Hypothesis Maker Online
Looking for a hypothesis maker? This online tool for students will help you formulate a beautiful hypothesis quickly, efficiently, and for free.
Are you looking for an effective hypothesis maker online? Worry no more; try our online tool for students and formulate your hypothesis within no time.
📄 Hypothesis Maker: How to Use It?
Our hypothesis maker is a simple and efficient tool you can access online for free.
If you want to create a research hypothesis quickly, you should fill out the research details in the given fields on the hypothesis generator.
Below are the fields you should complete to generate your hypothesis:
- Who or what is your research based on? For instance, the subject can be research group 1.
- What does the subject (research group 1) do?
- What does the subject affect? - This shows the predicted outcome, which is the object.
- Who or what will be compared with research group 1? (research group 2).
Once you fill the in the fields, you can click the ‘Make a hypothesis’ tab and get your results.
⚗️ What Is a Hypothesis in the Scientific Method?
A hypothesis is a statement describing an expectation or prediction of your research through observation.
It is similar to academic speculation and reasoning that discloses the outcome of your scientific test. An effective hypothesis, therefore, should be crafted carefully and with precision.
A good hypothesis should have dependent and independent variables. These variables are the elements you will test in your research method – it can be a concept, an event, or an object as long as it is observable.
You can observe the dependent variables while the independent variables keep changing during the experiment.
In a nutshell, a hypothesis directs and organizes the research methods you will use, forming a large section of research paper writing.
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A hypothesis is a realistic expectation that researchers make before any investigation. It is formulated and tested to prove whether the statement is true. A theory, on the other hand, is a factual principle supported by evidence. Thus, a theory is more fact-backed compared to a hypothesis.
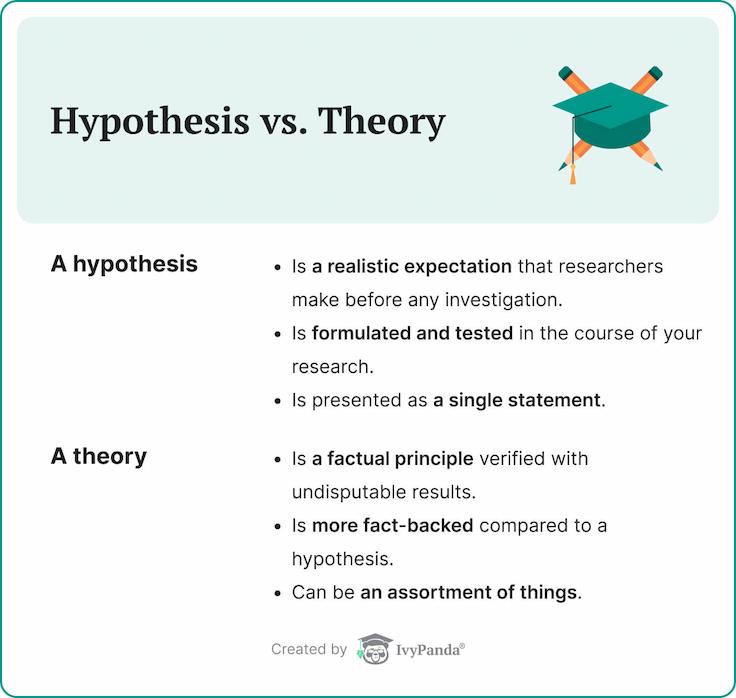
Another difference is that a hypothesis is presented as a single statement, while a theory can be an assortment of things. Hypotheses are based on future possibilities toward a specific projection, but the results are uncertain. Theories are verified with undisputable results because of proper substantiation.
When it comes to data, a hypothesis relies on limited information, while a theory is established on an extensive data set tested on various conditions.
You should observe the stated assumption to prove its accuracy.
Since hypotheses have observable variables, their outcome is usually based on a specific occurrence. Conversely, theories are grounded on a general principle involving multiple experiments and research tests.
This general principle can apply to many specific cases.
The primary purpose of formulating a hypothesis is to present a tentative prediction for researchers to explore further through tests and observations. Theories, in their turn, aim to explain plausible occurrences in the form of a scientific study.
👍 What Does a Good Hypothesis Mean?
It would help to rely on several criteria to establish a good hypothesis. Below are the parameters you should use to analyze the quality of your hypothesis.

🧭 6 Steps to Making a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis becomes way simpler if you follow a tried-and-tested algorithm. Let’s explore how you can formulate a good hypothesis in a few steps:
Step #1: Ask Questions
The first step in hypothesis creation is asking real questions about the surrounding reality.
Why do things happen as they do? What are the causes of some occurrences?
Your curiosity will trigger great questions that you can use to formulate a stellar hypothesis. So, ensure you pick a research topic of interest to scrutinize the world’s phenomena, processes, and events.
Step #2: Do Initial Research
Carry out preliminary research and gather essential background information about your topic of choice.
The extent of the information you collect will depend on what you want to prove.
Your initial research can be complete with a few academic books or a simple Internet search for quick answers with relevant statistics.
Still, keep in mind that in this phase, it is too early to prove or disapprove of your hypothesis.
Step #3: Identify Your Variables
Now that you have a basic understanding of the topic, choose the dependent and independent variables.
Take note that independent variables are the ones you can’t control, so understand the limitations of your test before settling on a final hypothesis.
Step #4: Formulate Your Hypothesis
You can write your hypothesis as an ‘if – then’ expression. Presenting any hypothesis in this format is reliable since it describes the cause-and-effect you want to test.
For instance: If I study every day, then I will get good grades.
Step #5: Gather Relevant Data
Once you have identified your variables and formulated the hypothesis, you can start the experiment. Remember, the conclusion you make will be a proof or rebuttal of your initial assumption.
So, gather relevant information, whether for a simple or statistical hypothesis, because you need to back your statement.
Step #6: Record Your Findings
Finally, write down your conclusions in a research paper.
Outline in detail whether the test has proved or disproved your hypothesis.
Edit and proofread your work, using a plagiarism checker to ensure the authenticity of your text.
We hope that the above tips will be useful for you. Note that if you need to conduct business analysis, you can use the free templates we’ve prepared: SWOT, PESTLE, VRIO, SOAR, and Porter’s 5 Forces.
❓ Hypothesis Formulator FAQ
Updated: