Executive Summary
Abu Dhabi is under pressure to supply power to meet its growing economy. As a result, the rate of energy consumption has overtaken the rate of production. Thus, it must look for alternative sources of renewable energy. Wind energy is among the best solutions Abu Dhabi can exploit to meet its energy needs. The report covers energy crisis in Abu Dhabi, wind energy as a potential source of renewable energy for Abu Dhabi, and recommendations.
The survey showed that there was overwhelming support for wind energy as a source of clean and renewable energy in Abu Dhabi. Though there are few challenges, the overall impacts of wind energy in Abu Dhabi counter such challenges. Besides, Abu Dhabi can overcome most challenges through proper site selection, mapping, and continuous research in wind energy.
Introduction
Many people believe that the top oil-rich nation would not focus on other sources of energy. However, wind energy is the next source of renewable energy that would ensure clean environment and sustainable use of natural resources for Abu Dhabi. Energy experts have projected that currently available sources of electricity and energy in Abu Dhabi would be insufficient, expensive, and cause harm to the environment in the future.
Project Description
Abu Dhabi has the responsibility of providing clean and renewable energy to its citizens. Based on the pressure on the available electricity, Abu Dhabi needs wind energy power in order to balance some demands for electrical energy in its major cities. This would also reduce the level of carbon footprint in the region. Specifically, Abu Dhabi has installed some wind energy plant at Sir Bani Yas in the west coast. These projects have harnessed wind energy resources and eased the demand on the national grid by producing renewable energy.
Abu Dhabi aims to use some of the largest turbines to generate its wind energy. The plant would generate power that would be conveyed to the station by using underground conduits for the project. The project should target the entire Abu Dhabi. However, Abu Dhabi must focus on energy intensive desalination plants in order to reduce dependence on electric energy and then spread the project to other regions.
Scope of the Study
- The need to identify areas with the potential to generate wind energy.
- Develop a database of renewable energy potential in the country.
- Identify project issues like quality of the wind, land use, city planning, and protection of natural resources, parks, fire hazards, and agricultural land use.
- Potential impacts.
Report Format
This report has three important sections apart from introduction and background information. The report presents survey participants, methods of data collection, and the place of data collection. It also presents results of the survey, and conclusion, and recommendation based on the study results.
Background
Wind is moving air. Wind energy comes from the harvested wind by using turbines that can generate electricity. The generated mechanical energy can provide power for running various tasks like desalination plants, water pumps, and even running conveyor belts. Still, it can generate electricity for domestic, industrial, and commercial uses.
Consequently, a number of nations have embarked on wind energy as a source of electricity. Wind is a renewable energy because it is present. On the same note, the oil-rich Abu Dhabi has focused on renewable energy in order to establish a new chapter in energy production (Wang, 2011). However, developing wind energy has been a tough project than initially anticipated.
Lara El Saad noted that Abu Dhabi would face a major energy challenges in the future (Saad, 2011). The country would not be able to “provide enough natural gas to meet the seven percent to ten percent yearly growth in electricity demand continuing up to 2020” (Saad, 2011). Figure 1 shows that the usage of natural gas has overtaken production in the region, and trend continues to rise.
Abu Dhabi Water and Electricity Company (ADWEC) noted that Abu Dhabi generates its electricity from gas turbines and steam, turbines, and diesel engines. However, the use of diesel to generate electricity has decline in the past few years.
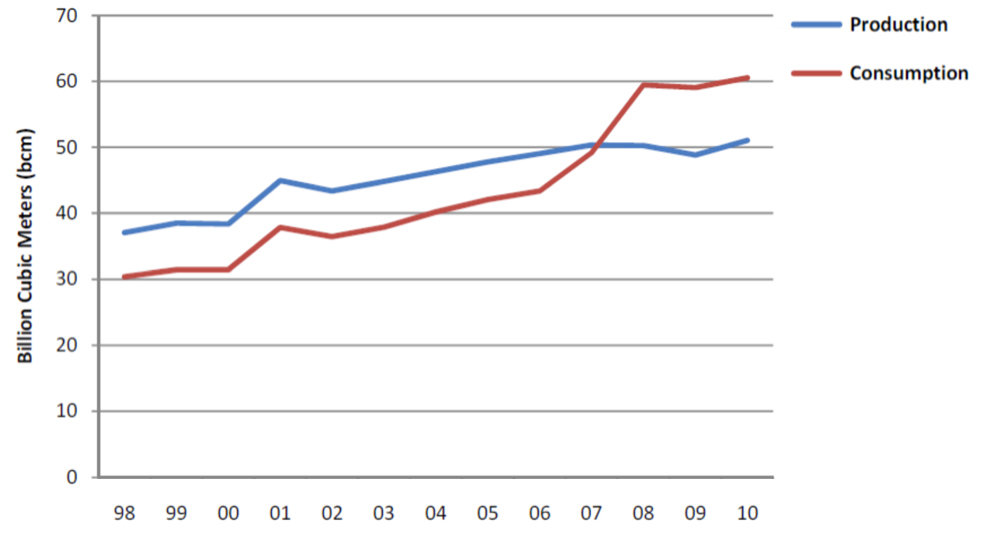
There might be abundant oil reserve in the region. However, Abu Dhabi and other UAE countries have created an energy crisis by making natural gas as their main source of generating electricity.
