Introduction
The purpose of this study will be to analyze the structure and governance of a national or international union that addresses the plight of workers.
The union that will be focused on in this study will be the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) which is a labor union representing the needs of workers employed in the electrical industry in the United States, Panama and Canada as well as other workers employed in the public utility and electrical manufacturing industry.
The union also represents the interests of workers employed in computer, broadcasting and telecommunications sector. The main objective of the IBEW is to promote reasonable working conditions for all electrical workers under the union and also cultivate feelings of brotherhood/friendship among the various employees that fall under the union (Hill, 2008).
History of the Union
The beginning of IBEW can be traced back to the Electrical Wiremen and Linemen’s Union which was founded in 1890 in St. Louis, Missouri. Both wiremen and linemen flocked to St. Louis to demonstrate their trade by wiring the buildings in the city with electricity lines so as to exhibit their trade.
During the exhibition, the workers got together to talk about their jobs and also the working conditions of electricians in the electrical industry. There was a general consensus that their jobs were hard and they worked for long hours with little pay (12 hours a day for 15 to 20 cents per hour).
The workers did not receive any training or apprenticeship during the first week of their jobs and the safety standards especially for the wiremen were nonexistent which meant that they were exposed to dangerous working conditions. These poor working conditions led to the industry having the highest mortality rates of one out of two hired employees in the whole of America. The Convention and the growing electrical industry were basically the starting points of the Brotherhood (IBEW, 2005).
The following year, 1891, saw a growing interest to have a national union that would address the plight of electrical workers in the US. The Convention that took place in St. Louis approached the American Federation of Labor (AFL) to receive a charter that would operationalise the Electrical Wiremen and Linemen’s Union.
The Electrical Wiremen and Linemen’s Union under the charter No. 5221 was established in 1981 as a national organization that would address the labor needs of electrical workers within the electrical industry as well as other workers in the telecommunications, telegraph and electrical manufacturing industry. During their first year of operation, the union organized a convention in St. Louis where ten delegates representing the 286 members of the electrical industry attended the convention (IBEW, 2005).
The ten representatives included Henry Miller, the president of the union, J.T. Kelly, W. Hedden, C.J. Sutter, H. Fisher, F. Heizleman, J. Berlowitz, T.J. Finnell, M. Dorsey and E. Hartung.
These ten delegates formed the founders of the union and they adopted a different name for the organization known as the National Brotherhood of Electrical Workers. They worked for hours drafting a constitution for the union which would stipulate the laws and procedures that would guide the operations of the union.
They also came up with the well-known emblem of the union, a fist grasping several lightning bolts, which would be used to distinguish the organization from other unions in the US. During the Convention, the delegates elected Henry Miller as the first Grand President of the union and they also elected T. Kelly as the Grand Secretary Treasurer of the union. In the 1899 Pittsburgh Convention, the union decided to change its name to the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers.
The membership during that time had reached 2,000 members with over 43 chartered local unions in the whole of America. The current number of members now stands at 750,000 in the four countries covered by the union (Panama, Canada, US and some parts of the Caribbean’s) (IBEW, 2005).
The type of employers the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers bargains with includes the electrical manufacturing industries, public utility companies that offer electricity to consumers, electrical installation companies, wiremen and linemen contracting agencies.
The union faced adversity during its first year of operation as it received a lot of criticism and indignation from employers working in the mentioned companies. Many of these employers were trying to drive out trade unions in the country by organizing open shop campaigns in the national level. The union however sought to reduce tensions between employers and employees in the electrical industry by forming the Council on Industrial Relations which would be used to represent the interests of managers and employees (IBEW, 2005).
Hierarchical Structure of the Organization
The IBEW is made up of three functional bodies which make up the structure of the union and these include the executive body which is made of the International President, the International Secretary-Treasurer, International representatives and the eleven International Vice-Presidents that manage the district level operations of the union. Other offices that fall under the executive body include the local union offices as well as the membership of IBEW.
