resources
- Sales and marketing
- Accounts and salaries
Finney, S. & Corbett, M. (2007) added that the Company’s success is achieved by pursuing opportunities to gain a competitive advantage, and projects have typically been set up to take advantage of these opportunities- to make something new or change (enhance) an existing facility. Ragowsky, A. and Somers, T. M. (2002) addressed that a key component of change is making decisions – ideally, these decisions would be based on complete information with a high degree of certainty of outcome- it is this uncertainty that leads to risk. Therefore, risk has always been an intrinsic part of project management.
It can be seen that uncertainty and opportunity are closely related. When a risk occurs, with some entrepreneurial ingenuity, this may be turned around to become an opportunity there will be associated risk.
Moon, Y. B. (2007) supposed that the Project Organisation Structures identifies the relationship between the project participants, together with defining their duties, responsibilities and authority. Because of the dynamic nature of projects it is possible to have a number of organisation structures running concurrently, and over the duration of the project it may use all of the organisation structures.
Vaziri, K., Nozick, L. K. & Turnquist, M. A. (2005) considered that the allocation of resources to the project tasks possibly would affect the likelihood distributions for undertaking period. He also argued for a uniform and symmetric resource distribution mission within the period where the allotment of supplementary resources transfers to the endpoint. The straightforward mechanism for resource distribution would effect on supplementary resources that has an unambiguous effect on the mean and inconsistency of project duration.
Vaziri, K., et al (2005) also added that the associated problem where resource distribution is limited to an action that trim down the unpredictability of its period of the project devoid of distressing its stand for a time length to put up investigative outcomes for distributing a solitary resource among the sequences to diminish the inconsistency in the project durations.
Lycett M, Rassau A & Danson J, (2004) argued that small project can follow simple chart but large project has to determine scope of work as big project has to perform huge number of activities; moreover, project managers, co-coordinators, contractors, accountants, planners as well as engineers should make planning using advance technology to consider the practicability of implementing large projects.
Project Description & Objectives
In terms of passenger, Stansted is the fourth largest airport in the Great Britain. In 2007, more than 22.2 million passengers take its service; more over, it has permission to provide service up to 25 million passengers within the year 2008. More than 185 companies and groups are situated on-airport area, which creates employment opportunities for more than 11,600 people. It pays vital role for the economic development of the UK particularly East of England for example in 2006 it contributed £80 billion.
In 2007/2008 its cargo operation has been transported over 240,000 tones of goods, which estimated value of greater than £16 billion. Every year many international and national tourists are visited the UK. Stansted Airport made huge profits from the tourists, for instance- minimum 3 million tourists used their service, which amounts to 12% in total tourists. Stansted airport pursues low cost strategy to provide service of the passengers. As a result it use airlines which rates is comparably low such as it take service from 50 low-cost airlines for example Ryanair.
Project Description
General Information
- Proposed Name: Stansted Airport Expansion Project or G2 Project
- Owner: British Airport Authority
- Proposed Location: Stansted Mountfitchet (In the District of Uttlesford in Essex 48 km (30 mi) north-east of central London)
The project planning cost of this project will be estimated by the government; however, the following figure has showed some benefits and cost of this project.
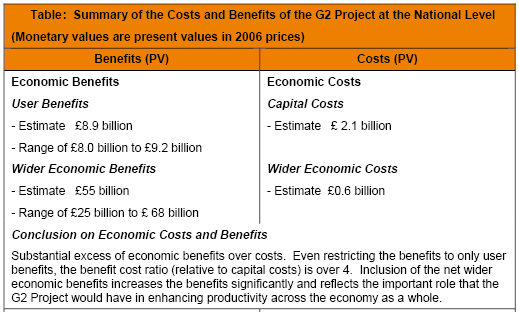
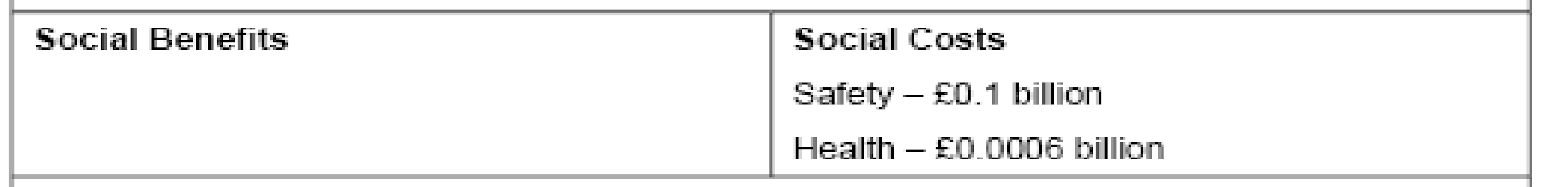
Expansion Costs or G2 Project Costs
G2 Project, Economic Impact Report – 2008 demonstrates that the expansion cost or G2 Project costs have been divided into two parts and these are external costs and internal costs. The whole internal cost will cover from the project itself but the external costs such as cost of environmental purpose will met up from individual.
