Introduction
Background to the study
Existing studies show that organisations are increasingly adopting project approach in their quest to attain their desired growth. For a project to succeed, it is imperative for organisational management teams to implement effective project management practices.
Artto, Kujala, Dietrich, and Martinsuo (2008) define project management as the application of techniques, skills, and tools in order to meet the set project requirements. Moreover, organisational managers have an obligation to ensure that the project plans and goals align with the set organisational goals. Artto et al. (2008) assert that projects are intrinsically complex due to their multi-stakeholder characteristics.
Some of the key stakeholders include customers’ project team members, the performing organisations, project managers, and sponsors. Therefore, the success with which projects are implemented is subject to the degree of inclusiveness of all the involved stakeholders. These stakeholders have varying project interests. Additionally, projects are usually resource intensive.
Subsequently, project failure can lead to loss of the desired competitive advantage. Considering the complexity projects, it is fundamental for organisational managers to appreciate the importance of effective project implementation (Nevitt & Fabozzi 2000).
In an effort to improve its competitiveness, the Petronas’ Chief Executive Officer announced the company’s decision to invest in a new project, which entailed implementing a Human Resource Information System (HRIS) in 2012. The decision was informed by the need linked to the company’s strategic human resource management practices.
Some of the aspects that the new HRIS would assist in include tracking the employees’ performance, hence improving the firm’s effectiveness in formulating employee training and development program. Furthermore, the new HRIS also aimed at improving the firm’s effectiveness in the recruitment and selection process. Subsequently, the firm will be in a position to improve its human capital base.
Aim and scope
The success of the project is greatly influenced by the project strategy adopted. Subsequently, the significance of adopting effective project management strategies cannot be underestimated. This report examines the project management strategies adopted by Petronas in implementing the new HRIS coupled with how it has contributed to the improvement in the company’s performance.
Company profile
Petronas is a government owned company, which was established in 1974. The firm operates in the Malaysian oil and gas industry and its headquarters are located at Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. The firm’s operations entail the production of natural gas, petroleum, and petrochemicals. Furthermore, the firm also provides shipping services.
Since its establishment, the firm has attained substantial growth, as evidenced by its ranking in position 75 amongst the Fortune Global 500. By the end of 2013, Petronas was ranked 12th amongst the most profitable organisations in the world. The company’s revenue during its 2012 financial year amounted to $97.35 billion, while its net income was $ 21.91 billion (Petronas 2014).
The firm has ventured into over 35 countries. Its operations around the world are facilitated by a well-trained workforce, which is comprised of over 40,000 employees (Petronas 2014). Furthermore, its success has arisen from the adoption of effective management practices.
One of the aspects that the firm has taken into account relates to the formulation of a comprehensive organisational structure, which ensures that operations are effectively coordinated. The firm has adopted a flat organisational structure in order to foster internal communication as illustrated by the organisational chart below.
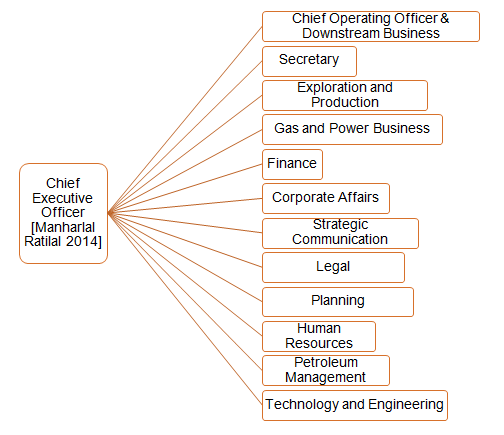
Source: (The OfficialBoard.com 2013).
Petronas has experienced significant growth in the level of its profitability. The figure below illustrates the growth in the firm’s revenues between 2012 and 2013.
Source: (Reuters, 2014).
