Introduction
Chemistry is a science sub-branch that studies matter and its substances. The branch explains how matter undergoes specific changes and why the modifications are relevant. Chemistry is an entrancing discipline as it plays a vital role in the lives of all humankind in various ways.
This science is essential for meeting our daily needs, such as water, food, shelter, clothing, energy, and clean air. Chemical technologies have advanced today to improve the quality of life by establishing new solutions to energy usage, materials, and healthcare issues. Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has been experienced globally, but the vaccines and booster shots were developed using chemistry.
Studying chemistry prepares an individual for the real world, as the knowledge is helpful in many circumstances. Knowing chemistry provides excellent insight into the physical universe where life is supported. In everyday life, chemistry is encountered on many occasions, like using antibacterial soap, eating safe meals, cooking, and boiling water to kill bacteria and make it safe. Chemistry touches many fields of study and is fundamental in providing quality healthcare, understanding climate change, and enhancing environmental protection.
Applications of Chemistry
The application of chemistry is vast, covering health provision, climate change, and environmental protection. In food, chemical molecules make up fiber, proteins, and vitamins, which promote safety as they enhance the growth of the body (Bonam et al., 2021). Chemicals often preserve and manufacture meals containing nutritional supplements and additives. They are further used in preparing fertilizers, resulting in healthy and nutritious crops, thus impacting health (Zhang et al., 2018). Chemistry is relevant in manufacturing medicines for treating sicknesses (Karges, 2022). It is further used to manufacture surgical materials for specialized hospital operations.
The current and future states of the Earth’s climate can be predicted using chemical formulas. Environmental chemical processes, such as burning fuels, contribute to global warming. Human activities contribute a lot to these processes, which in turn cause ecological issues. Green chemistry contributes to environmental protection by enhancing, monitoring, and protecting the living conditions that are likely to be affected, such as oil, air, and water (Karges, 2022). Each day, chemistry contributes to how people live, especially in healthcare, as all aspects affected by the field relate to the healthy living of individuals.
Chemistry in Healthcare
Importance of Chemistry in Food
Scientists have shaped the food we eat in various ways, thus indicating the significant role chemistry plays. The integration of chemistry procedures facilitates how food is produced, consumed, stored, and preserved. Cooking meals and combining ingredients to produce desired molecules are chemical processes (Science Museum, 2019).
The use of chemicals in meals dates back to the time. Paraffin wax was burnt in ancient China to ripen fruits, which was possible due to the combination of propylene and ethylene (Science Museum, 2019). Romans used to add potassium aluminum sulfate to bread, thus making it white (Science Museum, 2019). Egyptians, on the other hand, colored their meals with saffron, an essential spice that is linked to health benefits like improved sexual function, libido, and mood (Science Museum, 2019).
Chemical products are critical in the production and preservation of food. The cuisine additives developed through chemical processes can prolong edibles’ shelf life and make them attractive (Science Museum, 2019). Flavors are used to make feeds tasty, and the supplements act as sources of nutrition. The nutrients are attained from the specific molecules found in cuisine, which promote healthy living.
What is eaten can affect the consumer’s health, hence the need to take meals that are impactful in promoting healthcare. The major constituents of edibles include water, carbohydrates, vitamins, lipids, proteins, and minerals (McClements & Grossmann, 2021). The chemical compositions of these products determine the reactants available for a chemical transformation. Unlike grains, water is the primary food component, especially in fruits and meat.
Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the most frequent molecules in food and are nutritionally essential (Science Museum, 2019). They have different chemical properties, thus affecting how a meal turns out. Carbohydrates contain a mixture of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and provide energy (McClements & Grossmann, 2021).
Proteins are polymers of amino acids and mainly contain carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen (McClements & Grossmann, 2021). They are fundamental to people’s nutritional well-being as they are required for cell repair and development. Lipids act as vitamin carriers; they serve as energy sources, insulation, and organ cushioning, hence being a vital part of cell composition. The above chemical molecules are manufactured and preserved through additional chemical strategies, ensuring they are in good condition.