However, it will be easy for a government to expand the Stansted airport comparing other airport because of its geographical structure. Stansted Airport is situated in agricultural area, which is not too developed area. As a result, at the time of executing the plan, the government has to spend no money to remove the people from Stansted airport area.
The Objective of Stansted Airport Expansion
The main objective of this expansion project is to construct Stansted airport larger than Heathrow Airport and Gatwick airport by build a second runway; therefore, British Airports Authority (BAA) recommended that it would require c 1,000-hectare land to build the new runway and other expansion.
- Economies of scale: DfT stated in their consultation paper that economic development is the main goal of this project,
- Airport Expansion policy of cost or differentiation,
- Timing of project implementation,
- Linkages among activities,
- Institutional factors (regulation, union activity, taxes, etc.)
- Interrelationships among business units.
- Capacity utilization,
- Degree of vertical integration,
- Geographic location,
- Employment opportunity.
The Stansted airport expansion project will have the major involvement to the economy is one of the significant reason of the project. Additionally in order to advantages for the passenger and the operator of the Stansted airport, the key economic advantage of supplementary airport capability is in its role as a facilitator of other categories of monetary action. Economic Impact Report – 2008 also shows that this project expand the transportation business opportunity. The Government also published several report and inquiry regarding this issue. In 2006, the government published Eddington Report to describe the important impact on economic factors including development of transportation sectors. In addition, Economic Impact Report– 2008 provides that within low project cost it bring huge profits and opportunity for the economy of the UK.
Work Break Down Structure (WBS)
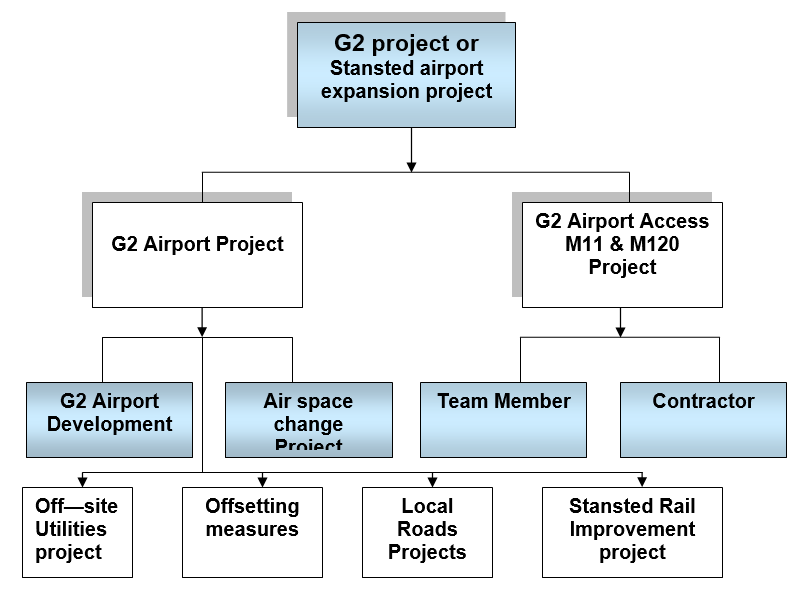
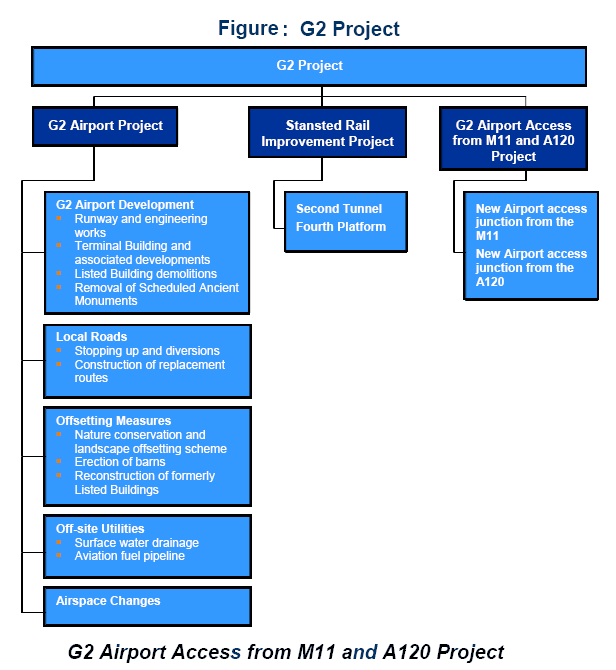
Burke, R. (2003), argued that to planning, secluding and allocation the resources it is essential to breakdown the work as the WBS provides a top down sub-project of the work, whilst estimating at the work package stage, suggests the bottom up roll-up of project costs. This figure has demonstrates the sub-division of Stansted airport expansion project such as G2 Airport Project and G2 Airport Access M11 & M120
Project and these two sub-project has own sub-project.
