Executive Summary
In current competitive service industry, companies are facing a challenge developing, managing, and retaining quality effective managers. The competitiveness that has been enjoyed by SUNNY in Chinese market can be attributed by its effective human resources management as well as favorable working condition; however, the industry in general is facing an increased job-hopping by effective managers.
To solve the challenge, SUNNY Optical need to enact effective talent management strategies that will enable the company nurture, develop, tap, and utilize their human resources talents and intellectual property. For an effective strategy, there is need for collaboration between the top management, line managers, and junior staffs.
Case background
Business management scholars have agreed that there is always a room for improvement in an organization despite how well its operations seem to be: there are different approaches leading an organization to improve performance, most of the approaches depend on the skills and knowledge of human capital in an organization. SUNNY as an international optical retailing company is doing well in the global scenes; it has high value for its employees and spends substantial amounts of its income to motivate, develop, and retain its human resources.
However, in current competitive business environment, the company is facing a challenge retaining its effective and quality managers as they are job-hopping in search for better employers with wages as the main motivator for the job-hopping. The new life employment policy has also added some pain to the company as it’s a challenge to develop, maintain, poach, and retain quality managers.
Despite the challenges SUNNY leaders have some strategic management approaches that it can adopt to ensure that the company remains competitive amidst the challenges it is facing as well as reduce the rate of influence of the challenges (Farrell and Grant, 2005). This paper analyses the problem facing SUNNY Optical in China and give recommendations on strategies that John Wu, the company’s president, would pioneer for a competitive business.
Problem analysis
The problem facing SUNNY Optical is not unique to the company however, it is experienced across the service industry; the main cause of the problem is deficiency in quality service managers and poaching as well as job-hopping among the existing quality managers. The development of new life employment policy has impacted the industry as it has the likelihood of reducing motivation and individual efforts among employees of a certain employer.
The main issue that John Wu is wondering about is how the company will be able to have new strategies that will guarantee that in the future, the company will have quality manager and leaders; he is wondering this despite there being a number of qualified graduates with some working experience however it can be noted that they lack some polishing to offer quality service and leadership skills.
SUNNY has had human resources policies that can be applauded, however as stated earlier, there is no optimal level, but every situation offers a room to improvement. The management has ensured that employees are well mentored; coached, developed and motivational strategies have been put in place.
The management has been successful in developing an effective communication strategy that ensures that all employees and the management mingle and interact with each other with ease and can share ideas freely; with such an environment, certainly the company has a favorable working condition yet managers are finding a reason to move to other companies.
The management fears the total loss of quality leaders that it has been able to develop over time. The issues facing the company can be solved with some minimal intervention by the management of the company’s policies on talents and psychological contracts fulfillment (Farrell and Grant, 2005).
Solution to the problem
To ensure that the problem does not recur in the future, the management need to have a lasting solution that will enable the company develop and retain managers; every human being has a talent that needs to be seen, developed, managed, tapped, and utilized for the good of the employer. As far as leadership is concerned, there are some people who have been born as charisma leaders, however if the power and the talent they hold is not well tapped, then they might not benefit their company with the talents (Lester and Kickul, 2001).
John Wu has the challenge of developing an effective talent management system in the company; with the strategy, he will be able to make quality managers and leaders from the pool of graduates with some working experience but whom cannot be relied upon on their leadership traits.
Effective talent management strategies take some steps and form; talent management is defined as a complex human resources management process where the human resources team develop measures and policies that facilitated in tapping human beings intellectual property.
According to Burbach & Royle, 2010, “Talent management as a corporate area of focus has been building steadily” (Burbach and Royle, 2010), the approach to managing and maintaining talents within an organization is one of the newest management approaches that is yielding satisfactory results in companies that it has been implemented. An effective talent management strategy that the company should implement will start from recruitments adopted by the company all the way to how the employees will be retained, the strategy is as follows:
Evaluation of current talent management within an organization
SUNNY human resources department has the role of creating an environment that can create an orchestrate team; they have the role of ensuring that the company human resources needs are well catered for; although it can be applauded for such successful efforts, it has to enact talent management policies.
The policies implemented are expected to facilitate the use of intellectual properties of their staffs (talents) although the objective may not be as explicit as other human resources roles. The initial step then to develop a deliberate talent management strategy in an organization is to understand the current position of the firm as long as tapping intellectual property is concerned (Renckly and Renckly, 2003).
The parameters to use include:
- Analysing the succession plans adopted at SUNNY
- Take a review of major and minor innovations that the company has had in the past and try to look at the source of the innovation
- Involve department and sector managers in the process and get their inputs on the calibre of employees already in the organisation.
The information derived will be crucial in determining the state that a company is as long as talent management is concerned (See diagram below on how talent is involved in business objectives).