The judicial and legislative bodies of the union are made up of the International Executive Council which is made up of a chairman and eight elected members working in the district offices. The International President is charged with the general administration of the IBEW and the responsibilities that come with the international office are varied and distinct (IBEW, 2005).
Some duties of the International President include implementing the laws of the Brotherhood, overseeing any controversial issues that might arise within the organization, acting on any appeals that might arise from decisions made by the International Vice Presidents, deciding on IBEW policies and procedures, chartering and amalgamating various unions that have been established in the local level and suspending or revoking any local union charters that do not serve the interests of IBEW’s members.
The International Secretary-Treasurer is primarily charged with the role of handling the financial matters of the IBEW International office such as investments and pension funds.
The responsibilities of the treasurer include collecting, disbursing and accounting for all union funds, maintaining records of the organization’s membership and receiving all signed applications for the local union charter. The treasurer is also charged with protecting the seal and emblem of the Brotherhood (IBEW, 2005).
The eleven International vice presidents that make up the district office and have been elected by the local unions work under the instructions of the International President of IBEW. The duties of the vice president include supervising the activities of all International Representatives within the district branch offices and also act on appeals that might come from members of the local unions.
The internal bodies that exist in the local unions include presidents who are charged with enforcing the constitutional provisions of the union, vice presidents who are charged with assisting the local president with office duties, recording secretary who is charged with the role of keeping the minutes of local union meetings as well as maintaining all meeting records, the financial secretary who is charged with handling all the funds collected by the local union (IBEW Constitution, 2008).
Another member of the local union is the treasurer who receives all collected funds from the financial secretary and deposits them in the bank under the name of the local union and the business manager who is charged with the role of representing the local union in any trade disputes with industry employers.
The business manager appoints all stewards within the local unions to effect bylaws that will be needed to effectively manage the functions of the local union.
The business manager also conducts training programs for all stewards as well as enforcing all collective bargaining agreements. The International Executive Council (IEC) and the legislative body are charged with managing the judicial and legislative aspects of the union. The IEC is the final authority that is used when granting pensions, disability benefits and also handling the vested interests of the union’s members.