Life Cycle Structure of Stansted Airport Expansion Project
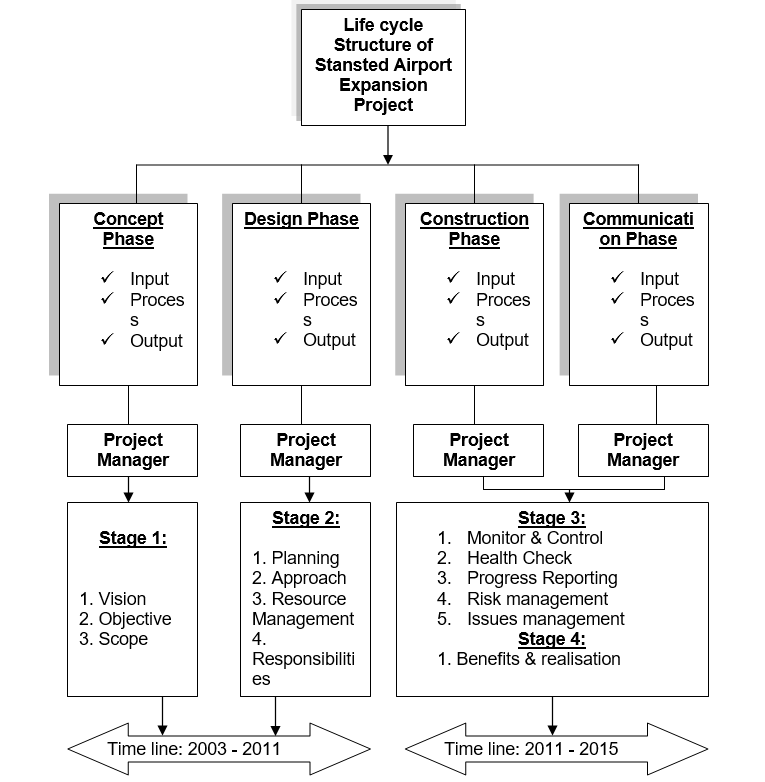
In the first stage is concept, which is a continuous process of long debate, started from 1963; however, in 2003, government white paper first provides their vision, objective and scope to the people. From that period, BAA started to design the project, where they consider planning & resource management of the project and key responsibility to implement the project and in budget of BAA decides to spend 37% of total UK airport expansion project. Stage 3- Construction phase is most important among the other stage because the success of the project depends on this stage and finally stage 4 assesses the benefits of the projects.
Scope of Work
The project is now in the second stage that means the planning is under construction therefore the initial scope of work (SOW) has not clear here. Moreover, SSE will be appeal against high court verdict regarding the expansion project so entire project description has not published by white paper. But this projects will consist of 160 sub-projects therefore the scope of work will be high. The figure demonstrates the entire scope of work for the Expansion project and sub-projects will also follow this chart.