Wind Energy Production in Abu Dhabi
Wind is responsible for a small amount of energy that Abu Dhabi utilises on a daily basis. In fact, Sir Bani Yas has developed a successful wind energy plant, but this shall improve as researchers and other stakeholders in the energy sector have turned their attention to renewable sources of energy in which wind energy has been on the focus (Lynn, 2008).
The major reasons why wind energy usages in Abu Dhabi are low are due to lack of research and sufficient investments in the sector. Wind can only be productive in places where it is optimum and blows at acceptable speed. As a result, there is a need to develop maps for potential areas with wind energy and create a database for renewable sources of energy in Abu Dhabi (Kader, 2010).
Impacts
Wind energy has a number of impacts on the environment. People have raised concerns that turbines make noise, affect clear view of the landscape, kill moving birds, and affect land use (World Bank, 2007). However, wind energy is a clean source of energy that has no pollution to the environment. Moreover, it is free to use. Therefore, it offers a partial solution to energy challenges in Abu Dhabi.
Survey Information
Research participants
The researchers collected data from 40 respondents in Masdar City. This population was suitable for generalization, and researchers believed that their opinions reflected those of other who did not take part in the research. Researchers selected participants randomly to take part in the study.
Data collection method
The researchers used survey questionnaires to gather information. This was a face-to-face method of data collection. It was important because the researchers were able to get information directly from the respondents.
However, there were some possible challenges in this method. The method could have been subjective. Second, the respondents’ bias could have influenced the outcomes.
The researchers designed surveys with scales and multiple items for selection with aims of understanding opinions about wind energy.
Place of data collection
The researchers collected data from Masdar City in Abu Dhabi. Masdar City was of significance to this research because the developers based its design on “a model of what a green urban development can be” (Sievert, 2010) by thriving on sustainable, zero-waste, car-free, and carbon-neutral energy.
Results
This survey on wind energy presents varied opinions of respondents. The results provide valuable data about wind energy in Abu Dhabi.
Wind Energy and other issues in Abu Dhabi
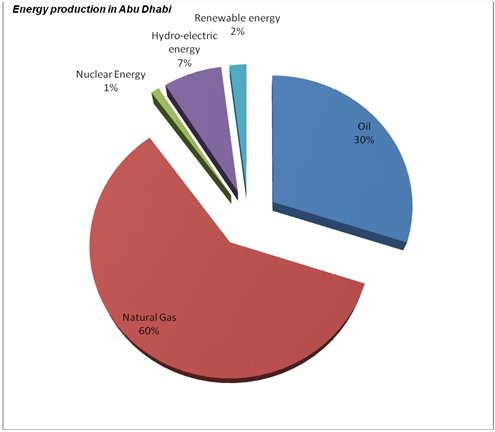
Researchers asked respondents about main sources of energy in Abu Dhabi. They noted that natural gas (60 percent) and oil (30 percent) were the major sources of energy in Abu Dhabi, and then hydro-electricity.
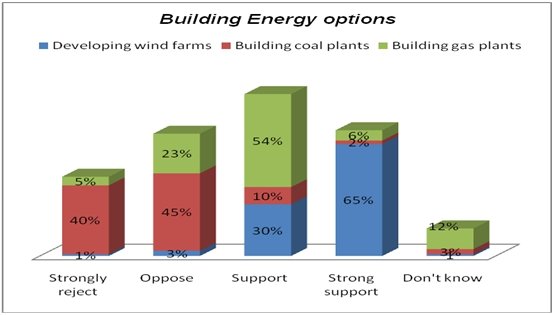
The demand for electricity in Abu Dhabi has increased over the last few years. We have several methods of meeting the rising demand for electricity in which some choices include building coal plants, renewable sources, and gas. The researchers asked respondents if they would support or reject the following sources of energy. Most respondents (65 percent) supported the construction of wind farms in Abu Dhabi.