The two bodies also act on appeals that are made by the International President and they try members of the local union who have been charged with violating the laws and rules of the IBEW (IBEW Constitution, 2008). The diagram below represents the hierarchical structure of the IBEW and the various offices/bodies that make up the organization.
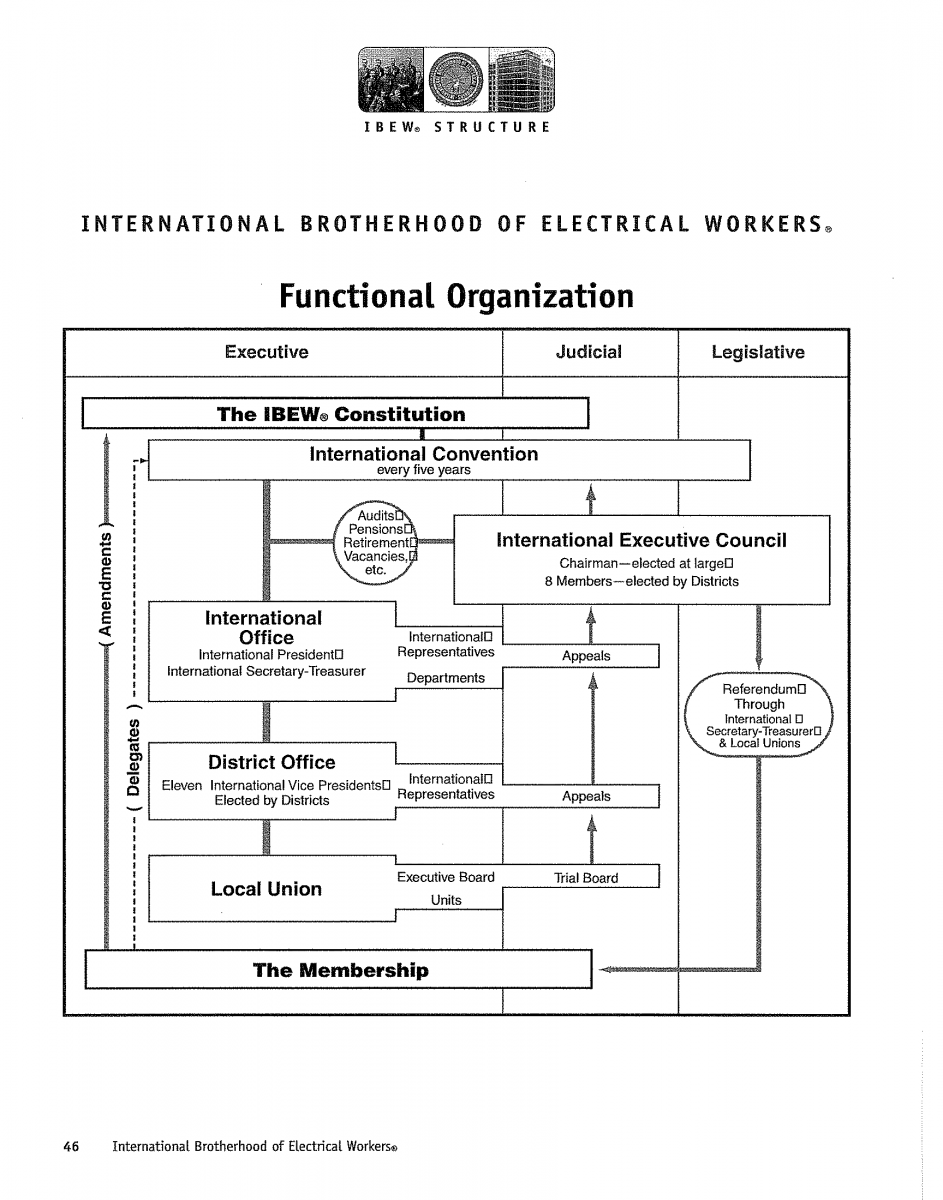
Source: IBEW, 2005
Financial Flow of the Union
The financial flow of the union is mostly made of funds collected from union dues, pension benefit funds and the general funds that are used to manage the day-to-day operations of the union. Members of the organization are meant to contribute $10 every month so as to manage the collective bargaining activities of the organization.
The amount of pension funds that are collected from individuals within the union amounts to $3.50 per month for each full year of continuous membership that the member has with the union. The fund also pays death benefit to any of the member’s beneficiaries which could be $6,250 if the member dies of natural causes and $12,500 for any accidental deaths (IBEW Union, 2011).
Union dues refer to the financial funds that are usually paid by the members of a union every month to support the general operations of the organization and its officers. The union dues structure of the IBEW covers two parts of the union’s structure which include the international and local union offices.
The dues that are allocated to the international office are basically used to maintain and support the administrative and legal functions of the office as well as legislative procedures such as court appeals and trials which have been forwarded to the IEC.
The bulk of union dues are usually allocated to the local union where the funds are used to manage the expenses of the offices as well as handle collective bargaining, member grievances, arbitrations and contract negotiations with employers. A basic union dues structure is made up of two parts: the local union and the IBEW per capital segment where the local union determines its dues by the operational costs and expenses incurred by every local union within the various districts of the US (IBEW Union, 2011).
Union dues are usually determined by the members of the local union as they are the only people who have the power and ability to change the amount of dues they have to pay ever month. The IBEW Per Capita structure of the union dues involves a monthly payment of $11set by the International Convention and which is meant to be paid by all members of the union.
The monthly charge is usually used by the local union to fund the operations of the First District Office and it can only be changed by the elected delegates of the Convention. The diagram below represents the structure of and distribution of union dues in the organization (IBEW Union, 2011).
