How the Hirschman-Herfindahl Index can be used to measure the level of competition between the three ports?
The Victorian state government will find the Hirschman-Herfindahl Index (HHI) to be very instrumental in measuring the level of competition among the three ports. This index is used to measure the level of competition by determining the size of the firm. According to Murthy, this concept is used to compare the market share of a firm against that of the industry (2009). The main assumption is that large firms are always more competitive than their smaller counterparts. By determining their market share, the government can determine whether or not the market leader is close to being a monopoly or not. In this case, the Victorian state government will use this index to determine the competitiveness of the three firms in the market.
When using the Hirschman-Herfindahl Index to calculate the competitiveness of top firms within a given industry, it becomes necessary to determine the percentage of their market share. The Victorian state government will need the market share of these three ports to use this index. For instance, we may assume that Port of Melbourne has a market of 40%, Geelong Port of 30%, and Port of Hasting of 30%. The HHI index of the three ports will be calculated as follows.
(40^2+30^2+30^2)= 3400.
The HHI value may also be calculated as a fraction instead of using percentages but the concept remains the same. The Victorian state government has a responsibility to ensure that there is healthy market competition in this industry. The research by Panneerselvam warns against the promotion of monopoly in any given industry (2012). That is why this government has developed antitrust bodies and competition laws to guide every industry in the country. In case the market share values presented above reflects the true status of affair in the industry, then one can argue that the market is competitive.
However, when the market leader has a very large percentage of market share, then the industry may be considered monopolistic. When a monopoly is allowed in the industry, innovativeness and industry growth are put in jeopardy. A competitive market environment promotes creativity among the firms as they struggle to remain relevant in the market.
Discuss the implications for the State Government
The implication of the Hirschman-Herfindahl Index will depend on the values obtained. According to Mahadevan, in many cases, the government will always try to promote competition in the market by allowing small players in the industry to grow to gain competitiveness in the market (2009). This may be done by using financial incentives such as tax holidays or any other measure that may enable the players to experience growth.
However, some industries may not support small players. The industry that the Victorian state government is handling in the case study is a good example. It may not be possible to have micro and small ports within the country. The existing players must just meet international standards because of issues of safety for the people and cargo using the ports. This means that the government cannot try to promote the emergence of smaller ports because this may not be economically viable. However, the existing firms must have a competitive business environment that can support their growth.
The data obtained from the HHI calculation may have varied implications for the Victorian state government. In case the data assumption made in section a, above may true, then it means that the government may not have much to worry about. It will be a clear sign that Port of Melbourne is the market leader but with a small margin ahead of the other two competitors. It may be easy to assume that this lead is due to the high population in the city of Melbourne.
The high population will translate to an increased number of clients using the port at any given time. The government may not try to intervene in such cases. As Mahadevan notes, the government is always discouraged from interfering with an industry where market forces are acting fairly on the existing firms (2009). It may not be realistic for the government to demand an equal market share for the three players because the population of the respective cities is different. In this case, the responsibility of the state government may only be to promote an enabling environment for all the players in the industry.
This ideal situation may not be the case in some instances. It may be easy to find a scenario where the market leader has a huge market share compared to its market rivals. For instance, the Port of Melbourne may have a market share of 80%, leaving only 20% of the market share for the other two competitors. When the government establishes that this is the existing scenario, it may need to act appropriately to correct the imbalance and fight the monopoly as a way of promoting the industry. However, Schneider notes that government intervention may sometimes be very complicated to implement (2010).
It is not realistic for the government to come up with punitive measures against the market leader as a way of promoting competitiveness in the industry. Several factors will have to be put into consideration before any measure can be taken. An investigation will have to be launched to help explain why a given player has a huge market share at the expense of the other rival firms.
The outcome of the investigation may justify or fail to justify the market share of the market leader. For instance, if Melbourne is used for both domestic and international transportation while the other two ports are not, then it is justifiable for this market leader to have such a huge market share. Another justification may be the population supported by the port. Some ports located in large cities are expected to handle a higher number of passengers and cargo compared to those located in remote locations where the population is low.
The investigation team will need to determine the population that supports each of the three ports before they can issue appropriate advice to the government. If the market shares of the three firms are justifiable based on the population, then once again the government will not interfere with the market forces.
The investigation may also reveal unfair competitive practices as the main reason why one firm enjoys a huge market share at the expense of other competitors. For instance, it may be true that ship companies prefer using the Port of Melbourne because they have noticed that there is no tight inspection at the port. This allows them to engage in unlawful business practices such as human trafficking. Chary says that it may be unrealistic to have one firm enjoying over 80% of the market share in a market where it offers similar products to its rivals and the environmental forces are the same for all the players (2011). It may only mean that there is something unique that makes clients prefer one brand over another. When the investigation reveals that unfair business practices are the reasons why one firm is enjoying the lead, then corrective measures will be necessary.
The measures that will need to be taken by the Victorian state government may be varied based on the report of the investigative committee. If the investigation reveals that unfair business practices are the reason behind the imbalance, then legal measures will have to be taken against the responsible individuals and institutions as a way of promoting fairness. Sometimes the imbalance may be caused by environmental forces such as bad roads leading to other ports or insecurity at some ports, which may make them unattractive. Corrective measures may be necessary in such cases.
The Victorian state government may need to put up the necessary infrastructure to ensure that passengers and cargo will easily go through all the ports without concerns of security and poor road network. The government may also consider creating an environment where the ports operate as partners instead of rivals. Instead of fighting for customers in the market, the government can encourage these firms to cooperate amongst themselves and find ways of making the entire industry within the state more lucrative compared to services offered elsewhere. They can engage in research to come up with innovative ideas for solving common problems they face in the industry. Such strategies may help in creating a competitive business environment.