Manufacturing and Preservation of Food
Chemistry is vital in manufacturing and preserving cuisine as it informs us of changes during processing and storage. Food constitutes organic substances consumed to attain some nutritional benefits. Chemical processes in meals determine their freshness, taste, texture, and nutritional value (Bell-Young, 2021).
Cuisine undergoes spoilage due to physical, chemical, and microbiological actions. They require proper preservation to retain their qualities for an extended period. Some household chemicals, such as salt, help preserve feeds, preventing them from spoiling. The standard methods used to store meals, ensuring they are fresh and healthy for consumption, include salting, refrigeration, canning, use of spices, boiling, and fermentation (Bell-Young, 2021).
Chemical preservatives like sorbic acid, citric, calcium propionate, sodium benzoate, and vinegar are commonly used to keep fruits and bakery products fresh (Bell-Young, 2021). Using chemical techniques enables the storage of feeds for a long time, ensuring enough to consume, as wastage is minimized. Food is critical in attaining good wealth as it provides all the nutrients the body needs.
Production of Farm Inputs
Most meals, such as vegetables and fruits, are grown naturally and require farm inputs to prosper. Like animals, crops are occasionally affected by diseases, hence the need for herbicides. Chemistry has provided the world with essential insecticides, fungicides, herbicides, and fertilizers, which contribute to the production of food consumed daily (Zhang et al., 2018). Fertilizer use in recommended portions results in increased harvests as they provide the needed nutrients plants require for growth. They are chemical substances commonly made from potassium, nitrogen, and phosphorus (McClements & Grossmann, 2021).
Pesticides help protect plants from diseases, weeds, and insect pests that can lead to the deterioration of harvests (Zhang et al., 2018). The common pesticides developed include copper sulfate and malathion (McClements & Grossmann, 2021). Agricultural outputs affect the population’s health, hence the need for adequate food. There is a relationship between food, agriculture, and health, with cultivation being at the center as it affects whether there is enough to eat if it is sufficient nutrition-wise, and safe.
Importance of Chemistry in Medicine
The treatment of injuries and diseases is facilitated through the use of drugs and medicines, which are chemicals. Chemistry is used in clinical laboratory analysis, medical research, and education. The development of new tools that make it possible to separate and identify important molecules in urine, serum, and blood has been advanced through chemistry (Karges, 2022). Determining the exact type of drug abused in cases of overdosing is now possible. Medications used in treating, preventing, and curing a health issue or disorder are made of chemicals (Karges, 2022).
The study and knowledge of chemistry are requisite for pharmacists, doctors, and nurses in the healthcare sector. Chemistry extensively involves diagnosis, sanitation, drugs, and sterilization (Karges, 2022). It helps give proper medical support to the clients with zero errors.
Apart from manufacturing medicines, this field of study is also in charge of testing the treatments and drugs, ensuring they are safe for use (Karges, 2022). Pills contain several chemical properties, like alkaline, water-soluble, and acidic (Karges, 2022). There is a need for chemistry to help medical officers know the properties present in medicine and how they will act.
Development of New Treatment Procedures
Chemistry techniques highly impact the development of new drugs and procedures used in treatment. Chemotherapy, a cancer treatment procedure using drugs to kill cancer cells, heavily relies on chemical principles to target the affected cells and minimize damage to healthy somatic cells (Bonam et al., 2021). New drugs are formed when chemists properly analyze and synthesize new compounds. The procedure is occasionally long and complicated, as it involves testing. After the emergence of COVID-19, scientists embarked on a process to identify a cure, which took time to be formulated before being issued to the public (Bonam et al., 2021).
Chemistry also contributes to using and preparing sterile materials, sutures, and artificial skin during surgery. Today, many surgical stitches do not require removal as they dissolve in the body after some time (Bonam et al., 2021). Artificial skin replaces human skin that has been destroyed by burning. The benefits of chemistry to the healthcare field are limited to the realization of new drugs, treatments, and equipment that make the procedures easy, safe, and successful.
Development of New Drugs
The various medications produced through chemistry have been helpful to humans by contributing positively to their health. This field of study has resulted in the production of painkillers and antibiotics. Patients with chronic or severe pain commonly use analgesics. They can be accessed over the counter or administered in hospital settings after surgery. Common types of these medications include fentanyl, morphine, tramadol, diamorphine, and buprenorphine (Bonam et al., 2021).