Governing Entities within the organization
The International Convention is the highest governing body of the Brotherhood. The union Constitution postulates that the IBEW member delegates meet every five years at a regular interval to discuss union matters and any labor issues that might arise in the electrical industry during the five-year duration. The international Convention therefore oversees these meetings during which it elects International Officers such as the president and secretary treasurer if there is need for reappointment or re-election.
The International Convention also determines the basic law that will be used by the IBEW through the number of votes that have been cast for proposed resolutions and constitutional amendments to the union Constitution. The international Convention also has the final authority and decision on any appeals that have been made in the international, national and local offices of the union. The various entities that make up the Convention include delegates and member committees (IBEW, 2005).
The delegates of the Convention are usually selected through secret ballots garnered from the members of the union. The level of delegate representation is usually based on the number of members a local union has registered where the maximum number of delegates per local union is 15. The Convention further stipulates that no local union is entitled to representation unless it has been of good standing for the last six months before the International Convention.
The committees in the Convention are usually formed by the International President who is authorized by the governing body to establish committees that will perform the basic functions of the Convention such as resolution action, the development of reports and recommendations that will be used to deal with disputes or conflicts between employers and employees.
Another governing entity that oversees the functions of the IBEW is the International Executive Council (IEC) which deals with the judicial or financial aspects of the union. The IEC is the final authority when it comes to making decisions on granting pensions, disability benefits and also dealing with the vested interests of the union’s members (IBEW, 2005).
The types of boards exist under the local union and these include the examining board and the executive board. The purpose of the examining board in the local union is to examine and review the various applications for membership forwarded to the union for consideration.
The examining board assesses the qualifications of various applicants according to the various sections of the union Constitution to determine if they qualify to be members of IBEW. The executive board on the other hand is involved in hearing all charges that are brought against the members of the union and trying them according to the bylaws and working rules of the local union (IBEW Constitution, 2008).
The executive board therefore acts as a trial board as it has to consider all matters properly before making any major decisions with regards to any charges or violations brought against a member of the organization. Apart from the IEC, other councils that exist in the IBEW include the railroad councils and system councils which address any union issue within the local union railroad industry.
Railroad councils are subject to the rules that govern local councils while the system councils are formed by the International President for collective bargaining purposes under the direction of the president. If the local union is unable to establish a railroad council, they can be able to form a system council to address any disagreements that arise (IBEW, 2005).
Appointment of Union Members
According to the union Constitution, the various officers of the IBEW are usually nominated and elected by delegates who have been duly selected in the International Convention.
The circumstances under which International Officers are chosen for the post of International President and International Secretary-Treasurer in the IBEW is when either of the two officers dies before completing their term, their term contract has expired, they are found to be in violation of the union Constitution or they have committed an offense that is deemed punishable by the International Convention (IBEW Constitution, 2008).
The only requirement for a person to be elected to any of the positions is that they should have a five-year standing relationship with the union. This basically means that union members who have not had any violations or charges placed against them can be able to apply for the post of International President or International Secretary-Treasurer.
The two International Officers are usually elected by secret ballot or per capita tax votes when there is more than one candidate for the position. Once they are selected, they are expected to assume office in 30 days and they can serve for a term of five years until their successors are nominated and elected (IBEW Constitution, 2008).
Other positions that are elected in the IBEW include the eleven positions for vice presidents which are usually elected by the respective vice presidential districts and the delegates that fall under the International Convention who are usually elected through a secret ballot election.
The positions that are appointed within the IBEW include the Resolutions Committee which is appointed by the International President to document any resolutions to trade disputes that have occurred between employers and employees of the trade union. The positions and offices within the Railroad Councils and the System Councils are also appointed by the International President in the IBEW where the IP follows the bylaws of the Constitution when selecting the various members of these councils (IBEW Constitution, 2008).
Culture of the Union
The culture that exists in IBEW is that of reform and business unionism where the union is interested in offering its members fair housing and better working conditions as well as attaining a 5% wage increase for all its members under IBEW.