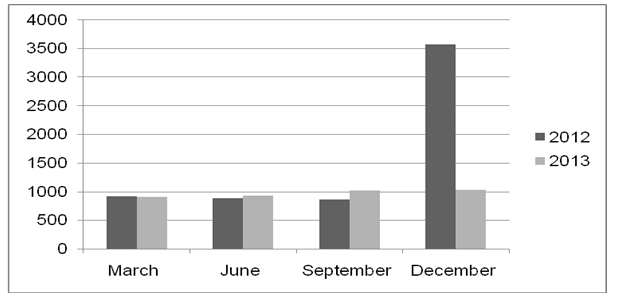
The firm’s profits increased to RM 12,763 7 million in 2012 (Petronas 2014). Petronas is committed to achieving a high level of sustainable development. One of the avenues through which the firm intends to achieve sustainability is by investing in effective information communication technologies.
Analysis; contribution of project management strategies to Petronas performance
Artto et al. (2008, p. 5) assert that strategically ‘managed projects are focused on achieving business results, while operationally managed products are focused on getting the job done’. Longman and Mullins (2004) are of the opinion that the success of strategic and operational projects is dependent on a number of elements, regardless of the nature of the organisation.
Some of the project management strategies adopted by Petronas are evaluated below. Failure to take into account these elements increases the likelihood of project failure.
Workplace communication
Effective internal communication is paramount in an organisation’s efforts to achieve the desired level of competitiveness. Adams, Means, and Spivey (2007, p. 76) is of the opinion that “workplace communication should be considered as an investment rather than a cost item in organisations’ operation’.
Organisational performance is influenced by the extent to which the various internal organisational stakeholders collaborate with each other. The Petronas’ management team understood the importance of effective communication in creating awareness to all the stakeholders involved.
The management was committed to ensuring that the project team members collaborate in implementing the project, which led to the achievement of the desired synergy. The project manager implemented an effective communication strategy in order to establish the critical links amongst the different stakeholders. Subsequently, the firm was in a position to promote the flow of ideas and information in the organisation.
Artto et al. (2008) argue that internal organisational communication is fundamental in fostering collaboration amongst the various stakeholders. According to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (2000, p. 117), “everyone involved in the project must be prepared to send and receive communications and must understand how the communications in which they are involved as individuals affect the project as a whole” (p. 117).
Poor project communication leads to breakdown in the project implementation process. In an order to improve exchange of ideas amongst the project team members, Petronas undertook a comprehensive project communication planning.
This goal was achieved by undertaking a comprehensive analysis of the communication and information needs of the various project stakeholders. The project manager provided frequent reports to all the stakeholders on the project status.
The project manager undertook a comprehensive analysis of the various information needs amongst the stakeholders. This goal was achieved by evaluating the appropriateness of the information required with regard to content, detail, and format (Adams, Means & Spivey 2007).
Furthermore, the communication planning process entailed determining how the information would be communicated to the respective stakeholders efficiently and effectively by formulating policy on the frequency of communication.
In order to ensure effective exchange of information, Petronas adopted different communication tools such as information communication technologies and internal memos. This move played a fundamental role in improving the effectiveness with which the stakeholders were conversant with the project.
The communication strategy has played a fundamental role in improving the firm’s competitiveness, and hence its performance. First, the firm’s employees appreciate the importance of collaboration in executing their duties.
Subsequently, Petronas has successfully eliminated the imbalance in its internal communications. Furthermore, the firm’s effectiveness in fostering interdepartmental communication has improved the competency level significantly amongst the firm’s workforce.
The adoption of effective project communication strategy has played a remarkable role in enhancing the effectiveness with which Petronas has improved the relationship amongst its employees. This aspect has arisen from the development of a high degree of trust amongst the organisation’s employees (Rad & Levin 2003). Therefore, the firm has minimised conflicts amongst employees remarkably.
Furthermore, the firm has successfully transformed itself into a knowledge-based organisation. Information and knowledge sharing are some of the most important aspects in an organisation’s pursuit for business excellence. Kalla (2005) further asserts that knowledge sharing is achieved through ongoing social collaboration and interaction, which fosters exchange of information in the organisation.