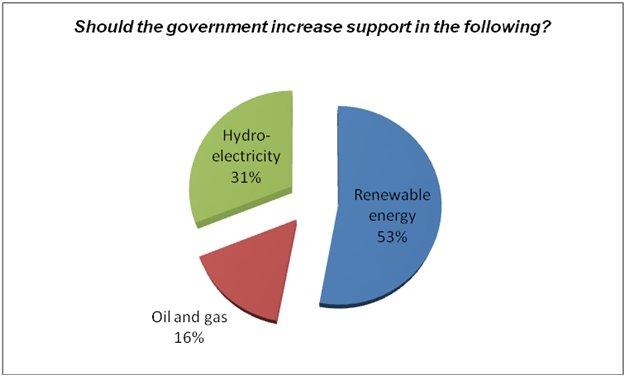
Respondents (53 percent) believed that the government should increase its support in developing new sources of renewable energy in Abu Dhabi (fig. 4). Many people cited effects of global warming as the main reason for developing sources of renewable energy to meet the rising demands.
These results showed that the government of Abu Dhabi should increase its support for clean and renewable sources of energy in the future. Respondents expressed such views after a meeting in Abu Dhabi that aimed at urging world leaders to increase their spending on renewable energy sources (AFP, 2013). More than 80 percent of the world’s energy comes from fossil fuels.
The use of renewable energy has gained momentum to over 15 percent. However, energy experts warn that it would not be possible to achieve the 30 percent objective by the year 2030 if governments fail to invest in the sector (AFP, 2013).
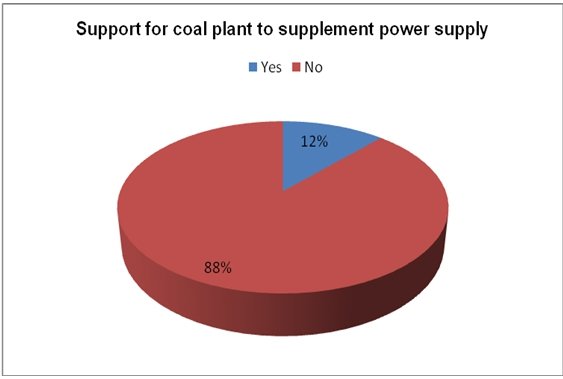
In 2006, Ahmed A. Elewa reported that Abu Dhabi could build the first coal-burning power plants in order to counter the rising demand for energy in the country due to economic growth (Elewa, 2006). The researchers asked respondents to indicate to what extent they supported the use of coal to generate energy with regard to its environmental impacts. A number of respondents (88 percent) did not support the idea of using coal (fig. 5).

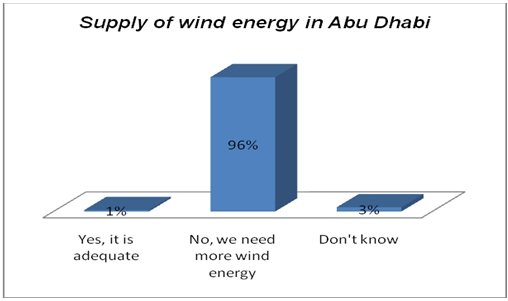
Abu Dhabi mainly relies on gas and oil to generate power. However, the current demand has put the reserve under pressure. The researchers asked the respondents if they believed that the share of wind energy in the country was adequate. Many (96 percent) noted that there were hardly any wind farms in the region.
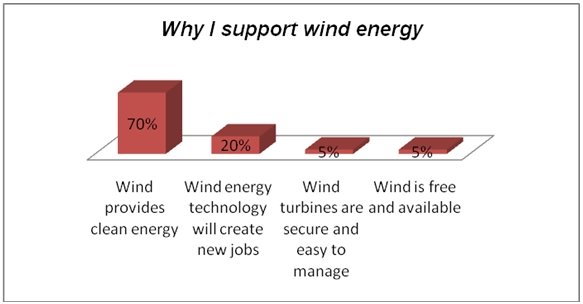
Research respondents also expressed various reasons why they supported wind energy. They cited clean electricity for the city, job creation through new technologies, and security and ease of control. Other respondents also noted that wind was free.
