Introduction
The purpose of this research will be to examine the ISO 9000 family of standards used to measure quality management systems within organizations as well as the requirements needed for ISO certification and registration within companies.
The ISO 9000 is a group of standards that are commonly used to measure the level of quality management within most organizations around the world.
They are also a set of criteria that are used to help organizations develop the capability of gaining and retaining satisfied customers. The ISO 9000 standards measure the type of service quality provided to the clients and customers of an organization.
Organizations that have met the quality standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization are given the ISO 9001 certification based on the standards of quality management (Hoyle 108).
The ISO 9000 standards were created originally to facilitate the mutual understanding of quality management system requirements that would be used in national and international trade activities.
The certification schemes which fall under the ISO standards were developed to reduce the costs incurred by companies when they conducted audits on their suppliers to verify their authenticity and genuineness.
Customers in the global market began to raise their concerns when they purchased goods or services in organizations that did not have any form of credentials (Hoyle 108). The ISO 9000 standards were therefore developed to address these concerns.
The ISO 9001 standard was also formulated to govern the contractual relationships that existed between customers and suppliers to ensure customers got value for their money.
Many customers usually depend on word of mouth or referrals from their friends, relatives and colleagues to purchase products or take advantage of a business’ products and services.
Referrals played an important role in providing customers with no prior knowledge of a company’s products with the necessary information which they would use to make a purchase decision.
Customers basically lack any relevant knowledge on whether a company’s products or services meet the requirements of quality as per the ISO standards. In the event customers have the capacity to verify the authenticity of a company’s products, a lot of time and effort is wasted in research activities.
The ISO standards have therefore provided customers with the requirements that can be used to obtain an assurance for the quality of a company’s product (Hoyle 109).
The ISO 9000 family of standards is applicable to all organizations be they governmental and non-governmental organizations. The standards can be used on companies of all sizes and types regardless of the products and services they offer to their consumers.
While the earlier versions of the ISO standards were focused on the manufacturing sector, the 2000 version has incorporated all industry sectors and it is applicable to all aspects of management within organizations (Hoyle 109).
The ISO 9000 contains the definitions of terms that are used in the family of quality management standards as well as the concepts and principles that can be applied to quality management systems.
The versions that fall under the ISO 9000 standards include ISO 9001, ISO 9004 and ISO 9000. The ISO 9001 which is the most commonly used quality management standard around the world is mostly used in contractual situations where the customer requests the supplier to demonstrate if they have the capability to produce products that can be able to meet the requirements of the customer.
The ISO 9004 version provides an organization with the necessary guidance when developing and improving the quality management systems used to govern the quality of products and services within the organization.
This standard is however not applicable in contractual relationships between consumers and suppliers because it mostly assesses the benefits that arise from using the contract (Hoyle 110).
Background and Origin of ISO Standards
The ISO 9000 family of standards were first introduced to the world in 1987 after the International Organization for Standardization developed six standards that would be used to assess the quality management activities of many companies around the world.
These standards included ISO 8402, ISO 9000-1, ISO 9001, ISO 9002, ISO 9003 and ISO 9004-1 (Hoyle 118). These ISO standards were modeled after the BS 5750 standards which had their background from the US Department of Defense after it published the MIL-Q-9858 standards in 1959 (Sharma 155).
During the 1990s, the need for ISO certification grew amongst many organizations around the world despite the fact that it was mostly reserved for companies in the manufacturing industry.
The introduction of ISO certification took place in the product-related service sector only in companies that offered education, transport and health care services.
The number of service related companies which had received ISO certification by 1993 was 27,000 and this number increased considerably to 274,040 companies globally which had received ISO certification (Hoyle 118).
The number of organizations and businesses globally which had attained ISO certification by the year 2000 amounted to 457,834 and 510,349 the following year.
This number continued to increase over the years with 100,000 more countries around the world gaining ISO 9000 certification. By 2009, the companies which had attained ISO certification amounted to 1,064,785 and this number was expected to increase as more and more customers searched for companies that were ISO certified (Hoyle 119). The diagram below represents the evolution of the ISO 9000 series of certifying organizations.