Human resource management
In the process of implementing the new HRIS at Petronas, the project manager was cognisant of the importance of developing a comprehensive project team. The project team members were sourced internally by selecting employees from different departments.
This decision was informed by the need to foster exchange of ideas and knowledge amongst employees, which would enhance the project implementation process. One of the aspects that the project manager took into account in establishing the project team is team development. The project manager selected the team members based on their competence in order to promote team project performance (Cobb 2012).
By adopting the concept of team development, Petronas has been in a position to integrate teamwork into its organisational culture. The organisation’s management team appreciates various team building elements such as managing the employees’ conflicts. Furthermore, incorporating team development in its operations has led to greater appreciation of the importance of employee development.
This aspect arose from the view that the process of implementing the project was undertaken in-house. Consequently, the firm undertook comprehensive training on the selected project team members in order to ensure that they are conversant with the relevant skills in implementing the new HRIS. Additionally, the firm has extensively appreciated the importance of delegating tasks amongst the team members.
This move has played a fundamental role in ensuring that the firm’s employees are provided with an opportunity to progress through their career path. According to Westland (2007), successful completion of a project is influenced by the quality of the organisation’s human capital.
Some of the team building activities that the firm undertook include ensuring that the team members were extensively involved in team performance. The firm also established rules and regulations that aimed at guiding the project implementation process. Furthermore, the firm undertook status review meetings periodically in order to assess team progress.
This move played a fundamental role in promoting interpersonal relationships amongst employees. Additionally, team-building activities have also improved the firm’s level of appreciation of the importance of implementing a comprehensive employee recognition and reward systems.
Subsequently, the firm has effectively reinforced the desired employee behaviours, which has led to improvement in the level of employee productivity. For example, due to the high level of motivation, the firm’s employees have become creative and enthusiastic in undertaking their job responsibilities.
Risk management
The process of implementing projects may be affected adversely by the occurrence of risks. Projects have unique features that vary from one project to another. Some of the sources of projects risks include the assumptions made, project budget, and project timing. Moreover, project risks originate from commercial, technical, and relational aspects.
Consequently, it is imperative for project managers to implement effective risk management strategies. The Project Management Body of Knowledge (2000, p. 127) defines risk management as ‘the systematic process of identifying, analysing, and responding to project risks’.
In the process of implementing the new HRIS, Petronas implemented a comprehensive risk management strategy. The strategy entailed focusing on a number of issues which include risk evaluation, risk assessment, and risk mitigation.
During the risk analysis phase, Petronas ensured that the various components that constitute the new Human Resource Information System were analysed. The project manager assessed the HRIS hardware, software, and data critically in order to identify possible gaps. This move was aimed at determining the likelihood of the project achieving the intended goal.
Furthermore, the project manager undertook a comprehensive risk mitigation process, which was achieved through risk prioritisation, risk evaluation, and control mechanism. Subsequently, the firm was in a position to implement the necessary security measures in order to minimise the likelihood of system failure upon its implementation.
Therefore, the HRIS project enabled Petronas to develop a broad perspective on the impact of risk in an organisation’s long-term survival. Available literature shows that poor risk management can cause organisational failure, as evidenced by failure of major organisations such as Enron and WorldCom.
Subsequently, Petronas has appreciated the role of implementing effective risk management techniques such as risk acceptance, risk avoidance, risk mitigation, and risk transference.
The contemporary business environment is characterised by numerous changes arising from the macro-environmental business environment. These changes are increasing the degree of uncertainty amongst businesses (Khosrowpour 2006). In order to survive in such an environment, it is imperative for organisational managers to implement effective risk management strategies.
Lau (2005, p. 4) asserts that an ‘organisation’s risk can proliferate at a faster rate than its ability to provide coverage’. Therefore, the appreciation of project risk-management strategies has improved the Petronas’ performance with regard to risk identification and prioritisation. Subsequently, the firm has successfully minimised occurrence of loss in its investment process.