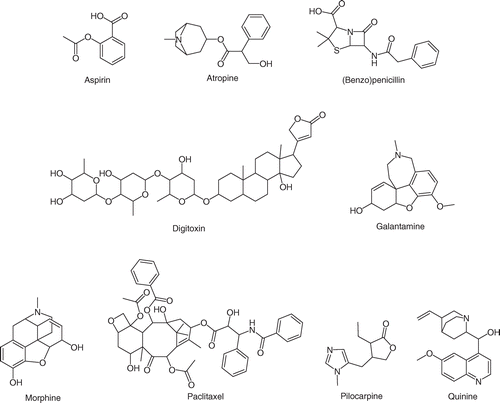
Antibiotics make it possible to prevent or treat some bacterial infections by killing or limiting bacteria from spreading and reproducing. In medical practice, they are often given to avoid the emergence of a disease. Before surgery, an antibiotic is sometimes applied to a specific area being cut. Common antimicrobials include penicillin for treating urinary tract, chest, and skin infections, aminoglycosides, and tetracyclines (Bonam et al., 2021). All essential medications like digitoxin, morphine, aspirin, galantamine, atropine, quinine, and many others are obtained from natural sources, thus giving them the unique chemical structures that display their properties, as shown in Figure 1 (Bonam et al., 2021). Besides applying to the healthcare field, chemistry also contributes to climate change.
Chemistry in Climate Change
Sources of Greenhouse Gases
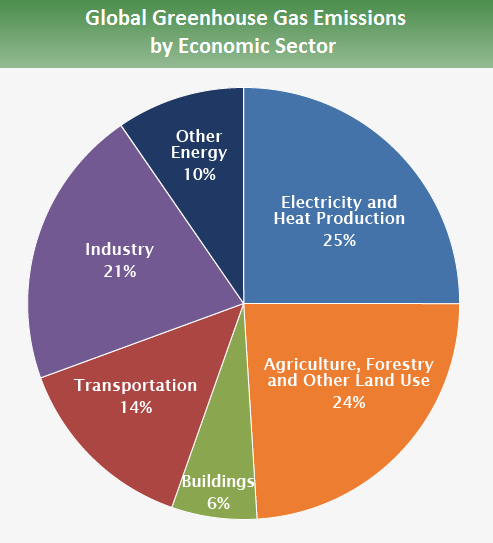
Global warming is a significant problem of the twenty-first century, mainly caused by human activities. The alteration is highly influenced by the release of poisonous gases into the environment, thus affecting the ozone layer. The primary greenhouse gases emitted include methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrous oxide (N2O) (EPA, 2023). Most global emissions occur from industries such as electricity and heat production, transportation, agriculture, and forestry (see Figure 2). The burning of fuels has drastically changed the climate more than any other activity.
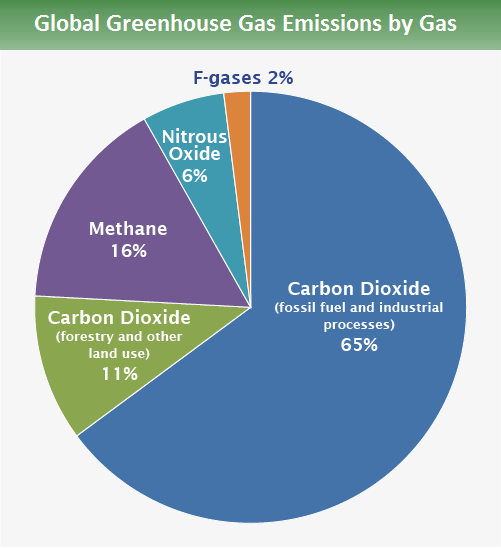
Carbon dioxide, at 76 percent, is the primary greenhouse gas, followed by methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases, constituting 16, 6, and 2 percent of the poisonous gases in the environment (see Figure 3). CO2 enters the atmosphere by clearing forests, biological materials, burning chemicals and fuels, and solid waste (EPA, 2023). The gas naturally occurs in the environment and is controlled through the carbon cycle. The burning of fuels for transportation and energy, land use changes, and industrial processes in the world have contributed to the emissions of CO2 (EPA, 2023). Other gases, such as CH4 and N2O, are formed differently and contribute to the greenhouse effect.
