Developing Economies are a major characteristic of majority of the Less Developed Countries which comprise of the so called third world countries. These countries are plagued by common macroeconomic problems like inflation, un-employment, high population growth rates and poor infrastructures among others. This set of problems commensurate to form bedrock called trading problems which come up due to the following reasons.
Due to the high income disparities between the poor and the rich in this Economies, majority in the populace have low real per capita income available for consumption, saving and for investing in trade. (Mahajan, 2007) Because of this, many would be entrepreneurs are unable to venture in business activities and if they do, they engage in illicit Economic activities like drug trafficking. The income disparities can be minimized through the institution of a minimum wage that would ensure that incomes are evenly spread and that everybody earns a per capita income sufficient to meet market demands. Alternatively the government should institute fiscal and monetary policies to narrow income disparities in the country. Fiscal policies would involve increasing government expenditure in community projects and involving the local people in the work. This would ensure the ploughing back of incomes back in the Economy and in totality increasing the disposable income of the people. Coupled with reduction of taxes, the consumers would have enough to consume and to invest in Business. Monetary policies, on the other hand, would require the government to encourage the public to invest in the capital markets and by such investments, trading activities will be enhanced.
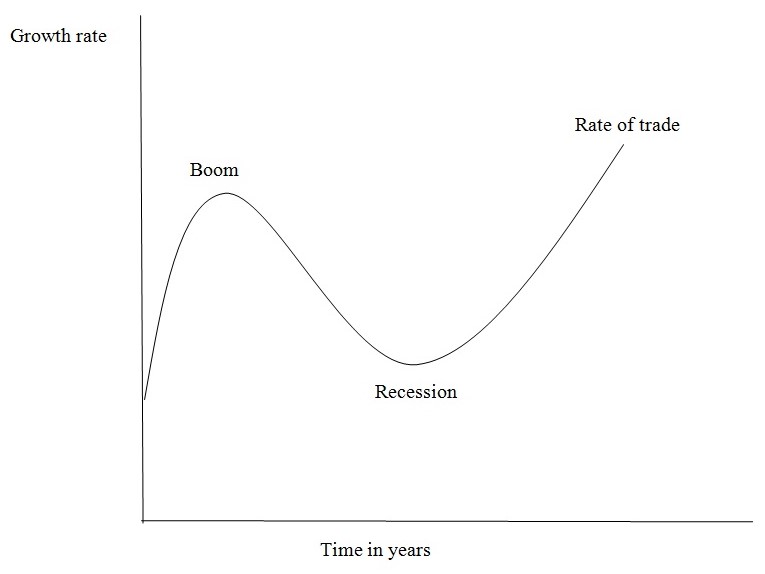
A clear look at the business/trade cycle will reveal that trading, whether in Developing or Less Developed Countries undergoes different Economic cycles at different times hence instituting proper Economic principles can help an Economy move upwards.
The Business / Trade Cycle
In appropriate Education systems in the developing nations have also hindered trading in these Economies. The systems of Education in these countries are irrelevant in that they provide theoretical abstractions which do not match the current markets demands. As such its graduates and the elites offer irrelevant manpower which is a set back to trade and development. The solution to this would be to orientate such Educational systems to meet the current Economic demands so as to enhance increased bilateral and multilateral. Trading activities.
As noted by Mahajan (2007) inadequate provision of Health facilities in such Economies have also affected trading negatively. This is because of the fact that Life expectancy is very low and as such the young and productive workforce is tremendously lost to death. This deprives the Country of manpower which is potentially able to engage in worthwhile trading activities. To curb such losses the government can introduce Economic policies of subsiding health services or offering free health insurance to all its workers.
Colonialism and Neo-colonialism are factors that have also hindered the growth and development of trade in the developing Economies. Such countries rely mainly on their colonial masters directly or indirectly for Economic guidance. They depend on the Economic activities that were introduced to them by their colonial masters and they must continue with them because of certain conditions given to them like stoppage of foreign Aid and donations. Such vices can only be removed through total overhaul of such inherited Economic activities and the encouragement of local and foreign investors in order to promote trade.
Mahajan (2007) observes that un-employment and inflation are other major related factors which have hindered trading activities in such Economies. While un-employment deprives the people of enough incomes to invest in trade, inflation ensures that prices of goods and services are rapidly skyrocketing making the people to work hand to mouth only as they fight to raise more incomes to meet the increasing costs of living. The J curve phenomenon illustrates this unique relationship between un-employment and inflation
The J-Curve Phenomenon
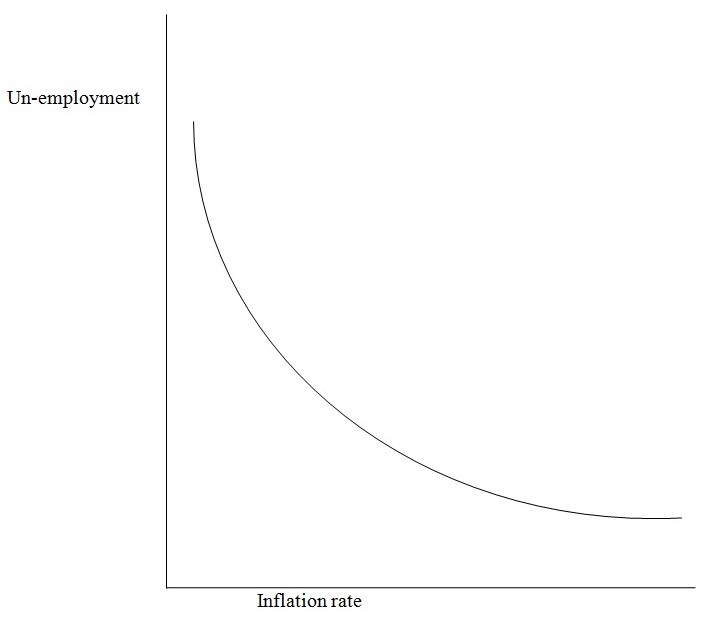
It can be clearly seen that inflation and un-employment are inversely related: as inflation rates increases at an increasing rate, the un-employment rate increases at a decreasing rate and vice versa. To contain these twin problems, both monetary and fiscal policies (discussed above) should be instituted as they will ensure creation of more employment opportunities hence availing more disposable income for investing in Business.