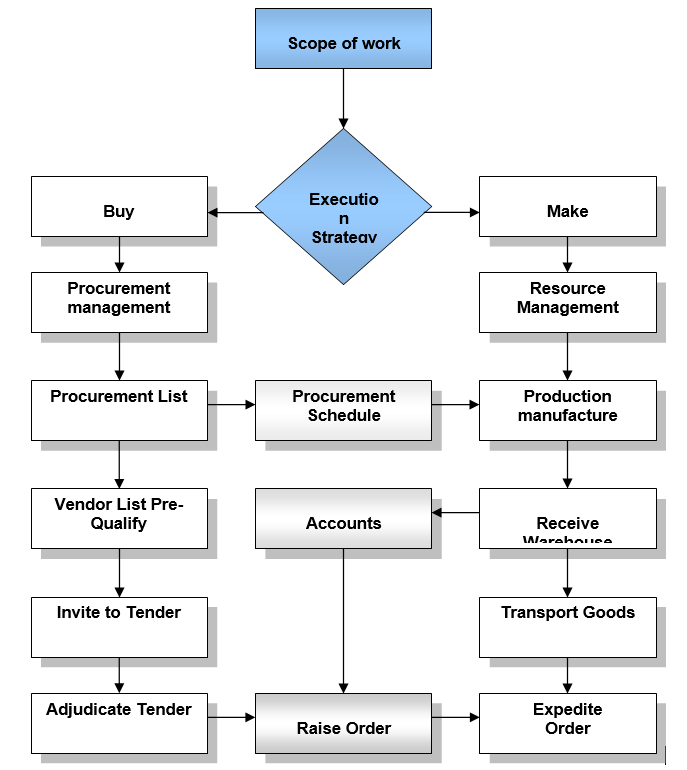
Discussion
Opportunities of G2 Project
The opportunities of this project are user benefits, social and economic befits and these are discuss as follows-
User Benefits
User, passengers or the airport operator of the Stansted airport will be highly benefited from the implementation of the project. The G2 Airport Project inevitably increases number of new passengers; therefore, airport will make profit from freight and transportation business. Within the year 2030, more than 68million passengers will pass from this airport.
Economic Impact of Stansted Airport Expansion Project
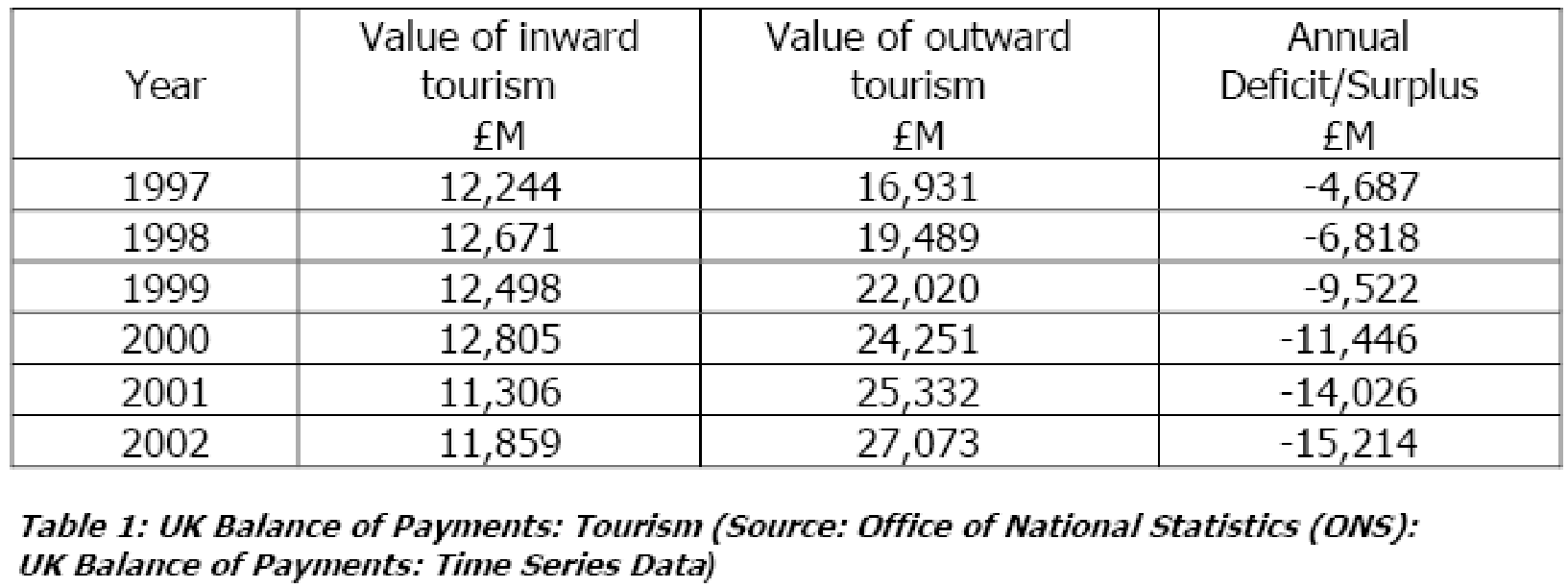
There is no doubt that the Stansted airport expansion project increases the earnings from tourist but it has no effect on economy. SSE logically describes the effect of the expansion of low-cost airlines. The main problem is that a large portion of general people of UK takes this low cost opportunity for traveling. As a result they spend more money in outside in the UK than the foreign tourist spend in UK. On the other hand, it will effect on government’s fiscal and monetary policy.