Methane is produced during oil, coal, and natural gas production and transportation. The major emitters of methane globally include the agricultural sector and the petroleum and natural gas systems (EPA, 2023). Farming and livestock keeping also influence the release of CH4 and the decay of organic waste and land use. Domestic animals such as cows, goats, sheep, and cattle produce methane as part of their digestion process through manure. Since natural gas is mainly composed of CH4, the gas is emitted during the production, processing, and storage of natural gas and the refining and transporting of crude oil (EPA, 2023).
Nitrous oxide is produced when human activities like fuel combustion, agriculture, and industrial processes are performed. Farming significantly contributes to N2O emissions in America, followed by industrial activities (EPA, 2023). About 40 percent of this chemical is obtained from human activities in farms, on the road, and in industries (EPA, 2023). Manufacturing nitric acid in producing fertilizer and adipic acid generates nitrous oxide as a by-product. The greenhouse gases cause significant effects on the surroundings, primarily by destroying the ozone layer, resulting in increased Earth temperatures.
Effects of Greenhouse Gases
The high rise in chemical gases like CO2, N2O, fluorinated gases, and CH4 affects the planet’s climate by causing massive changes. Climate change impacts the economy, environment, and health of living things (Prakash et al., 2022). Many regions around the globe are experiencing severe heat waves and oscillations in rainfall, which lead to droughts or even floods.
The increase in greenhouse gases contributes to the rise of global surface heat (Prakash et al., 2022). More severe storms are witnessed as much water is evaporated due to the sudden increase in temperature. Areas with minimal water sources are further affected as the availability is limited. As a result, crops and animals die, and farming is made impossible.
High temperatures make outdoor work impossible and contribute to heat-related illnesses like heat stroke, exhaustion, and cramps (Prakash et al., 2022). Wildfires are started quickly when the conditions are hot, thus affecting the ecosystem. Many species risk becoming extinct due to threats like forest fires, invasive diseases, and pests. Most of the world’s water bodies are acidic due to the release of high amounts of harmful gases in the environment.
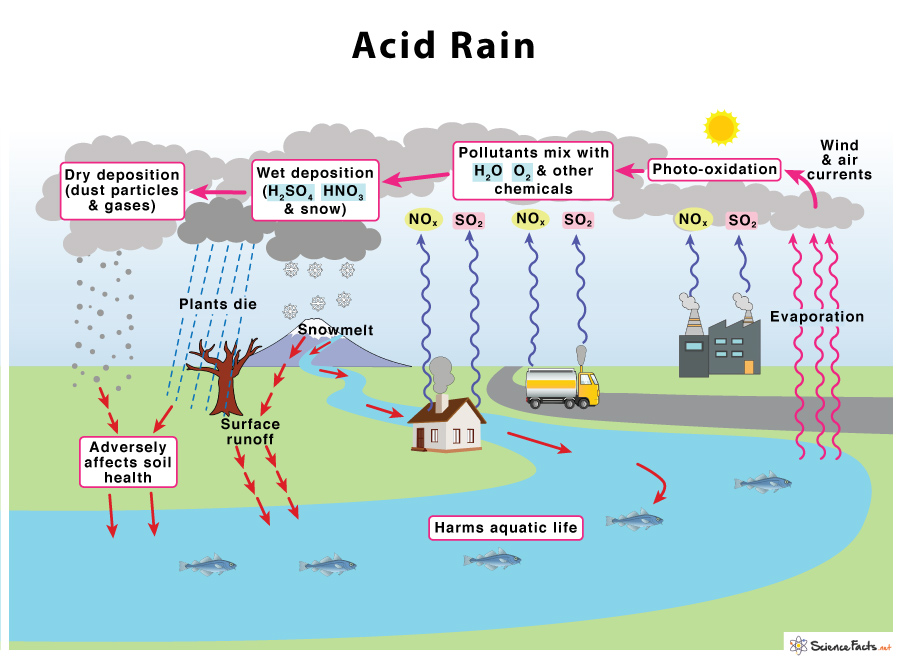
Acidic gases cause immense effects on living organisms in different ways. The common acidic gases include nitrogen and sulfur oxides (Mukherjee, 2023). During rain formation, the caustic fumes emitted react with water, oxygen, and other materials before falling to the ground as rain, causing diverse effects on water sources, soil, and plants (see Figure 4).
