Introduction
Decision-making is regarded to be one of the most important issues in any sphere of everyday life. The fact is that few approaches may be regarded as effective, nevertheless, fewer than a few are helpful. The aim of this paper is to review the decision-taking tool from the perspective of uncertainty, and by the means of calculating the credibility of the possible outcomes. Thus, the case, which will be analyzed is closely associated with the matters of business decisions and financial management.
Case and Research
The N business company, which is specialized in the matters of financial loans and leasing of mining equipment, has decided to change the way of serving the financial leasing and loan accounts for their consumers. The previously accepted leasing practice presupposed the serving of the accounts by the means of banking accounting and the procedures, associated with the accounting insurance. The new decision presupposes using the internal accounts for consumers after the banking department of the company will be arranged. On the one hand, it will cause increased comfort in the issues of baking cooperation, on the other hand, the efficiency of the banking operations will be essentially decreased (as well as the banking expenses). In accordance with the initial statistical data, the companies, which transform their financial activity by arranging their own banking system inevitably experience losses on the banking operations for at least one and a half fiscal periods. These accounts can not be insured, and up to 30 % of the accounts appear to be closed because of the inability of the banking system to satisfy the requirements of accounting safety. Moreover, in accordance with the statistical data, up to 5 % of the consumers terminate cooperation with such companies. (Cooper and Schindler, 2006)
The main question is whether the N company should arrange its own banking system and transform the financial management principles and practices by terminating its cooperation with the reliable banking partner.
Probability Calculation
Originally, calculation of a probability associated with the issues f banking and accounting entails too many factors and aspects for calculating in accordance with any system. Nevertheless, this case may be regarded from the perspective of financial cooperation, and accounting information. Thus, by Lind, Marchal, and Wathen (2008, p. 216), the following statement should be emphasized:
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution identifies either the probability of each value of an unidentified random variable (when the variable is discrete) or the probability of the value falling within a particular interval (when the variable is continuous). The probability distribution describes the range of possible values that a random variable can attain and the probability that the value of the random variable is within any (measurable) subset of that range.
Thus, accounts may be closed or proceeded with the variability 30 / 70:
- A1 – closed because of security failure
- A2 – is not closed
Thus, the decision, whether the banking system should be arranged in the following:
- The banking system is already defined
- The probability of terminating the cooperation with a customer is 5% (Termination probability is 0,05)
- 30% of the accounts appear to be closed by the company (termination 2 = 0,3)
The specification of the mining equipment leasing industry is emphasized by the fact, that the clients are reliable and wealthy enough for keeping their financial reserves safe, thus, the probability of full termination of the cooperation is 10%. (Cancellation = 0,1)
The probability will be calculated the following way:
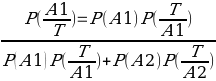
Thus, (0.05)(0.9) = 0.045
(0.5)(0.9) + (0.95)(0.15) 0.1875
Based on the calculations, the data illustrates the probability that the account will be terminated, considering the statistical data of similar operations.
The accounting information stated that if an account is selected during the instability period, the probability that it will be terminated is.05. Nevertheless, if the insurance is not available, the probability for termination rises from 0.05 to 0.24
Event Prior Probability
- P(Ci) Conditional Probability
- P(B|Ci) Joint Probability
- P(Ai and B) Posterior Probability
- P(Ai|B)
- Account terminated.05.90.0450.0450/.1875 =.24
- Account not terminated.95.15.1425.1425/.1875 =.76
- P(B) =.1875 = 1.00
Based on the above calculations, there is a.24 probability that the account will be terminated and a.76 probability that the consumers will continue their financial cooperation with N company.
Decision
In the light of the performed calculation, there is a strong necessity to emphasize that the credibility of terminating and closing the banking account based on the leasing financial principles is high enough, as the arrangement of the new banking system for expanding the leasing opportunities of the company is a risky and financially dangerous idea. Nevertheless, all the risks are justified if the company has the reputation of a reliable leasing and financial partner. On the other hand, the lack of financial insurance is a serious factor, which may distract potential consumers.
References
Cooper, D. R. & Schindler, P.S. (2006). Business research methods (9th ed.) Boston: McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Lind, D. A. Marchal W.G. and Wathen, S.A. (2008) Statistical techniques in business and economics (13th ed). Boston: McCraw-Hill/Irwin