What is the Earliest Start of the Finish?
To determine the Earliest Start (ES) of the Finish, it will be necessary to develop a critical path diagram or a Gantt chart to determine the number of days that each activity will take. The diagram below can be used to determine the date.
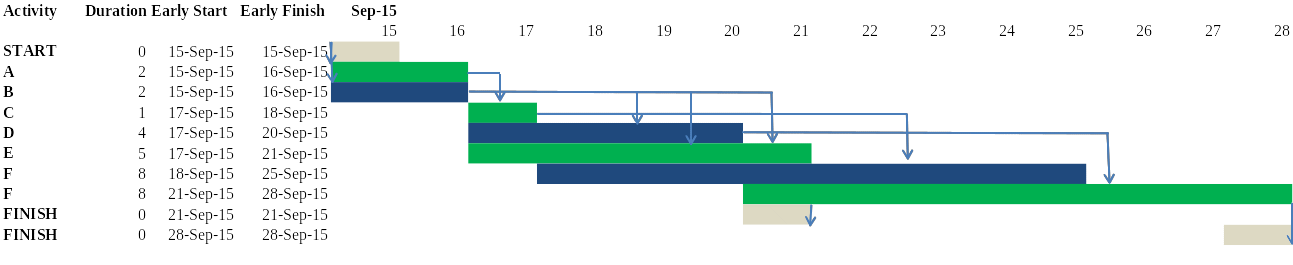
As shown in the figure above, the Earliest Start of the Finish will be on or before September 21, 2015. The assumption is that Activity E will be completed as per the schedule without any delays or completion before the expected time. Any changes in the completion date of Activity E will affect the Earliest Start of the Finish. It is important to note that the Earliest Start of the Finish will depend on the Earliest Finish of Activity E. In the schedule, it is established that Activity E should end on September 21, 2015. However, there is a possibility that Activity E and the activities preceding it may take shorter durations than the specified time.
It would lead to a scenario where Activity E ends before September 21, 2015. If that is the case, then the Earliest Start of the Finish will be before the stated date. That is why the date is stated as before or on September 21, 2015. Finally, it is also necessary to note that unlike other activities, the start date of Finish must be on the end date of the previous activity because it takes 0 days. It means that if the end date of Activity E (the preceding activity) is on or before September 21, 2015, then that will be the start and end date of Finish.
What is the Latest Finish of Activity E?
To determine the Latest Finish (LF) of Activity E, it will be necessary to determine the maximum duration needed to complete the project and its Latest Start date. The diagram below can be used to determine these values.
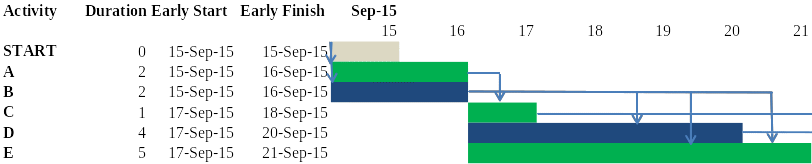
As shown in the diagram above, the Latest Finish of Activity E will be on or after September 21. In the schedule, Activity E is assigned 5 days. It is also stated that this activity can only commence after the completion of Activity B. It, therefore, means that any delays in activity B will affect the date of commencement of Activity E. In the case of Activity E also takes a longer time than as stipulated in the schedule, then the two delays will affect the date of completion of Activity E. Given the fact that the project is yet to commence, it may not be easy to predict whether or not there will be delays in the two activities.
That is why the date of the Latest Finish of Activity E is stated as on or after September 21, 2015. The major assumption made when determining this date is that the two activities will either be completed on time or there will be delays. It is a fact that the activities may be completed ahead of the schedule or one activity may be completed on time while the other is completed earlier. If this is the case, then the date may be on or before September 21, 2015. However, given that we are only interested in the Latest Finish date, then assumptions that the project could be completed earlier than scheduled will be ignored.
Discuss the applications of the Critical Path Method in port and terminal management a practice
Critical Path Method (CPM) may have several implications in port and terminal management practice. According to Kamauff, the critical path helps the management to determine when a project will start and when it is expected to end based on its duration and the end date of the intermediate predecessor (2010). CPM is always very critical for planners. It helps them to have a predetermined date when a given activity may be completed. In the context of a port, the management may be in the best position to inform their clients when they should expect their cargo cleared and ready for transportation out of the port.
However, the assumption is always that the scheduled activities will be completed as per the set duration and that the sequence of activities will not be interrupted in any way. In reality, this is rarely the case. Interference may be experienced and sometimes activities may take longer or shorter than the stipulated period.
Completion of the project before or after the date specified in the CPM may have numerous implications on port management. If the processing of cargo is completed before the scheduled time, the port may be overwhelmed because it will be forced to look for extra storage facilities as the clients are informed of the unexpected early delivery of their cargo. If the cargo is delivered after the scheduled date, the port will have to deal with the dissatisfaction of its customers. It is also possible that the cargo may stay longer at the port because the clients will not be sure when they are expected to pick them. This may pile pressure on the storage facilities at the port.
List of References
Chary, S 2011, Production and Operations Management, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.
Kamauff, J 2010, Manager’s Guide to Operations Management, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Mahadevan, B 2009, Operations Management: Theory and Practice, Pearson Education, New Delhi.
Murthy, P 2009, Production and Operations Management, New Age International Publishers, Print New Delhi.
Panneerselvam, R 2012, Production and Operations Management, Cengage, New York.
Schneider, M 2010, Operations Management. Thomson/Delmar Learning, Clifton Park.