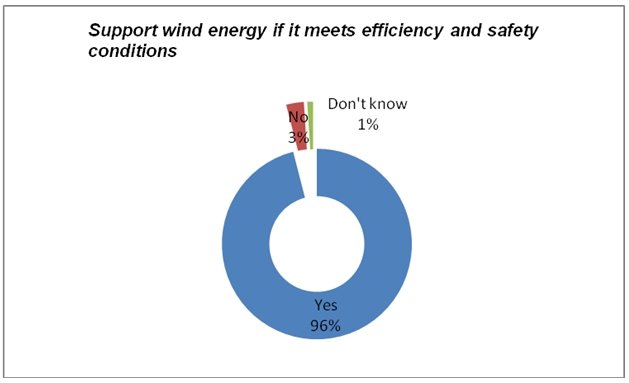
Wind farms must meet some criteria in order to ensure their safety and effectiveness in production of energy. This is necessary to avoid negative impacts on the environment and people, and resistance from the residents. For instance, some criteria involved wind speed, enough space, residential area consideration, and protection of natural environments, and resources. As a result, a majority of the respondents (96 percent) supported building of wind farms if such efficiency and safety conditions could be met.
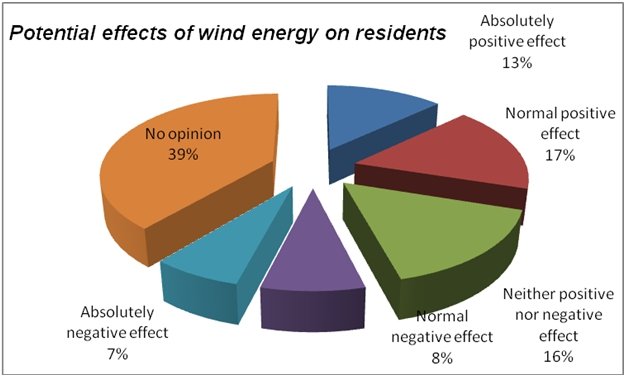
Most respondents (39 percent) noted that they had no opinion on how wind energy would affect them (fig. 10). While many believe that wind energy would transform their lives positively, a number of respondents took a neutral stand about the issue. This suggests that the government must educate people about the importance of using renewable energy and potential impacts of such energy on people and the environment.
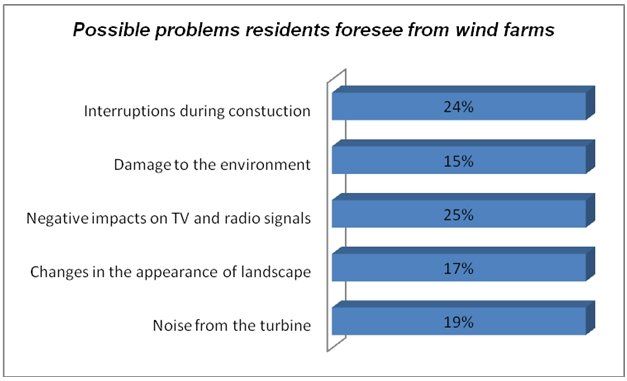
On this note, the researchers asked respondents to note what problems they thought the presence of a wind farm in the neighbourhood would cause. Majorities (25 percent) believed that such projects near their neighbourhood would interfere with their television and radio signals (fig. 11).
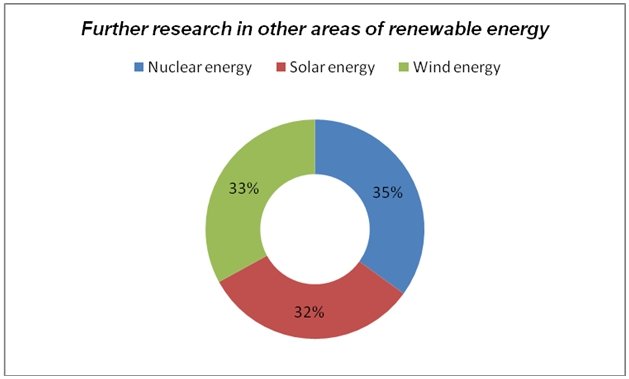
Respondents also noted that there was a need for thorough and ongoing research in the area renewable energy in order to find solution other than wind and solar energy. As a result, some respondents noted that Abu Dhabi should invest in nuclear plants as the ultimate solution to its pending energy crisis.
Research should identify potential areas with strong and adequate wind and open areas where buildings and vegetation would not interfere with wind farms. Thus, creating a comprehensive database for Abu Dhabi renewable energy development is necessary.