The inconsistency of expenditure between inward tourism and outward tourism increase the deficiency in national economy each year. For example, in 1997 the deficit from the inward tourism and outward tourism was £4687 million, which has increase £10527 million within 5 years. In 2005, the total deficit was £15,214. SSE stated that theoretically it may have good impact of economy but practically expansion project only increase deficiency in economy.
Social Costs and Advantages
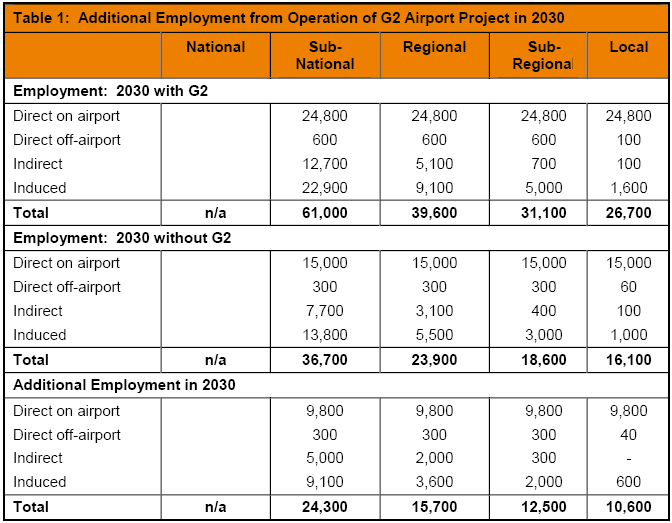
Government considered four significant social aspects, which demonstrates that for social benefits this project play a vital role. The expansion project will create new job opportunities. It may increases the sector of temporary and permanent employment opportunities. The employee or worker who will directly involve with the Stansted airport expansion project will be considered as temporary worker.
On the other hand, after proper completion of the whole project it creates permanent job opportunities in the inside of the airport. For instance this new employment opportunity may effect on fiscal policy in UK. Moreover, in airport area, National Rail and taxi companies will also profits for increasing the rate of passengers. In argument for this Stansted airport expansion is that government believed it is an investment in the future. It will create direct and indirect job opportunities for example it creates 25,400 new direct employment opportunities.
- It may effects on the security of the individuals and property: The policy maker always consider the issue of safety, so to minimize the risk of accident and risk of property damage they will give more emphasis on safety issue
- It will creates the scope to travel and take associated advantages; and
- This project considered the impact on health.
- At the time of construction segment, for noise and dust Hatfield Forest will be affected. Therefore, cost will be increased to implement this project but adverse effects on Hatfield Forest will be temporary, and after completion, the rate of visitors and tourists will be increased. After the completion of the project connected benefits and price of the house will attract the migrant people to purchase houses.
Environmental Costs and Advantages
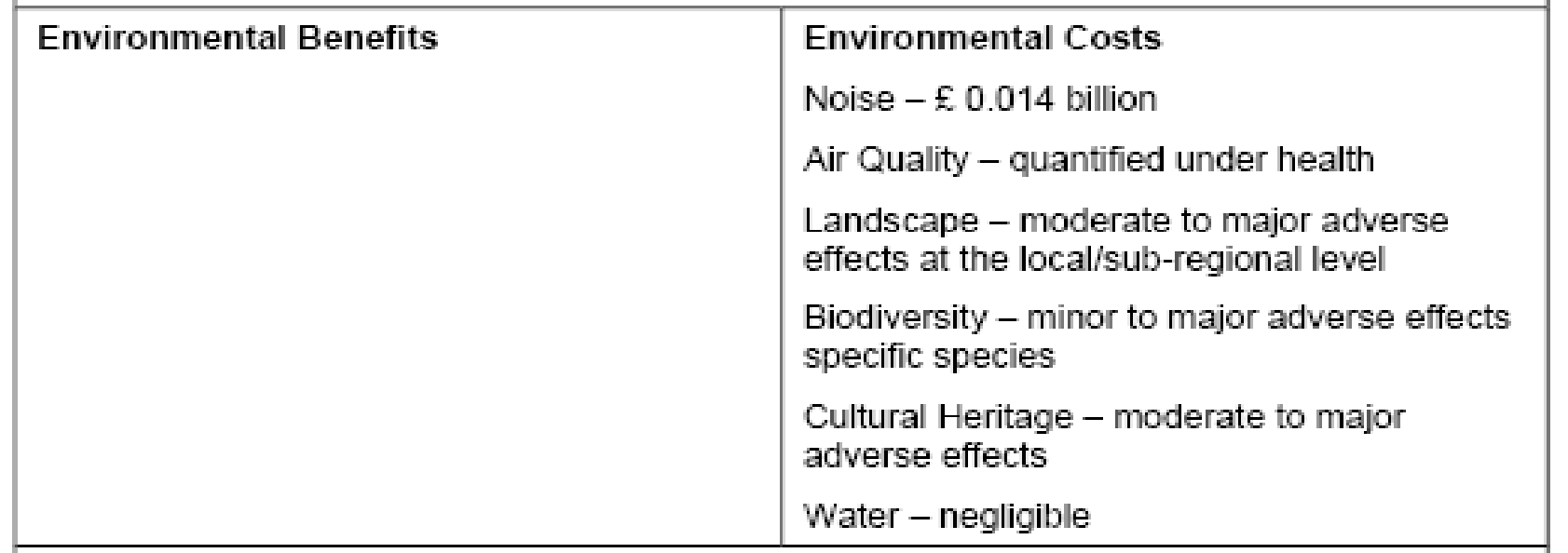
The government is much more concern in case of environmental issue because it is the main controversial issue of this project. Before published the white paper government has considered the both positive and negative impact of the expansion of the Stansted airport. The environmental issue such as noise, air quality, greenhouse gases, landscape, nature conservation/biodiversity, cultural heritage, and water environment has been considered. However, government believes that the environmental problem is not a major problem because it can remove by increasing cost in environmental purpose.
Problems of G2 Project