Acid rain affects the Earth by robbing it of essential nutrients like calcium. It results in the release of aluminum, which prevents plants’ water absorption. Crop production is also inhibited as the soil composition is affected (Mukherjee, 2023). Plants get damaged as the acidic components in the water destroy the protective coating of leaves. Stunted growth is further experienced as the essential components in the soil are washed away.
Rivers, streams, lakes, and oceans are made more acidic, thus adversely affecting aquatic animals and plants (Mukherjee, 2023). Acidic water results in water pipes’ corrosion, which contributes to the leaching of heavy metals like copper, lead, and iron into the water meant for consumption, which is harmful to health (Mukherjee, 2023). Besides contributing to climate change, chemistry can also be used for environmental protection practices.
Chemistry in Environmental Protection
Importance of Green Chemistry
Chemistry is crucial in every aspect of life as it is used for production, resulting in different impacts. The knowledge attained from this field of study makes it possible to understand, protect, monitor, and improve the world. The basic concepts of Chemistry help measure and observe water, air, and soil pollution. In contemporary society, environmental issues like renewable energy, biodiversity, contamination, and conservation have been hot topics (Kumar, 2021). As a result, new technological advances have been made in scientific research to counter the shortcomings by inventing environmentally friendly objects and industrial applications.
Green chemistry is the term used to describe the positive contributions of these subjects to environmental protection (Kumar, 2021). Sustainable chemistry deals with the chemical products and processes that reduce the production or use of harmful substances to humans, animals, and the environment. Toxic waste is hazardous to current and future generations as it affects the means of livelihood. In producing chemicals, most products are petroleum-based, which is severe since they are not renewable (Kumar, 2021). Through practical Chemistry applications, scientists have derived better alternatives to protect the environment from pollution.
Bioplastics Production
Sustainability is crucial in attaining long-lasting changes that result in the long-term productivity of the Earth. Bioplastics are from renewable biomass sources like recycled food waste, woodchips, corn starch, vegetable oils, and fats (Kumar, 2021). These materials can be manufactured from recycled plastics and agricultural by-products. They are commonly made from sugar merchandise, including lactic acid, starch, and cellulose (Kumar, 2021).
Bioplastics are biodegradable or biobased as they contain either one or both properties. Kumar (2021) says that biodegradability is a chemical process that facilitates breaking down materials into natural substances like compost, water, and carbon dioxide without affecting the planet. The process is made possible by environmental microorganisms and is influenced by surrounding conditions such as oxygen, water, and temperature (Kumar, 2021).
Bioplastics provide energy savings in manufacturing and also limit the carbon footprint. Through their fabrication, non-biodegradable wastes that pollute the Earth are reduced. They contain zero additives like polybrominated diphenyl ethers, phthalates, or bisphenol, which are dangerous to plant and animal health (Kumar, 2021). Apart from biodegrading, chemical recycling also facilitates the protection of the world.
Chemical Recycling
The amount of plastic waste around the world has been increasing tremendously. Despite being sent to landfills and incinerated, the number is still high and results in environmental pollution through the emission of CO2. The chemical industry is changing this through modern technologies that promote mechanical recycling.
This new engineering can break down plastics into impactful secondary materials that are later used to manufacture new plastics and chemicals of high quality, similar to those made from fossil fuels (Mensink, 2020). The chemical firm has successfully implemented this by developing consumer merchandise like dashboards, mattresses, food packaging, and carpets (Mensink, 2020). Using this process reduces the overdependence on carbon products, which affects the globe through pollution.