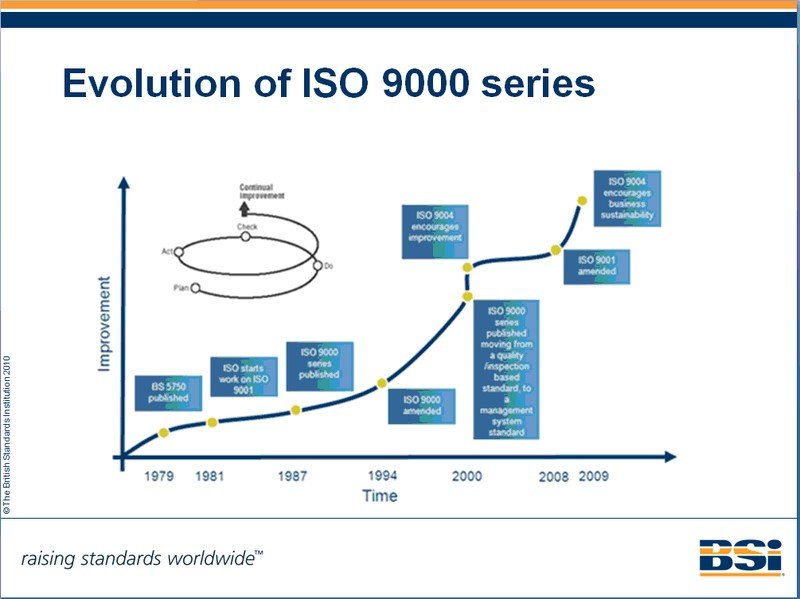
(De Silva 1)
Reasons and Benefits of ISO Certification
The major reasons that have been attributed to the increasing number of companies getting ISO certification include the number of purchasers who now require their suppliers to be ISO 9001 certified to ensure the goods or raw materials supplied to them are authentic and genuine.
A number of studies such as those conducted by Corbett et al (1046) have revealed that ISO certification is usually beneficial to companies in terms of the financial benefits that are gained by a certified organization.
Corbett et al (1046) were able to demonstrate that the companies or organizations which were ISO certified were able to receive higher returns on assets when compared to the companies which did not have any certification.
The researchers also noted that by implementing the ISO 9001, companies were able to achieve superior operational performance which ensured that they had a stronger market share in the external environment (Corbett et al 1046).
Other studies conducted by Rao et al in 1997 (Sharma 156) on the benefits of ISO 9000 certification on manufacturing companies in China, India and the United States revealed that the certification had a significant impact on the quality management practices of organizations within those industries.
The quality management practices included leadership, supply chain management, quality planning systems and customer management within the organizations.
ISO certification also increased the productivity and market share of organizations that had received the certification of bureau veritas. This in turn increased customer bases as consumers were confident that they were buying quality products from the organization (Sharma 156).
Elmuti and Kathawala who conducted a study in 1997 on the ISO certification of two manufacturing plants in the US were able to note that having ISO 9000 certification ensured that the plants had an improved quality of business operations compared to when they were not certified.
The researchers were able to note that being ISO certified increased employee motivation within the manufacturing plants thereby increasing the levels of productivity within the organization.
Because employees were motivated to perform, the plants were able to achieve their goals and objectives meaning that there was goal congruence as a result of the certification.
Chittenden et al who conducted a study on UK firms that had attained ISO certification in 1998 were able to note that employee morale and productivity improved because their organizations had received quality management certificates for the quality of products and services produced (Sharma 156).
In their analysis of the motives used by most companies to attain ISO certification, Low et al in their 1999 study were able to note that the lack of observed positive association between being ISO certified and the company’s general performance drove most business managers to acquire ISO certification to improve their business performance.
Low et al (Sharma 156) focused on the ISO 9000 certification of contracting companies in Singapore which utilized the CONQUAS score to determine the quality of services offered by contractors in the country.
Based on their assessments, Low et al were able to note that most contracting companies sought to attain ISO 9000 certification so as to take advantage of government projects and rebates which were only offered to contracting companies that had attained ISO 9000 certification (Sharma 156).
Corbett et al (1047) were able to note in their research that companies which did not attain ISO certification went through substantial deteriorations in their business operations which mostly occurred in employee productivity levels and company sales.
On the other hand, companies that were able to achieve ISO certification were able to experience increased employee morale which in turn lead to increased productivity and production of goods and services within the organization.
Basically, companies which received ISO certification were able to experience a notable improvement in their business operations (Corbett et al 1047).