Diagram 1
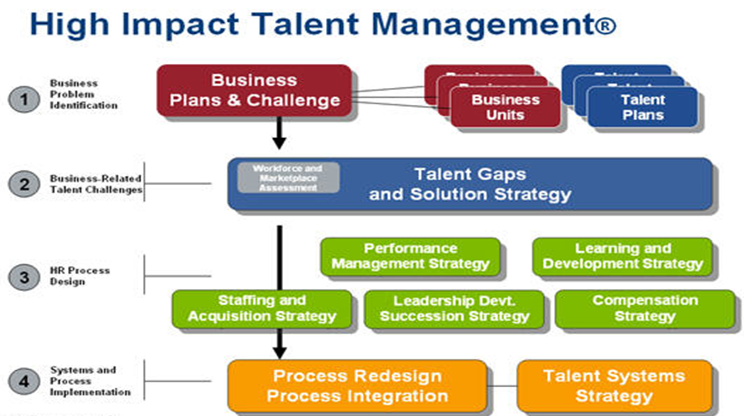
Talent Entry and Retention
John Wu should understand that SUNNY needs to have a recruitment method that considers talent development and management in the company: when applications are received, they are sorted, and short listed candidate are contacted, when short-listing the experiences given by the employees should be reviewed to ensure that those applicants with the sort talents have been established.
To enable employees perform their duties effectively and have a chance to improve some systems though their talents, creativity and innovativeness; then continuous system and employee’s appraisal is important. When this is done, it helps human management to interact and share with employees on their experiences and relax the air to the employee that he can recommend areas that needs improvement and probably offer recommendations on the way forward.
Relaxing an environment and involving an employee in its improvement is a psychological approach that assists employees to own up a certain function, the ownership triggers innovativeness and use of their talents. On the other hand, offering employees challenging environment is important to trigger their use of talents.
In cases where the weak point is because of employees ignorant, then programs are set up to address this. Training is another way that talent can be natured and developed; some organizations have employees training as a continuous process with the aim of ensuring that the employees are up-to-date with the changes in the industry (Anthony, Kalmar and Perrewé, 2002).
Development and Passing out
With a favorable environment developed, the next step is to expect results from the human capital in the organization; the employee is given some more challenging roles that are in line with his line of strength that has been established.
When operating in the roles, the company should make the employee as centre for the project; for example, an employee may be made the head of a certain project that the management believes he has the potential of developing better processes and products through his talents. When developing an employee for talent management, then the following are the areas that development should look into:
- Knowledge that the employee has acquired
- The special skills that an employee have
- The attitude that an employee have towards development of new methods of doing things
- The behaviour of the employee (Schweyer, 2010).
A well-planned development assists the company to nurture, develop and retain employees with talents in the company. To facilitate talent development, knowledge development cannot be ignored; knowledge and talents are intangible assets, which are unique to different business and can be improved with experience and information interpolation (Lester & Kickul, 2001).
The following diagram summarizes the process of talent management:
Diagram 2
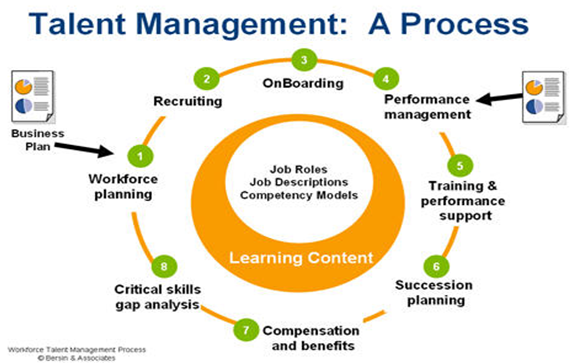
Conclusion
The global optical retailing industry has become competitive; SUNNY needs to have effective human resources talent management policies if it will remain competitive in Chinese market.
Personnel’s have different talents and capabilities; however tapping this asset requires strategic management; they need to be natured, developed and managed before they are exploited. Other than utilizing the knowledge and experience that the employees have, there is the need to use available information to grow and develop knowledge and expertise in employees.
To effectively manage talents, SUNNY should start by understanding the current strategies and processes and how they support talent management, with the understanding, they will be able to tap talents from entry level, nature, develop and retain them to the benefit of the organization. When a talent has been developed, there should be effective passing out mechanism so as the benefits of the talents can benefit an entire organization.
References
Anthony, W. P., Kalmar, K. M., &Perrewé, P. L. (2002). Human Resource Management, A Strategic Approach, (4th ed). South-Western, Thomson Learning.
Berger, A. & Berger, D. (2003).The talent management handbook: creating organizational excellence by identifying, developing, and promoting your best people. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Farrell, D. and Grant, A. (2005). China’s Looming Talent Shortage. McKinsey Quarterly, 1(1), pp.1-4.
Lester, W. and Kickul, J.(2001). Psychological contracts in the 21st century: What employees’ value most and how well organizations are responding to these expectations. Human Resource Planning, 24(1): 10
Renckly, B. R & Renckly, G. R. (2003). Human Resources. New York: Barron’s Educational Series.
Schweyer, A. (2010).Talent Management Systems: Best Practices in Technology Solutions for Recruitment, Retention and Workforce Planning. New York: John Wiley and Sons.