One of the areas in which the firm has been successful in relates to effective allocation of the scarce resources. In an effort to improve its performance, the Petronas’ management team has adopted a broad approach to risk management, which has improved the effectiveness with which it transforms risks into results as illustrated by the diagram below.
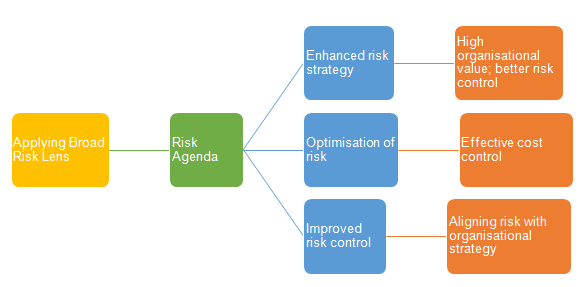
Source: (Lau 2005)
Quality management
Project managers have an obligation to ensure that the quality of the project is maintained, which underscores the importance of adopting effective quality management strategies. Additionally, quality management is focused at ensuring that the outcome of the project contributes to a high level of satisfaction amongst the target project stakeholders (Rose 2005).
In the course of implementing the new HRIS system, the Petronas’ project manager ensured that high quality standards were maintained. This goal was achieved by taking into account a number of quality management concepts, which include quality control, quality assurance, and quality planning.
Petronas undertook a comprehensive quality planning by identifying the quality standards that were relevant in the process of implementing the new HRIS project. By implementing the new HRIS project, Petronas has gained sufficient knowledge on a number of quality planning tools and techniques. Some of the techniques utilised include benchmarking, cost-benefit analysis, and flow-charting.
Benchmarking will improve the effectiveness with which Petronas sets and achieves its desired targets. Subsequently, the firm will be in a position to develop ideas on the most effective way to undertake improvement of its products and services. Furthermore, the firm’s management team has also gained sufficient knowledge on the importance of evaluating the cost and benefit tradeoffs (Satzinger & Burd 2008).
The firm’s performance has also improved due to additional knowledge on how to solve different organisational problems by utilising the cause-and-effect diagrams or the fishbone diagram. The use of flowcharting technique has significantly improved the effectiveness with which the organisation’s management team understands how the various organisational elements are interrelated.
Schwalbe (2010) asserts that lack of poor problem solving strategies can adversely affect the productivity of an organisation, and hence its performance. The Project Management Body of Knowledge (2000, p. 98) asserts that the ‘primary benefit of meeting quality requirements is less re-work, which means higher productivity, lower costs, and increased stakeholder satisfaction’.
Through effective quality management, Petronas has remarkably improved its performance by minimising the cost involved in the process of developing its products. Furthermore, the firm has appreciated the importance of developing a comprehensive quality management plan, which describes the elements that the firm will follow in its quest to adhere to quality management.
In addition to quality planning, adoption of project quality-management strategies has improved the Petronas’ performance through the appreciation of the concept of quality assurance. Quality assurance refers to a systematic and planned process through which the project manager ensures that the project being implemented will adhere to the set quality standards.
The Petronas’ project manager was committed at ensuring that the new HRIS was implemented successfully in the organisation. In order to achieve this goal, the project manager undertook periodic quality audits in order to determine how the quality management process could be improved.
The quality audits were undertaken under the watch of a trained in-house auditor. Subsequently, the organisation was in a position to enhance the employees’ skills and knowledge.
Petronas improved performance has also arisen from its improved commitment to quality control. During the process of implementing the new HRIS, the firm’s management team appreciated the importance of undertaking effective equality control in order to identify possible quality gaps and to eliminate unsatisfactory elements in the project (Taylor 2008).
The firm has appreciated the importance of undertaking continuous quality control, as evidenced by the establishment of a quality control department. Additionally, the firm has gained sufficient knowledge on the different quality control tools and techniques such as trend analysis, use of Pareto diagrams, flowcharting, and statistical sampling.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Investing in the new HRIS system has played a significant role in improving the Petronas Company’s performance. This assertion arises from the view that the firm’s management team has gained additional knowledge on different project management strategies, which are being applied continuously in the firm’s day-to-day operations.
