Background
Habitat loss and fragmentation are considered by many to be the leading threat to biodiversity around the world. When people alter natural areas, for example, through agriculture or urban sprawl, the habitats needed to sustain native species are often eliminated. The remaining natural areas are left isolated. This process is referred to as habitat fragmentation. This problem is one of the major concerns of conservation biologists. In this exercise, you will compare the diversity of spiders to test the effect of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Spiders are a highly species-rich group of invertebrates that exploit a wide variety of niches in virtually all the earth’s biomes. Some species of spiders build elaborate webs that passively trap their prey, whereas others are active predators that ambush or pursue their prey. Spiders represent useful indicators of environmental change and community-level diversity because they are taxonomically diverse, with species inhabiting a variety of ecological niches, and they are easy to catch. These spiders were captured by a biologist traveling along transects through the patches and striking a random series of 100 tree branches. All spiders dislodged that fell onto an outstretched sheet were collected and preserved in alcohol. They have since been spread out on a tray for you to examine. Two forest patches were sampled. Forest patch “1” is a large undisturbed patch of mature forest covering an area of approximately 5 square miles and is protected as part of a state park complex. Forest patch “2” is located in the center of a subdivision. This patch is only 0.75 square miles and is isolated from any other forested habitat by development.
Develop a hypothesis on which forest patch would have higher diversity given your knowledge of island size and distance to other suitable habitats.
Hypothesis: (You may use an “if…then” type of statement for your hypothesis).
Is your hypothesis testable? Yes, the hypothesis is testable since the number of different species could be caught and counted and a diversity index calculated.
Activity
Your first task is for you to sort and identify the spiders. To do this you have to identify all the specimens in the collection. To classify the spiders look for external characters that all members of a particular group of spiders have in common but that are not shared by other groups of spiders. For example, leg length, hairiness, relative size of body segments, or abdomen patterning and abdomen shape all might be useful characters.
- Assign each species a working name, preferably something descriptive. For example, you might call a particular species “spotted abdomen, very hairy” or “short legs, and spiky abdomen.” Just remember that the more useful names will be those that signify to you something unique about the species.
- Use the data tables found in iCollege for each forest patch listing each species and the number of occurrences (species abundance) of the species in the collection.
- Use the data in the table to calculate the Diversity Index for forest patch 1 and forest patch 2.
Conclusion Questions:
What was the species richness for the forests?
What is the Simpson’s Diversity Index for each forest patch?
Which forest patch is more diverse? How did you develop this conclusion?
The first forest patch was more diverse since it had more species richness as compared to the second patch. This conclusion is arrived at by calculating the number of different species of spiders sampled. Identifying the different characteristics of the spiders helped in grouping them according to species.
How might the impacts on the forest patches differ between the two sites?
The first site is undisturbed and preserved as compared to the second site that has been subdivided and some of the natural ecosystem lost. The first site was also a bigger site as compared to the second site.
How might this lead to the differences in diversity you have observed?
Natural and undisturbed environments still have ecosystems that support the thriving of various species of a given organism. When this environment is disturbed, some species die off due to lack of adequate natural resources or poor environmental conditions for their growth and reproduction. Reduced ecosystem size also plays a huge role in species diversity decrease as fight for resources increases and only the fittest species survive (Potapov et al., 2019). These are some of the reasons that have led to the differences in species diversity in site 1 and site 2.
Diversity Index Worksheet
Diversity Index => write the equation here
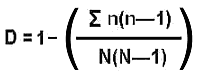
Calculate the numerator => 370
Calculate the denominator => 71(71-1) = 4970
Divide => 370/4970= 0.07445
Answer is 1-0.07445= 0.9256
That is the Diversity Index for Site 1.
Site 2.
Diversity Index =>
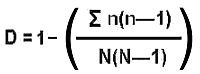
Calculate the numerator => 380
Calculate the denominator => 43(43-1) = 1806
Divide =>
380/1806= 0.21
- 0.21= 0.79
That is the Diversity Index for Site 2.
Reference
Potapov, A., Duperre, N., Jochum, M., Dreczko, K., Klarner, B., Barnes, A. D., Krashevska, V., Rembold, K., Kreft, H., Brose, U., Widyastuti, R., Harms, D., Scheu, S. (2019). Functional losses in ground spider communities due to habitat structure degradation under tropical land‐use change.Ecology Society of America, 101(3). Web.