Feedstock recycling helps fight ocean contamination and lowers carbon footprints. It involves depolymerization, gasification, solvolysis, and pyrolysis (Mensink, 2020). The potential benefits of implementing sustainable chemistry approaches include reduced usage of resources, waste production, and limited chemical gas emissions. In cases where greenhouse gases are produced, the quantity is so tiny compared to the original form of production. Chemistry is also applied to derive solutions geared toward preventing air contamination.
Tackling Air Pollution
Chemistry plays a big part in establishing technological solutions to environmental pollution. Tackling air contamination requires approaches like consumer behavior, scientific fixup, engine design, and regulation (Mensink, 2020). Besides increasing the motors’ ability, chemists develop cleaner fuels that decrease harmful gas emissions in the environment. Chemists are also advancing new transport technologies like batteries for electric cars, which limit the amount of contamination produced by vehicles using fossil fuels (EPA, 2023; Kumar, 2021).
Chemistry has also allowed new energy sources to be developed, and the over-reliance on fossils has been prevented. Renewable energy sources include the sun, wind, hydro, and bioenergy, which can generate the electricity needed to run machines at home and in industries (Kumar, 2021; Mensink, 2020). Solar energy is now available in areas experiencing a high amount of sunlight thanks to the scientific invention of solar panels.
Another strategy scientists use to limit impurities from vehicles is the attachment of pollution control devices to exhaust pipes. Today, chemistry improves and develops absorbers, particulate filters, and catalysts that control toxin discharge (Mensink, 2020). The presence of chemistry has resulted in the emergence of problems and solutions.
Conclusion
The application of knowledge from chemistry is made possible by doctors, chemists, engineers, and scientists who use it for various purposes. In healthcare, it is used to determine the safe meals with the nutrients needed for consumption. It is also used to preserve food through the development of safeguarding chemicals and strategies like refrigeration. Farm inputs used in the planting of agricultural products are made from chemical components. In medicine, drugs and other equipment used in surgical procedures are developed.
Chemistry further contributes to global warming by emitting poisonous gases into the environment. Greenhouse gases affect plants, soil, and water sources, thus inhibiting all living animals, including humans. Their production result in the death of plants and other possible food sources through their acidic properties, especially when they fuse with rainwater.
Chemistry has played the most prominent part in environmental protection. It equips scientists, chemists, and engineers with the needed skills to produce systems and strategies that limit the destruction of the environment through impurity production. The most effective ways include bioplastic production, chemical recycling, and air purification methods like embracing renewable energy.
References
Bell-Young, L. (2021). Chemical methods of food preservation. ReAgent. Web.
Bonam, S. R., Sekar, M., Guntuku, G. S., Nerella, S. G., Pawar A, K. M., Challa, S. R., Eswara, G. K., & Mettu, S. (2021). Role of pharmaceutical sciences in future drug discovery. Future Drug Discovery, 3(3), 1–15. Web.
EPA. (2023). Global greenhouse gas emissions data. United States Environmental Protection Agency; US EPA. Web.
Karges, J. (2022). Combination of chemistry and material science to overcome health problems. Biosafety and Health, 4(2), 64–65. Web.
Kumar, S. (2021). Role of chemistry in environment: A review. International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, 8(2), 331–337. Web.
McClements, D. J., & Grossmann, L. (2021). A brief review of the science behind the design of healthy and sustainable plant-based foods. Nature Partner Journals, 5(1), 1–18. Web.
Mensink, M. (2020). Chemical recycling: Greenhouse gas emission reduction potential of an emerging waste management route. The European Chemical Industry Council (Cefic). Web.
Mukherjee, S. (2023). Acid rain: Definition, causes, effects, and solutions. Science Facts. Web.
Prakash, J., Agrawal, S. B., & Agrawal, M. (2022). Global trends of acidity in rainfall and its impact on plants and soil. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 23(1), 398–419. Web.
Science Museum. (2019). Food: A chemical history. Science Museum. Web.
Zhang, L., Yan, C., Guo, Q., Zhang, J., & Ruiz-Menjivar, J. (2018). The impact of agricultural chemical inputs on environment: Global evidence from informetrics analysis and visualization. International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies, 13(4), 338–351. Web.