Blokdijk (62) was able to identify the benefits of ISO 9000 companies to be those that had an improvement on the corporate culture of the organization as a whole where employees were accustomed to producing or delivering quality products and services.
This translated to the bottom line improvement of the organization’s effectiveness and efficiency when performing business operations. ISO certification also meant that companies are able to optimize the workforce to deliver better results because of the strict quality standards that have been placed on the organization’s quality management systems.
Blokdijk (64) offered more benefits of being ISO 9000 certified to include enhanced marketing activities as a result of increased sales, reduced internal and external audit exercises because the company’s performance complies to the strict standards set out by the ISO 9001 guidelines, increased employee motivation and morale within the organization which in turn leads to increased job performance, increased customer satisfaction and retention, reduction of wastage of company resources such as raw materials, labor or financial resources and an increasing opportunity for the company to engage in international trade (Blokdijk 64).
Requirements for ISO Certification
The main purpose of the ISO 9000 family of standards is to facilitate the common understanding of the various concepts used to govern quality management within organizations.
The ISO 9001 quality management system certification provides the requirements for quality management which organizations can use to attain certification.
The most general requirement is that organizations have to develop consistent quality management systems which will be used to ensure that the organization continually improves its business operations.
The requirements for ISO 9001 certification have been classified into four groups which include management responsibility, resource management, measurement and analysis of business improvement and product realization (Pfeifer 69).
The requirements under management responsibility incorporate all aspects of management with the most fundamental being the formulation of quality policies and objectives.
The ISO 9001 requires managers to develop a quality plan that will be used to achieve these quality policies and objectives. The quality plan has to specify all the measures and techniques that will be used to achieve the quality objectives.
Another requirement which falls under management responsibility is ensuring that the system used for quality control and distribution has been properly maintained and important documents and records have been kept safely for future use.
Other requirements that fall under this category include the evaluation of management practices, the definition of managerial duties and responsibilities and the management of documents which are used for quality management practices (Pfeifer 69).
The resource management category focuses on the facilities, work environment and staff of an organization where a company has to utilize these resources to demonstrate its ability of developing products that are customer-oriented.
Achieving this requirement will involve selecting and training suitable staff who are customer focused as well as providing them with the necessary machinery and tools to develop customer-oriented products.
The company has to also provide a suitable work environment which will ensure that the selected and trained staff has the ability to attain the quality management standards stipulated by the ISO 9001 guidelines (Pfeifer 69).
The requirements for product realization are mostly focused on increasing customer satisfaction with the organization’s products and services. Product realization requires companies to demonstrate their ability in identifying and harmonizing the requirements of customers with the products and services developed by the company.
For a company to be ISO 9001 certified it has to submit a verifiable process management plan which can be used for development, procurement and production processes within the organization.
The company therefore has to demonstrate that it can be able to manage its development, procurement and manufacturing processes. The company should also introduce a quality system that will be used to test equipment within the organization (Pfiefer 70).
The measurement, analysis and improvement requirement stipulates that companies must plan and introduce process measurements so as to close the quality control loops that exist in quality management systems.
This requirement stipulates that companies have to measure the satisfaction of customers with regards to the products and services offered by the company.
Organizations are therefore required to develop detailed plans that will be used to measure and monitor production operations. Measurement and analysis also requires organizations to conduct internal audits to ensure that business operations have met the requirements of customers.
Companies are also required to make continuous improvements to their business processes and take any corrective and preventive actions in the event production processes are flawed or have defects (Pfeifer 70).
Other requirements that are needed by organizations to attain ISO 9001 Quality Management System certification are the need by an organization to consistently demonstrate their ability of providing products and services that meet customer expectations while at the same time observing the statutory and regulatory requirements for quality products.
Companies should also aim to enhance customer satisfaction by effectively applying quality management systems that will continually improve the business operations of the company or organization as well as ensure there is product conformance to the needs and expectations of consumers (Pfeifer 70).
Method and Results
To examine the benefits of ISO 9000 certification on the productivity and performance of companies, the methodology for detecting improvements in business operations will focus on the manufacturing industry.
The methodology and research design that will be used in this case will be an event study based on secondary information collected from Corbett et al’s study on ISO certification.
The use of secondary data will be beneficial to this research because it will provide suitable information on the validity of being ISO certified for companies that have achieved certification.
Secondary data will also be useful for the study because it will save on the time used to collect information that will be relevant to this study.