The problems of this expansion project have been discussed with the outlook of governmental white paper and protest of Stop Stansted Expansion (SSE) and it consider how and why G2 project has become controversial. SSE is an Action Group, which was established in 2002 but it has moved from 1964 under the North West Essex and East Herts Preservation Association (NWEEHPA). It has been established to protest the expansion of Stansted airport since government declared that Stansted must become London’s third largest airport. Stop Stansted Expansion has more than 3,700 employees and members and at least 60 corporate members who organize the movement against the expansion of Stansted.
At the consultation period, SSE arranged 48 meetings where about 4,000 people were present and millions of people supported their activities by visiting their websites, by letter or by phone calls. Their main objection was that G2 Project creates serious environmental problems such as air pollution, harm of public health and the impacts of urbanization, the fastest-growing cause to climate change, serious noise problem in airport area and global warming. This organization also considered the economic aspect that many UK citizens spend money in other countries for tourism purposes. SSE strongly fights against further runway development. However, government did not respond their argument regarding this project and the High Court held that the project should not stop
The Environment- the National and Global Prospect
- The opponent of the expansion project argued that the effectual protection of the national and global environment is one of the main goals of the policy maker in its national development projects but G2 project will violate this terms.
- This project may affect global warming movement though prime minister explains the Government’s strategy to bring this problem under control. Government launches the Energy White Paper to describe the whole protection policy.
- It will be impossible for the administration to reduce aviation CO2 emissions. With in the year 2050, it will amplify eightfold, though government has taken initiatives to decrease CO2 emission up to 60% from all other area.
- The cautious use of natural resources is another major goal of the government. The Energy White Paper-2003 demonstrates that they reserves oil for 30 years. There are no clear pragmatic alternative energy resources for aviation on the horizon which indicates that the expansion of Stansted airport only be expected to survive only 1 or 2 more generations.
If the government does not stop the expansion of Stansted Airport, this project will produce 9.3 million tonnes of CO2, within the year of 2030. Whereas, initially it produced only 3.4 million tones gas from aviation. As a result, Stop Stansted Expansion goes against this expansion project. On the other hand, DfT estimated that it should required £0.014 billion to save the climate from greenhouse gases.