The history of IBEW has been one of business unionism and reform where the various officer holders have tried to negotiate for better working and living conditions for the various members under the union. As a result of reformist cultures within IBEW, the wages and working conditions of the union’s members have improved considerably when compared to other industries in the country.
Because of the culture of reform and socialist unionism, members of IBEW have been able to enjoy better health care and welfare services as well as improved pension benefits, longer holiday vacations and shorter workdays. These reforms have been able to take place because of the cultivation of intelligent people to manage the affairs of the union (IBEW, 2005).
The culture of reform has been instilled in the various office holders to necessitate changes for employees working within the electrical industry so that they can enjoy proper working conditions as well as long-term benefits. The heritage of IBEW is vibrant and strong as the various beliefs and value systems practiced by all previous office holders have been passed down the line of successors.
The use of local leadership has also enhanced the culture of reform within the union where talented and tenacious leaders have been selected to represent the union in various forums. Proper leadership has ensured that a culture of social reform is established in the union where the individual needs of members and their beneficiaries/families are addressed to maintain a high standard (IBEW, 2005).
The mission and priorities of IBEW include organizing all workers in the US or Canadian electrical industry and other member countries as well as organize workers in the public utility and electrical manufacturing industry. IBEW is also charged with promoting reasonable work conditions for its members as well as reasonable salaries and wages.
Another mission of IBEW is to settle any disputes that might occur between the employers and employees of the organization and also assist each of the members and their families through periods of distress, death and sickness or material loss. The main priority of IBEW is to reduce the number of hours daily laborers such as the wiremen and linesmen work as well as seek higher compensation, improved standards of living and working for its members (Hill, 2008).
Union Mergers
In 1908 when the union was experiencing a period of success and stability, an internal struggle emerged within the organization that saw the secession of a large percentage of the Brotherhood. This split was mostly caused by a growing dissension amongst the wiremen and linemen of the poor management of the union’s high-ranking offices.
At the same time, employers within the electrical industry were bent on destroying the Brotherhood so they fostered the internal struggles that were taking place within the union at that time. The secession that took place IBEW was referred to as the Reid-Murphy split after the two officers who were elected by the seceding factions of the split (IBEW, 2005).
While the Reid-Murphy group split from the Brotherhood, Frank J. McNulty and Peter W. Collins remained the recognized office holders of the Brotherhood.
The result of the secession saw two trade unions being formed to address the concerns of employees in the electrical industry with the Reid-Murphy faction having the majority of members. The structure of the Brotherhood was not affect in a major way as McNulty and Collins were able to remain as the official office holders of the union but their functions were somehow impeded because of the separation of funds and resources between the two factions.
These split was however reversed by a court decision in 1912 that saw the 1908 Convention null and void. Union funds that had been taken by both factions were restored to the recognized group under the union Constitution by the court. The seceding group later merged with the Brotherhood in 1914 after they agreed to end their differences and focus on serving the needs of IBEW members (IBEW, 2005).
Union Affiliations
In 1982, the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers become affiliated with the Canadian Federation of Labor to enhance its activities of safeguarding the welfare of wiremen and linemen in Canada while in 1989, IBEW entered into an affiliation with the committee on political education (COPE). This was meant to improve the involvement of organized labor in the active education and registration of voters during the union election process.
Another affiliation that the IBEW had was with the Canadian Labor Congress in 1997 which has been identified as a re-affiliation in the historical records of the Brotherhood. The unions and associations that have allied themselves with IBEW include the Electrical Workers’ Benefit Association, the Canadian Signal and Communications Union and the Pension Investment and Employee Benefits Department (IBEW, 2005).
Conclusion
The sole purpose of this study has been to analyze the structure and governance of IBEW, a union that deals with the labor issues of employees working in the electrical industry. The discussion has focused on the structure of the union by looking at the various positions and office holders that make up the union as well as examining the various roles and responsibilities that these members play in the union.