With Corbett et al’s research forming a foundation for this study, this event study will analyze and compare the performance of companies within the manufacturing industry that have undergone ISO 9000 certification and those that have not received any ISO certification.
Event studies are commonly used in financial research and also in total quality management activities to assess the performance of a company with regards to its quality management activities (Corbett et al 34).
The event study for this case will involve specifying the event or time period needed for the implementation of ISO 9000 certification which is typically 6 to 18 months.
The time period will therefore be one year depicted by t where the company received its first certification. The period that is preceding certification will be referred to as t-2 while the period after the event years will be denoted by t+1, t+2 and t+3. These periods will be used to determine whether companies experienced any significant changes in their performance (Corbett et al 34).
The charts below summarize the findings of the event study where the performance of companies that have received certification are measured by the continuous line while those that have not received any ISO 9000 certification are represented by the dashed line.
As mentioned, the certification was awarded in year t and the measures that will be used to measure the performance of the companies will return on assets (ROA), Tobin’s Q, Cogs/Sales and Sales/Assets measures.
The charts basically compare the performance of certified and noncertified companies in the manufacturing sector so as to gain useful information of whether ISO 9000 certification is beneficial to organizations (Corbett et al 34).
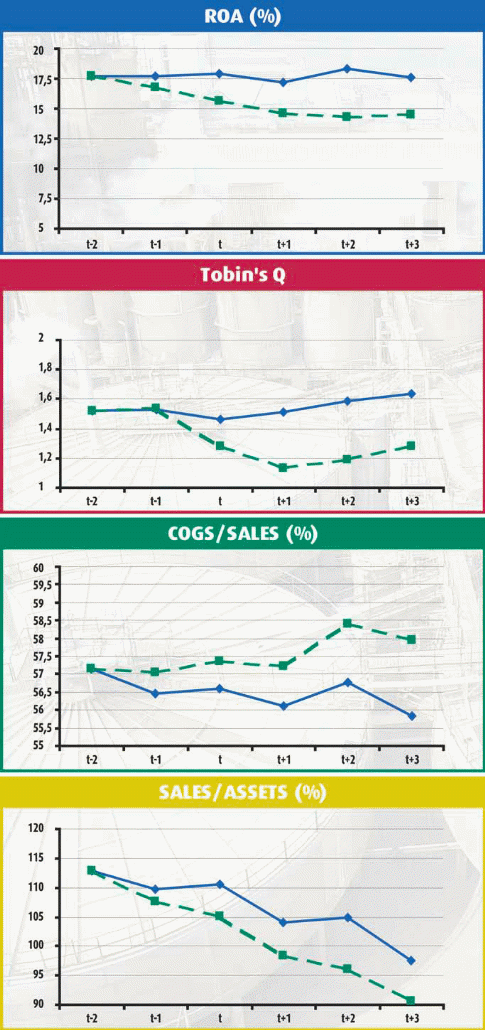
In the first chart which compares the return on assets between certified and non-certified companies in the manufacturing industry, companies which did not have any ISO certification saw their return on assets dropping when compared to those of companies with ISO 9000 certification which remained fairly constant.
If a company within the industry has a ROA of 17.5% which is the average ROA for companies that have been certified in the t-2 event period, their ROA would remain constant prior to the company receiving ISO 9000 certification.
For companies not receiving certification and with a ROA of 17.5%, their return on assets would experience a significant drop compared to companies in the same industry which have received certification. In the second chart which represents Tobin’s Q, the effect of ISO 9000 certification eventually materializes during the t-1 period.
The difference in performance between the two organizations becomes notable during the year of certification. By t+3, the Tobin’s Q rate of the certified companies is 0.45 higher than that of the non-certified companies.
The Cogs/Sales chart demonstrates that the certified companies are experiencing a Cog/Sale ratio of 1.5 percent lower than that of the certified companies.
This can be attributed to the increased productivity levels of the firm where increased production has seen more goods being consumed by customers who are willing to purchase from the company because of ISO certification.
The last chart which is the sales/assets chart demonstrates that the certified companies have a smaller decline in sales/assets during the first two years after they have gained their ISO certification. In the long term however, this effect does not have any effect on the sales and assets of the certified company.
In terms of the profitability of ISO and Non ISO certified companies, companies that have been able to reduce the cost of producing goods are able to experience higher profit margins when compared to non-certified companies.