Gantt Chart of Stansted Airport Expansion Project
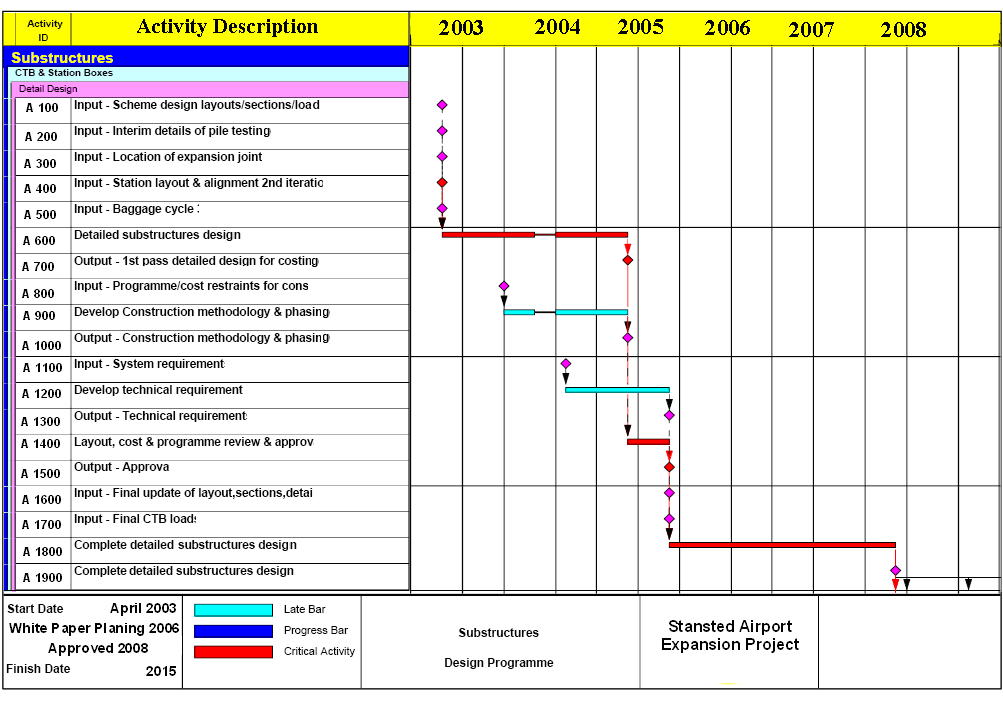
This chart has demonstrates that the project planning has been started in 2003 and the project will be finished in 2015. But the refurbishment work will be continued for 2030 to maintain the airport and to keep the environment safe and sound. However, the red colour has demonstrated the critical activity during the planning the project and blue colour has shows the progress of G2 project. The scheduling of each activity is represented by the horizontal line from start to finish, where the length of the activity line is proportional to its estimated duration.
The Critical Path Analysis
Stanted Airport Expansion project will consider the following issues to analyse CPM –
- Activity: Completion of the project involved a set of specific tasks those requires to employ resources and a target time to be end and Stanted Airport Expansion project also fixed the project activities.

- Network: Network defines the arrangement of all activities (in specific cases considering events) under a logical sequence, represent by different symbols and also delineate the relationship between the project and the activities. Typically, networks are drawn using direction flow from the left side and end at the right side. Direction flows are for ensuring predecessors. Predecessors ensure that immediate activity has been completed before next activity needs to start. GERT (Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique), CPM (Critical Path Method), PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique), ADM (Arrow Diagram Method) Gantt chart etc. are the modes or concepts of network drawing.
- Path: Path is a set of activities that attached every events of a network.
- Critical: Terminologies of a project determine the project’s operation speed. One of them like- events, activities or paths delayed completion of the project would be delayed. Critical path of a project combines a sequence of critical activities or events that connects the projects. Construction of this G2 project will be completed with in 4 years but comparing to the Heathrow terminal 5 has taken only 525 days to complete the project. This long period is not acceptable though Construction terminal space will be 500m2.
The Problems Related to the Planning and Resource Management and Solution
Stansted airport expansion project has to face the following problems and to mitigate the problems it should consider the demand of resources and limitation of resources. However, the planning and scheduling may create problem for example Heathrow Terminal 5 has been completed before finishing project deadline but G2 project is the large project so it is difficult to estimate the time. First of all, it should identify the problems then it will be possible to mitigate the risk or control the risk.
Resource Limitation
Based on industry type limitation of resources are classified into- resource loading, resource leveling, resource schedule sketching and optimizing the resources. To measure resources limitation G2 project will use the common method and this is “Heuristic methods, 1983”.
Resource Scheduling Method
Minimum value is denoted as “dij”.

The comparison occurs on the basis of pair wise all activities under the conflict set.
Estimation of Optimal Resource Demand
Stansted airport expansion project will estimate the resource demand to avoid risks by following the formula of optimal resource demand, which is shown follows-

Most of the time resource requirements way in the common form of currency- “dollar, $” and the Heuristic methods mostly used in bottleneck perception (both in production scale and inflation rate) and it this case it should be considered as well.
Recommendations
- There is a risk to hamper passenger service at the time of completion project. The civil association authority will imposed penalties up to £10m, if Stansted airport fail to provide satisfactory service to passengers as well as airlines; therefore, it should require to scrutinising the project plan before start working and it should provide report accordingly.
- It should reassess the cost of the project as the refurbishment cost of this expansion project is £1.320 billion, which is creates another controversy regarding allocation of costs.