The study has also focused on the various governing bodies that govern the operations of IBEW which include the International Convention and the International Executive Council. The study in general has been an analytical analysis of the various faucets and bodies that make up the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers.
Questions
Qn.1: Sections 1 up to 21 of Article XX of the AFL-CIO Constitution sets forth the various provisions that will guide the relationships of affiliates within the Federation and how each of the affiliates should relate with other affiliate members within AFL-CIO.
For example Section two of the article sets forth that every affiliate member of the organization shall observe the established collective bargaining relationships that exist amongst the affiliate members of the organization which means that no member affiliate will attempt to represent employees who have an established collective bargaining relationship with another affiliate in the federation.
Article XX is important for unions such as IBEW as it provides an established work relationship amongst the various unions that fall under AFL-CIO. The article provides a basic framework of how unions representing the interest of employees in one industry should conduct themselves to avoid any union disputes.
Article XXI of the AFL-CIO Constitution talks about the organizing of responsibility procedures where the various member affiliates of the federation resolve to organize competition in situations where competition might be detrimental in serving the best interests of workers. This article is important for unions that want to represent the interests of workers from one industry.
Section 2 of the article stipulates that any affiliate members of the federation that is actively engaged in representing and organizing employees from a particular industry can be able to seek for authority to enable them be the exclusive representative of these employees within that industry. Article XXI is therefore meant to limit the amount of competition amongst unions willing to represent the interests of workers within one industry (AFL-CIO, 2011).
Qn. 2: One constituent group of the AFL-CIO is the coalition of black trade unionists (CBTU) which serves the needs of African American workers in the United States. While CBTU is not a civil rights organization, it provides the black workers in the US with a forum within the union movement to voice their concerns about organized labour in the country. The mission of CBTU is to meet the working needs of African Americans within the US by presenting their concerns to the union movement, AFL-CIO.
The main activities of the organization include; improving the economic development of black workers by providing suitable employment opportunities, working together with the trade union movement so as to provide a voice for black workers in America, increase the union involvement of black workers by increasing awareness through voter education and voter registration, actively supporting civil rights groups that are trying to improve the working conditions of black people within the country and organizing black or minority group workers who are unorganized (CBTU, 2011).
CBTU provides value to its members as it seeks to support programs and initiatives aimed at reducing the level of unemployment amongst black Americans in the United States. The organization collaborates with school systems to ensure that black students are equipped with the necessary skills that will allow them to gain useful employment once they complete their education.
CBTU also adds value to its members by looking for ways to deal with the escalating prices in food, housing and medical services. It has established important alliances with various organizations within the American community to ensure that the financial burden is reduced (CBTU, 2011).
Qn.3: One campaign under the Change to Win affiliate program is the Warehouse Workers United campaign where the Warehouse Workers United is an organization that seeks to represent the interests of warehouse workers in California’s Inland Empire. The main purpose of the organization is to join all warehouse workers together so as to improve their working conditions and also build a better future for the workers and their families.
The Change to Win campaign for the Warehouse Workers United is focused on improving the terms of pay as well as working conditions for all warehouse workers in the Inland Empire. The Change to Win campaign for these workers is meant to build an effective response to the poor assault on worker rights by forming a stronger labour movement that will provide hope to many minimum wage workers.
Change to Win has the ability to affect a response from the various unions in America as it has the voice and the support of stronger affiliate federations such as AFL-CIO in addressing the concerns of workers such as the Warehouse Workers United (Warehouse Workers United, 2011).
References
AFL-CIO (2011). AFL-CIO Constitution; article XX and XXI. Web.
CBTU (2011). About CBTU: mission statement. Web.
Hill, E.D. (2008). Constructing Bright futures. IBEW Journal, 107(2): 1- 52.
IBEW (2005). International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers: History and Structure. Web.
IBEW Constitution (2008). IBEW Constitution as amended SEP. 2006 at Cleveland, Ohio. Web.
IBEW Union (2011). IBEW union dues structure. Web.
Warehouse Workers United (2011). Why we fight. Web.