The graph below demonstrates the difference in profit margins between a company that has received ISO certification and one that has not been certified. The graph is meant to demonstrate whether ISO 9000 certification leads to the profitability of a company.
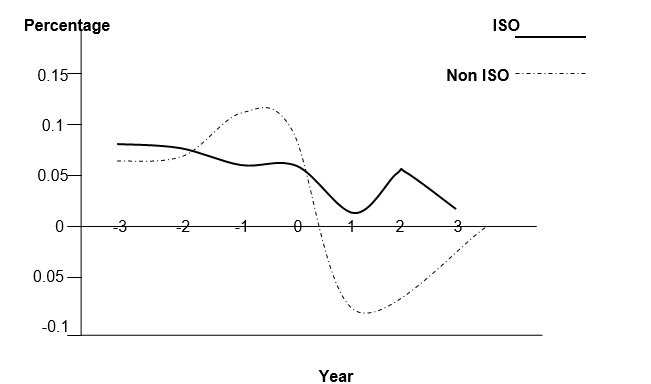
According to the graph, companies that have received ISO certification have a higher and stable profit margin when compared to companies that have not received ISO certification.
The high profitability margins can be attributed to the increased level of productivity experienced by the organizations as well as higher employee morale which motivates them to perform their work effectively and efficiently.
The increased production and sale of products ensures that the organization is able to record a profit and higher returns on its revenue (Heras et al 72).
Based on studies conducted by Casadesus et al and Padibjo on the relationship between ISO certification and profitability, the researchers were able to note that profit margins and the return on capital utilized by certified companies was usually double that of average companies operating within the industry (Heras et al 74).
Haversjo was able to note that companies which were ISO certified had a higher rate of return compared to when they not certified. Since companies that wanted to be certified had to reduce their expenditure, the reduced wastage of funds led to the company recording higher returns on their investment as well as increased sales.
The limited studies that have been conducted on ISO certification and profitability have been able to highlight the fact that quality certification allows companies to exhibit superior financial performance. Companies that are profitable are able to attract a larger market share within an industry thereby gaining more customers and increasing their sales even further (Heras et al 74).
Discussion
From the results of the study, it can be noted that companies which have received ISO certification are able to achieve higher productivity levels when compared to companies that do not have ISO certification.
ISO certified companies are also able to achieve significant cost reduction measures because of the effective quality management systems which have been implemented within the company to manage the efficient use of resources.
The results of the study were also able to demonstrate the significant sales that companies with ISO certification were able to have which in turn improved the return on assets of these companies.
The noncertified companies on the other hand recorded lower return on asset ratios which was attributed to the decline in performance of these companies especially when they were operating within the same industry as the certified companies (Corbett et al 38).
An interpretation of the results reveals that firms experience a significantly better performance once they decide to pursue their first ISO certification process.
The implication of starting to pursue certification means that companies have already began streamlining their operations to meet the quality management requirements stipulated by the ISO 9001 requirements.
The preparations that companies make before they embark on the ISO certification journey usually lead to superior performance and productivity as the company wants to demonstrate that its quality management systems are ready for certification (Corbett et al 39).
Being ISO certified will mean that the company has an improved quality management system that places a lot of emphasis on the quality and how quality can be achieved in a consistent way.
ISO certification also means that companies are able to minimize the wastage of resources when producing goods thereby ensuring that quality products are produced to meet the needs and expectations of consumers.
The results have also been able to highlight the fact that being certified reduces the costs that are used to produce goods because the right amount of resources are being used to develop the products. Companies that have received certification also have fewer customer defects meaning that their sales and profit margins are on the increase.
In addition, the badge of quality which is usually given to a company once it has received ISO certification opens more opportunities for sales as more customers want to be associated with a company that offers quality products.
Because the cost of producing goods has reduced considerably, the company can be able to experience higher profit margins and returns on its investment.
The economies of scale and lower sales acquisition costs are important factors which contribute to the overall profitability of a company and these can further be increased in the case of a company that has received certification (Heras 73).
The results have been able to provide a link between the reasons why companies decide to pursue ISO certification and the benefits that accrue from being ISO certified.
The analysis of the charts was able to reveal that companies with ISO certification were able to record higher sales, return on assets and profitability as a result of their decision to implement quality management systems.
