- Introduction
- Points of comparison
- Differences and similarities in the concept of “self”: Jung vs. Kohut
- The origin of self: Kohut vs. Jung
- The origin of self: Kohut v Jung
- The concept of splitting Psyche: Kohut vs. Jung
- The concept of splitting Psyche: Kohut v. Jung
- Origin of intrapsychic structure: Kohut v Jung
- The Idea of Wholeness: Jung vs. Kohut
Introduction
- Jungian school of thought remains controversial.
- Most use empirical evidence to support or refute Jung’s claims.
- The concept of “self” has received critical review.
- Kohuts theory is the best critical approach to Jung.
- The two theories are important in psychoanalysis of the self.
- They are concerned with human concept of self.

Points of comparison
The theories show several similarities and differences.
The main question relates to the relationship between the two concepts.
Psychoanalyst attempts to find a consensus between the theories.
The similarities and differences are observed in three major aspects:
- The concept of self,
- The origin of self,
- The splitting nature of self,
- The idea of wholeness.
Differences and similarities in the concept of “self”: Jung vs. Kohut
- Both psychoanalysts stresses on the importance of the self.
- Both emphasize that the self has an intrapsychic structure.
- It makes their descriptions of the self and its nature seem to overlap.
- Their schools of thought differ in a number of ways.
- Differences only arise due to different approaches to “self”.
- Similarities are more profound than differences.
- Both state that the it is impossible to fully describe the “self”.
- Kohut- self refers to the cognitive impenetrability.
- Jung- self cannot overpower human power of compression.
- Kohut- self is the way in which an individual experiences “himself as himself”.
- Kohut – self is a permanent mental structure of human behaviors, memories and feelings.
- Each individual experiences this with time, and it gives them the feeling of “being oneself”.


The origin of self: Kohut vs. Jung
- Jung’s theory is the wire armature for a sculpture.
- Kohut’s self is the clay to finish Jung’s work.
- It is a metaphorical approach to the differences.
- Jung – humans become involved with other individuals who correspond to the human essential nature.
- Jung- Other humans are objects to form archetypes.
- Kohut- Other humans are objects to satisfy child’s needs.

The origin of self: Kohut v Jung
- Kohut- goals are the realization of the objective of life.
- This blueprint objective has been laid on in a person’s nuclear self.
- Jung- based on the process of unfolding the self throughout an individual’s life.
- Jung- it aims at achieving the possible personality’s wholeness.
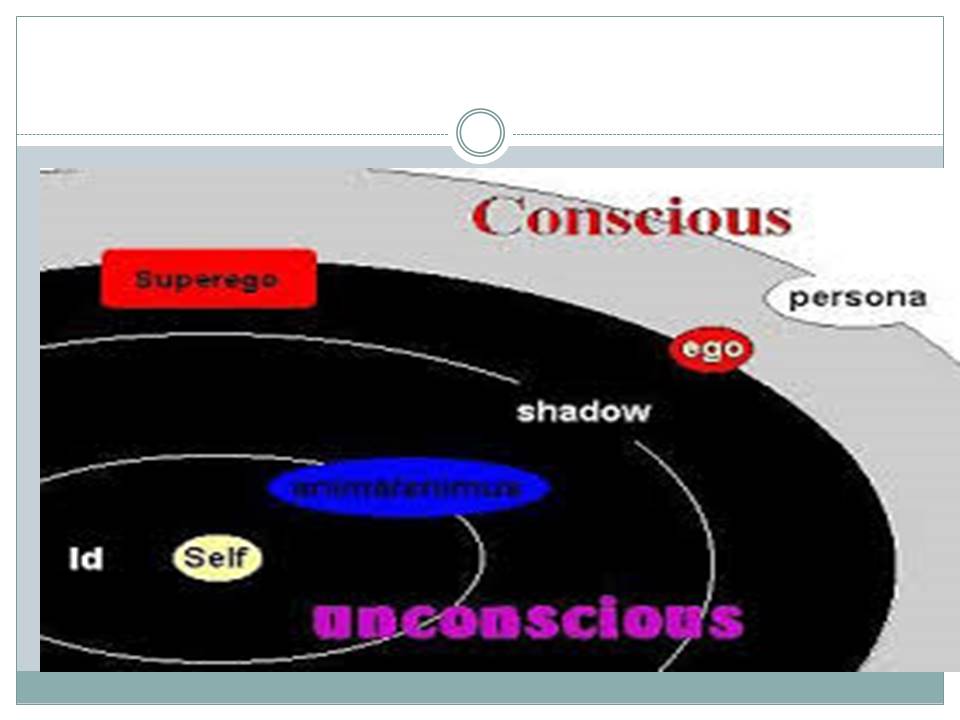
- Jung- self is a totality of both conscious and unconscious human psyche.
- It is purposive in nature and acts as a center for organizing.

The concept of splitting Psyche: Kohut vs. Jung
- Kohut and Jung emphasize on the importance of splitting.
- Kohut- draws a clear line between vertical and horizontal splitting.
- Vertical splitting- there is no material thing.
- But the significance of emotional material is ignored.
- Leads to the coexistence of two intrapsychic contents.
- But there is no communication between these components.


The concept of splitting Psyche: Kohut v. Jung
- Jung- stresses on the theory of neurosis.
- Concerned with the idea of the tendency of the psyche to split.
- Also the autonomy of the split components or associated associations, ideas or feelings.
- The components behave like splinter psyches.
- But they are in harmony with the overall human personality.
- Kohut’s splitting is evident but less important.

Origin of intrapsychic structure: Kohut v Jung
- Kohut- structuralization of the inner world of a child results from the parent’s self objects.
- Their emphatic responsiveness to the inner needs of the child.
- Jung’s theory- a child’s prior psychological matrix is inborn.
- Experiences determined by the child-environment interaction.
- Kohut- eating and assimilation of food illustrates the process of creation of intrapsychic structure.
- The food has been assimilated into the body of the person.

The Idea of Wholeness: Jung vs. Kohut
- Kohut- personality of a patient exists in wholeness.
- This total personality is the intrinsic constituent of the whole stance.
- Psychologist should see his patient from an overview perspective.
- The concept of totality is present in Jung’s idea of wholeness.
- Emphasizes on the idea of totality of psyche.
- All psychological aspects are part of the whole psyche.