Wind Energy: A Renewable Non-Polluting Resource
Wind energy can provide a constant free and renewable energy in Abu Dhabi. It is also a source of a clean that Abu Dhabi needs to avert effects of global warming that results from the use of fossil fuels because it does not produce any greenhouse gases and air pollutants. Thus, a model city like Masdar can achieve its objective of “sustainable, zero-waste, car-free, and carbon-neutral energy” (Sievert, 2010).
Cost Issues
The cost of generating electricity has declined over the last few years. However, the initial costs of investments in the production of wind energy are quite high than using generators that run of fossil fuels. Machines consume nearly 80 percent of the total costs. The rest of the investments go to site preparation and setting up of the system. However, wind energy is cost-effective on a long-term basis because it does not need any fuel to run it.
The ongoing gas shortage in Abu Dhabi has also made the government to focus on alternative sources of energy. Moreover, the country has increased its usages of oil. Abu Dhabi should strive to reduce its rising costs of electricity.
Abu Dhabi government can benefit by investing in renewable energy and exporting its oil. Oil revenues should provide funds for investments in the renewable energy. The government also sees investments in green energy as a way of creating jobs and technology transfer.
Environmental Concerns
Wind energy has low effects on the environment. However, Abu Dhabi residents have expressed concerns about the level of the noise and visual effects on the landscape. In some cases, turbine blades kill birds and bats when such animals fly to the rotor. There are technological ways or a proper selection of wind farms can greatly reduce such negative impacts.
Supply and Transport Issues
The challenge is a steady and constant supply of minimum wind that provides electricity without interruption. Moreover, it is difficult to capture and store wind energy. Another challenge is that not all areas have the required minimum wind that can generate electricity.
Thus, researching, database, and maps are mandatory (Kader, 2010). Abu Dhabi government can only get such sites in remote locations, which may create transmission challenges. Finally, there are other areas of competing interests, which the government of Abu Dhabi has focused on in order to generate clean energy. Still, residents also view their neighbourhoods as potential areas for other developments.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Abu Dhabi experiences rising demands for electricity supply in order to support its rapid economic growth. As a result, there is a call to alternative sources of energy that can reduce reliance of natural gas and oil to generate electricity. Wind energy provides suitable opportunities for Abu Dhabi to ensure production of clean and renewable energy as it meets electricity demands and reduces global warming.
From the study, it was evident that there was high-level of support for wind energy in Abu Dhabi. Therefore, Abu Dhabi can develop wind energy to supplement its dwindling natural gas resources. As Miles’ survey indicated, wind energy can provide electricity for cities without depending on other sources of energy (Miles, 2006). Moreover, new technologies can also allow Abu Dhabi to integrate its wind energy within the city high-rise buildings.
Recommendations
- Initial costs are high, but the project is cost-effective than generating electricity from natural gas and oil.
- There is a need for continuous research in wind energy and other areas of renewable energy in Abu Dhabi.
- Wind turbines have visual impacts in the area. This depends on the area and public perception. Therefore, it is necessary to perform proper mapping and site selection in order to avoid unwanted poor visual impacts.
- Wind turbines generate considerable amount of noise when in use. Therefore, it is important to conduct a proper site selection in Abu Dhabi to avoid areas close to residential areas, school, and hospitals, and other institutions.
- Some birds and bat die or sustain injuries from wind turbines. Proper mapping and selection of wind farm locations can reduce such cases. Moreover, it is also necessary to avoid migration pathways.
- A proper selection of a wind farm location can minimise changes to the environment. It is also necessary to set wind farm away from environmentally sensitive locations
- Developers must observe community health and safety by mitigating any potential harm, fire, hazardous outcomes, and interference with the television or radio waves. It is also appropriate to provide safety alternatives in case of emergency.
References
AFP. (2013). 2030 target for renewable energy in doubt: Abu Dhabi energy conference. Web.
Kader, B. A. (2010). Wind speed, solar energy maps soon. Web.
Lynn, L. (2008). Mid East’s largest wind turbine comes on line in Abu Dhabi. Web.
Miles, C. (2006). Survey of Urban Wind Energy Technology. Web.
Saad, L. E. (2011). Averting Crisis: Managing Energy Use in Abu Dhabi. Web.
Sievert, T. (2010). Abu Dhabi – Wind power for the world’s most sustainable, zero- waste, car-free, carbon-neutral city? Web.
Wang, U. (2011). Abu Dhabi: Rise of a Renewable Energy Titan? Web.
World Bank. (2007). Environmental, Health, and Safety Guidelines for Wind Energy. Washington, DC: World Bank.