Being ISO certified has allowed organizations and businesses to improve their performance and maintain it and also improve their financial standing within their industry of operation. The decision to pursue ISO certification is therefore a beneficial venture for organizations seeking to improve their quality management systems.
The limitations of the research have mostly been the limited amount of research that has been conducted on the benefits of ISO certification on companies.
Very few researchers have conducted considerable research on this topic which has presented a major challenge in gathering vital information that can be used to conduct the study.
Another limitation was that the few studies used for the research were unable to provide any considerable information on whether companies which had attained ISO certification had a competitive advantage over their rivals.
Since ISO 9000 is a public standard, it is difficult to determine whether one firm or company can be able to gain any sustainable competitive advantage from the certification.
The results of this study can also not be generalizable to companies that are non-listed and small medium enterprise businesses. This is because they do not have profit margins and return on assets that can be measured on the same scale as those of large companies. This is a limitation to the study where future research should consider these companies to determine whether ISO certification is a beneficial exercise for them or not.
The major criticisms of the study have been that ISO certification within organizations is seen as a necessary condition that is meant to maintain the current performance of a company rather than a way of improving the organizational performance of the company as a whole.
Companies that want to achieve ISO certification view this process as an important milestone in maintaining the performance levels of the company.
However, the research used in this study has been able to prove that companies that do not have any ISO certification experience a gradual decline in their productivity and performance especially if they are operating within an industry that has many companies which have attained ISO certification.
This study is beneficial for companies that are looking to undertake ISO 9000 certification for their quality management systems. This is because the study offers the various motives and reasons that are used by organization managers to attain certification.
Having a badge for quality systems creates a positive image amongst the customers and clients of the company as the company has been recognized for its delivery of superior products and services.
Customers of a company are more than likely to purchase their products from a company that has been accredited by the International Organization for Standardization.
The information collected in the research can be used by managers who want to determine whether attaining ISO certification will be of any benefit to the company.
Because many organizational managers are concerned with the performance of their organizations, this research and other studies which have been conducted on ISO certification can be able to provide useful statistical information that can gauge how an organization will perform once it has fully implemented the ISO certification process.
The results of the analysis and discussion have been able to provide useful information which associates ISO certification with performance improvements within organizations.
Being an ISO 9000 certified company allows an organization’s managers to build the reputation of the company within the industry in which it operates in.
Managers can use the ISO 9001 badge to market the company’s products to customers and also retain the old customers who patronized the organization before it received its certification.
ISO certification can help managers who want to increase they customer base because the mark of quality indicates that the services and products offered by the company are of a superior quality than those of other companies within the same industry.
Conclusion
The study focused on the ISO 9000 family of standards by first defining the meaning of these standards and then offering background information on the origin of these standards.
The study has assessed the requirements that companies should have for them to meet the ISO 9001 criteria for quality management systems.
The reasons and benefits for being certified were also discussed in this research study by analyzing data collected from companies that were certified and not certified within the manufacturing industry.
Analysis of the information was able to reveal that companies which had ISO 9000 certification were able to experience better performance of their business operations when compared to companies that were not ISO certified.
The results were also able to show that companies which had received certification had higher sales returns and return on assets which meant that ISO certification was a beneficial exercise for most companies.
Works Cited
Blokdijk, Gerard. ISO 9000, ISO 9001 100 success secrets. New York: Lulu Publishers, 2008. Web.
Corbett, Charles J., Maria J. Montes, David A. Kirsh and Maria Jose Alvarez. Does ISO 9000 certification pay. ISO Management Systems. 31-40. Web.
Corbett, Charles J., Maria J. Montes, and David A. Kirsh. The financial impact of ISO 9000 certification in the United States: an empirical analysis. Management Science, 51.7(2005): 1046-1059. Web.
De Silva, G.M.S. Basic metrology for ISO 9000 certification. Oxford, UK: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2002. Print.
Heras, Inaki, Marti Casadesus and Gavin P. Dick. ISO 9000 certification and the bottom line: a comparative study of the profitability of Basque region companies. Managerial Auditing Journal. 17. ½ (2002): 72-78. Web.
Hoyle, David. ISO 9000 quality systems handbook. Oxford, UK: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2006. Web.
Pfeifer, Tilo. Quality management. Munchen, Germany: Hanser Verlag, 2002. Web.
Sharma, Divesh. The association between ISO 9000 certification and financial performance. The International Journal of Accounting, 40 (2005): 151-172. Web.