The report shows that the firm’s ranking amongst the Fortune 500 companies has increased significantly. Additionally, the firm has also experienced remarkable growth in the level of its profitability as illustrated in the company profile.
One of the strategies that the firm took into account in implementing the new HRIS entails ensuring that all the project stakeholders were conversant with the firm’s decision to adopt a new technology and its contribution to all the stakeholders.
This goal was achieved by communicating the decision to all the stakeholders. This aspect has significantly enhanced the firm’s communication to its stakeholders, hence nurturing a high level of collaboration.
Additionally, adopting effective project communication has significantly improved the firm’s communication culture. The firm’s improved performance has also emanated from the improved appreciation of the importance of effective risk management.
The Petronas’ management team has gained additional knowledge on how to apply a broad view in identifying and managing risks. Subsequently, the firm is in a position to turn possible risks into results.
The process of implementing the new project also took into account effective quality management practices. Therefore, the company’s management team has developed a higher appreciation on the significance of ensuring that all its target stakeholders are satisfied.
This goal has been achieved by incorporating different quality management practices such as quality control, quality assurance, and quality planning in its strategic management practices. Moreover, the firm’s performance has also been enhanced by the adoption of effective human resource management practices. Some of the skills that the firm has nurtured relate to team building and development.
The firm has also appreciated the importance of integrating effective employee reward system in order to nurture a high level of motivation. Subsequently, the firm has successfully improved the level of productivity amongst its workforce.
The benefits gained from the project management strategies may not be sustainable in the future. Consequently, it is imperative for the firm’s management team to evaluate continuously the developed organisational culture with regard to quality management, risk management, workplace communication, and human resource management in order to identify possible gaps.
This move will enable the firm to undertake the necessary improvements, hence improving its ability to remain competitive in the global oil and gas industry.
Reference List
Adams, T, Means, J & Spivey, M 2007, The project meeting facilitators: facilitation skills to make the most of project meetings, John Wiley, Hoboken.
Artto, K, Kujala, J, Dietrich, P & Martinsuo, M 2008, ‘What is project strategy’, International Journal of Project Management, vol. 26 no.6, pp. 4-12.
Cobb, T 2012, Leading project teams: the basics of project management and team leadership, Sage, Thousand Oaks.
Kalla, H 2005, ‘Integrated internal communications; a multidisciplinary perspective’, Corporate Communications; An international Journal, vol. 10 no. 4, pp. 302-314.
Khosrowpour, M 2006, Emerging trends and challenges in information technology management, Idea Group, Hershey.
Lau, L 2005, Managing business with SAP: planning, implementation and evaluation, Idea Group, Hershey.
Longman, A & Mullins, J 2004, ‘Project management; key tool for implementing strategy’, Journal of Business Strategy, vol.25 no.5, pp. 54-60.
Nevitt, P & Fabozzi, F 2000, Project financing, EuroMoney, London.
Petronas: Sustainability. 2014. Web.
Project Management Body of Knowledge: A guide to the project management body of knowledge 2000, Electronic Imaging Services Inc., Oak Street.
Rad, P & Levin, G 2003, Achieving project management success using virtual teams, Ross, Boca Raton.
Reuters: Petronas gas Bhd. 2014. Web.
Rose, K 2005, Project quality management; why, what and how, J. Ross Publishing, Boca Raton.
Satzinger, J & Burd, S 2008, Systems analysis and design in a changing world, Course Technology, Cambridge.
Schwalbe, K 2010, Information technology project management, Cengage Learning, Boston.
Taylor, J 2008, Project scheduling and cost control: planning, monitoring and controlling the baseline, Ross Publication, Boca Raton.
The OfficalBoard.com: Organisational chart; Petronas 2013. Web.
Westland, J 2007, The project management lifecycle: a complete step-by-step methodology for initiating, planning, executing and closing a project successfully, Kogan Page, London.