- It should not take long time for construction and refurbishment work to provide customer service as the project is expected to complete construction within 2014, and further work and refurbishment will goes up to 2030.
- The white paper 2003 of the government had introduced the issue of stansted airport expansion but still now it is a controversial issue to the action group Stop Stansted Expansion and this group takes legal action against this G2 project (Stansted Expansion Project). Therefore, it should research the cause of the controversy and take initiative to remove those issues from the project but it should not stop the entire project because it will be successful project.
- BBC News Channel (2008) has reported that SSE has protest to save the nation and environment from serious pollution though the budget of the project keep a large amount of money to save environment from the noise, water and air pollution.
- Expansion project of Heathrow Terminal 5 is a successful project, which creates no controversy so it should examine interim planning and allocation of resources of Heathrow Terminal 5 project.
Conclusions
From the above discussion, it can be said that the expansion of Stansted airport is a controversial issue and it has both optimistic and pessimistic view. Group of Stop Stansted Expansion believes that G2 Project is the great mistake of the Government; on the other hand, government considered the project as the future of air transport. SSE focused on the conflict between planning management and environmental issues. SSE expressed that the project should not be implemented by the government because the price will rise for export and import therefore prices of petrol and food will become higher.
Protestor of this project also argued that national economy will gain nothing from this project, moreover, it may create deficit. It is important to say that SSE does not give any statement in question of employment opportunity. However, government does not consider this objection in the white paper 2003.
After considering the dilemma, it can be concluded that this project has some problem in time management, planning and resource management capabilities issues such as the budget and time management is poorly implemented. But economically people will be benefited from this project as it create 23,200 new jobs within 2015 and passengers and airlines get extraordinary facilities from this project.
Bibliography
Burke, R. (2003), Project Management: Planning and Control Techniques, 4th edition, John Wiley & Sons (ASIA) Ltd, ISBN: 9812-53-121-1.
Blisma N G, et al, 2004, Factors influencing project delivery within construction clients’ multi-project environments, Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, Vol-11, No. 2, 2004, pp. 112-126.
Branconi C. V. & Loch C. H, 2004, Contracting for major projects: eight business levers for top management, International Journal of Project Management, Vol-22, pp- 120-131, Web.
Elonen, S & Arttok, A. K., 2002, Problems in managing internal development projects in multi-project environments, International Journal of Project Management 21 (2003) 395–402, Web.
Finney, S. & Corbett, M. 2007, ERP Implementation: A Compilation And Analysis Of Critical Success Factors, Business Process Management Journal, Vol. 13 No. 3, 2007, Emerald Group Publishing Limited,, Web.
Hiemstra, R., 2000, Critical Path Analysis: A Planning/Time Management Tool for Managing Research, Web.
Hatzithomas, L. Stamelos, I, Fotiadis, T. & Mylonakis, J. 2007, Quality And Effectiveness Of Enterprise Resource Planning – Customer Relationship Management Systems: Implications For Information Systems Marketing Strategies, The Journal of Applied Business Research, 3rd issue, 2007 Volume 23, Number 3, Web.
Kupakuwana, P. S. & VanderBerg, G. J. H. 2009, The Goalposts for Project Success Have Moved: A Marketing View, Journal of the Association for the Advancement of Cost Engineering International. Web.
Lycett M, Rassau A & Danson J, 2004, Programme Management: a critical review, International Journal of Project Management, Vol. 22, 2004, pp. 287-298, Web.
Moon, Y. B. 2007, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): A Review Of The Literature, International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, Vol. 4, No. 3, 2007, NY: Syracuse, Web.
Ragowsky, A. and Somers, T. M. 2002, Enterprise Resource Planning, Journal of Management Information Systems, Vol. 19 No. 1, Summer 2002, Web.
Rittel & Webber 1973, Dilemmas in a General Theory of Planning, pp. 154-168, Policy Sciences, Vol-4, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Inc
Stansted Airport, 2006, Stansted Airport Interim Master Plan, Web.
Stansted Airport, 2008, G2 Project Economic Impact Report, Web.
Starkie, D., 2004, Testing the Regulatory Model: The Expansion of Stansted Airport, Web.
Stop Stansted Expansion, 2003, Stansted – The Case against Irresponsible Growth, Web.
Vargas, R. V., 2009, Using Earned Value Management Indexes as Team Development Factor and a Compensation Tool, Journal of the Association for the Advancement of Cost Engineering International. Web.
Vaziri, K., Nozick, L. K. & Turnquist, M. A. 2005, Resource Allocation and Planning for Program Management, Winter Simulation Conference Article 2005, Web.