It is worth noting that developing Economies are also plagued by low levels of productivity due low natural resource endowment. On the other hand, the natural resources are depleted while man made resources are very scare due to lack of technical expertise. In other cases there is the prevalence of un-skilled labor to exploit the available resources if any. Because of this, trading in such countries declines drastically with the effect that the Economy plunges in to recession. With low Economic productivity comes low balance of payments where imports exceed exports. To solve such a crisis the Development of local industries should encouraged and protected so as to improve domestic productivity and consequent involvement in trade.
A major characteristic of Developing Economies is the use of inappropriate and outdated technologies in trading and production. Such technologies are inefficient and unreliable especially in the modern age of market liberalization and E-Commerce.Information, Communication and computer technology is lacking in these countries making trading very disadvantaged. The way out for this would be only to institute Economic policies that are flexible enough to accommodate the use of current and emerging technologies especially in E-Commerce. Such will ensure increased levels of trading in the global village resulting to high foreign exchange earnings. (Mahajan, 2007).
High ratios of dependency in the population are also a cause of alarm in the developing Economies. The working minority are in stress to provide for their dependents from their meager earnings. As such, the working population uses all her incomes to cater for the needs of their dependents leaving investing in trade at stake. The institution and educating the people of family planning methods would go along way in reducing such high dependency ratios and people would have enough disposable incomes to invest in trade.
Kaushik (2003) asserts that rural-urban migration is another menace that has plagued Developing Economies. People especially the young elites move en mass in to the urban centers to look for white collar jobs which are not available in the cities. This leads to overcrowding in towns and urban centers leading to formation of informal dwellings called slums and shanties which characterize life in most urban centers in the Least Developed Nations. Due to frustrations, these people start to practice social evils and crime which negatively affect trade. To combat this, the government should develop Economic policies of decentralizing job opportunities to the rural areas so that the movement is checked. Such a move will ensure balanced infrastructural development which is a recipe to trade.
Market imperfections are a major drawback to effective trade development in the developing Economies. They are poorly developed and sometimes the financial markets are not there at all. People therefore do not invest in the capital markets hence trading declines. Where such markets are existing, they are poorly developed causing investors to loose their investments to unscrupulous management who embezzle the investor’s funds. Corruption and inefficiency in the underdeveloped markets also causes fear to invest to the populace. This affects trade negatively. The institution of private market regulators would be an important Economic policy to streamline market development in such Economies. (Chand, 2002).
In addition Chand (2002) observes that overdependence on Agriculture as the mainstay in the developing Economies is also a threat to the development of trade in the Developing Economies. Majority of them depend on Agriculture which is very un-reliable due to unpredictable weather conditions. These countries are mostly plagued by adverse weather conditions which adversely affect farming activities. These leads to dependency an donors and foreign Aid and imports which absorb all the foreign exchange leaving nothing to plough back in the local industries. Such a problem is solvable through engaging in different Economic activities to minimize risks associated with the failure of one Economic activity.
Inadequate infrastructural development in the Less Developed countries is a major cause of reduced trading activities. The socio-economic infrastructures are either absent or poorly developed and as such hinder economic development in such Economies. Physical infrastructures like roads and and telecommunication networks are also poor, insufficient and inefficient in most of these nations. When such infrastructural overheads are poor Economic growth and development is greatly hampered since trading does not occur in a vacuum – there must be infrastructural mechanisms. The governments of such nations should invest heavily in the development if infrastructures that promote Business and trade. The privatization of such projects can also go along way in enhancing the appropriate infrastructures.
Kaushik (2003) points out that over reliance on foreign debts and Aids is also a crisis plaguing the growth and development of trade in the developing countries. The belief that such Economies cannot be reliant and self sufficient has seen them beg for foreign aid which comes with strings attached among other conditions detrimental to the growth of trade in such Economies. The less developed nations therefore should strive to be self reliant through planning budgets which are within the limits of their available resources. Cutting off on foreign reliance would also boost the development of local industries which would go along way in increasing trading activities.
Another major characteristic of the under developed Economies is the small and the underdeveloped industrial sector which is unable to absorb the poorly educated elites. The capacities of such industrial sectors are very minimal both to expand and to absorb more workforces. This is complemented by the lack of capital both human and financial capital to develop and establish the industrial sectors. The remedy for these would to institute industrialization policies to enhance the growth of both the local and the foreign industries. The government can give such investors incentives like tax holidays, subsidized raw materials to encourage their establishment and development. (Kaushik, 2003)
In conclusion, the use of Economic tools of analysis to solve the macro-economic problems plaguing these Economies will go along way to enhancing the development and growth of trade in these countries.
References
Anne O. Krueger (1993). Economic Policies at Cross-purposes, Newcastle, Brookings Institution Press.
Chand, K. (2002).Economic Policies, Bombay, Anmol Publications PVT. LTD.
Kaushik, B. (2003). Analytical Development Economics: The Less Developed Economy Revisited, New York, MIT press.
Mahajan, S. (2007). The Current International Economic Problems, New York, Prentice Hall.
Developed countries protection from problem counter trade, 2008. Web.
Developing countries shaping future of world agriculture trade, 2008. Web.
Start of a process to manage globalization, 2008. Web.