Detailed Application Implementation
System implementation is the process of converting system design into actual code. The implementation is carried out in a development environment. Depending on the nature and scope of a project, it can be implemented in an integrated development environment or just a text editor. The proposed system was implemented on the VS Code text editor. The editor supports different languages including JavaScript and type script. The system was developed using the MERN stack, which is MongoDB, Express, React, and Node. The Mongo DB was used for database data storage, react was used for frontend development, and Nodejs was used for server development. The express.js was used to develop features for a web application that ran on the Nodejs server. The front end and the back end were implemented independently, as shown in the project structure below.
Algorithms
The system algorithms are presented in the pseudocode below.
Database Design
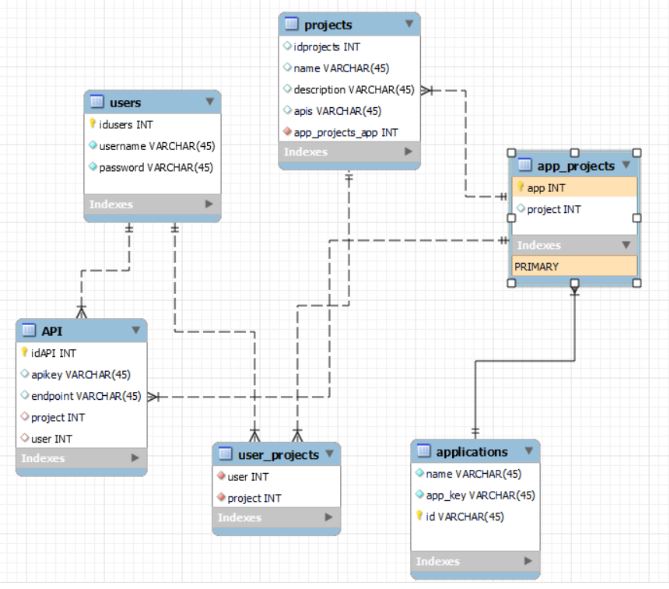
The system database is comprised of six tables, namely: users, projects applications, APIS, user_projects, and app_projects. The databases are characterized by one-to-many relationships which are essential for normalization. Each table contains a primary key (in the case of independent tables). Tables that are purely generated for relationships and normalization (app_projects and user_projects) are solely made up of foreign key attributes. The database diagram was designed and generated using the Workbench community version, which is a graphical tool for designing relational databases. The complete database diagram is presented in the figure below.
Detailed Project Structure
The structure of the software implementation is presented in the figures below.
Frontend
The frontend part of the system is comprised of several components: the navbar, footer, forms, the submit button, and inputs. The components are exported and used in several interfaces.
The public folder contains the index.html page as well as images used in the site.
The src folder contains the main source code for the frontend. It contains the API, components, configurations, App JS and CSS files as well as the application logo.
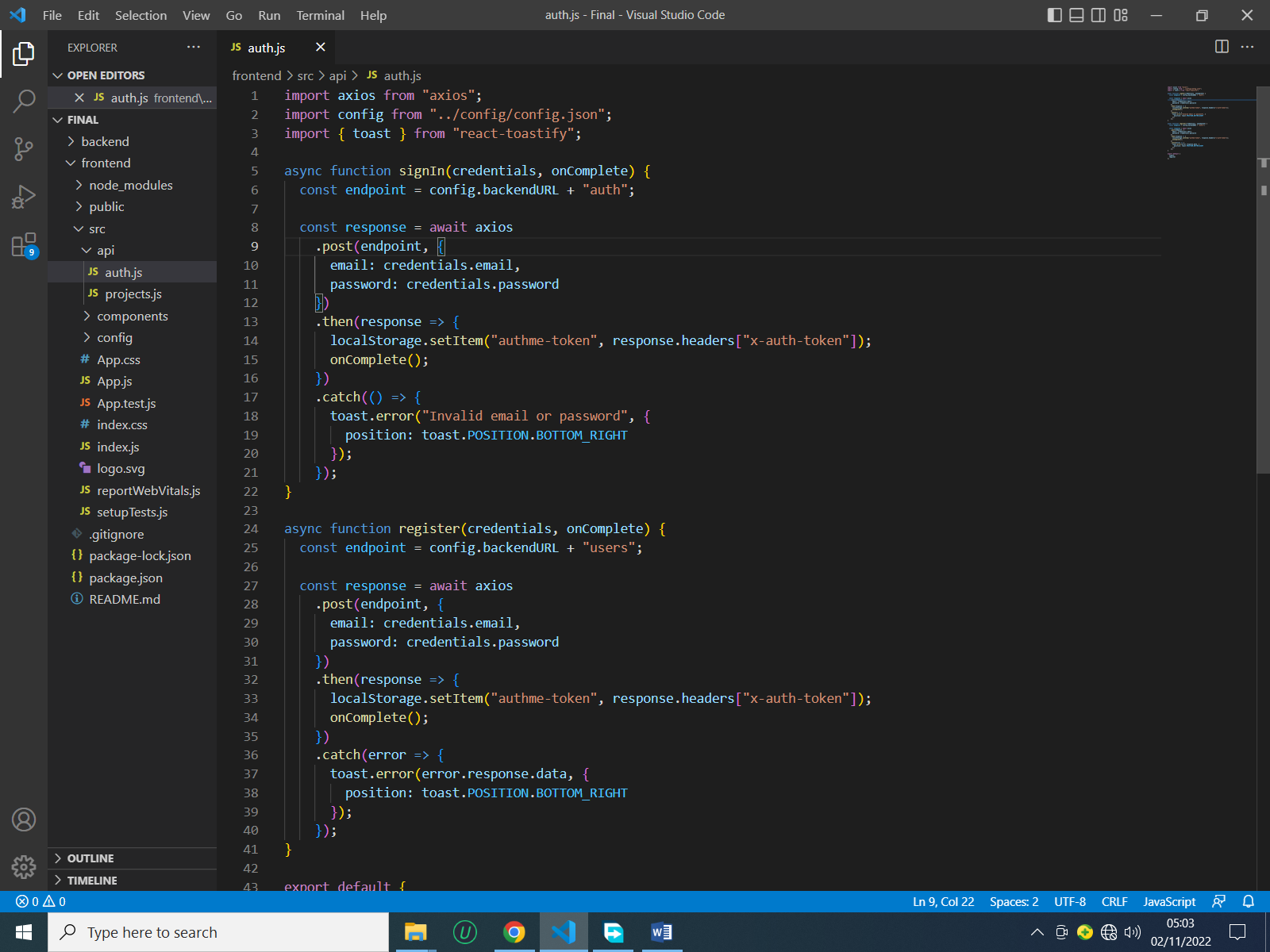
The auth.js script is responsible for the authentication process and is contained in the API module.
Backend
The backend is comprised of a configuration module, middleware, models, and routes. The routes led to user account management, project authorization, project management, and linking user to projects.
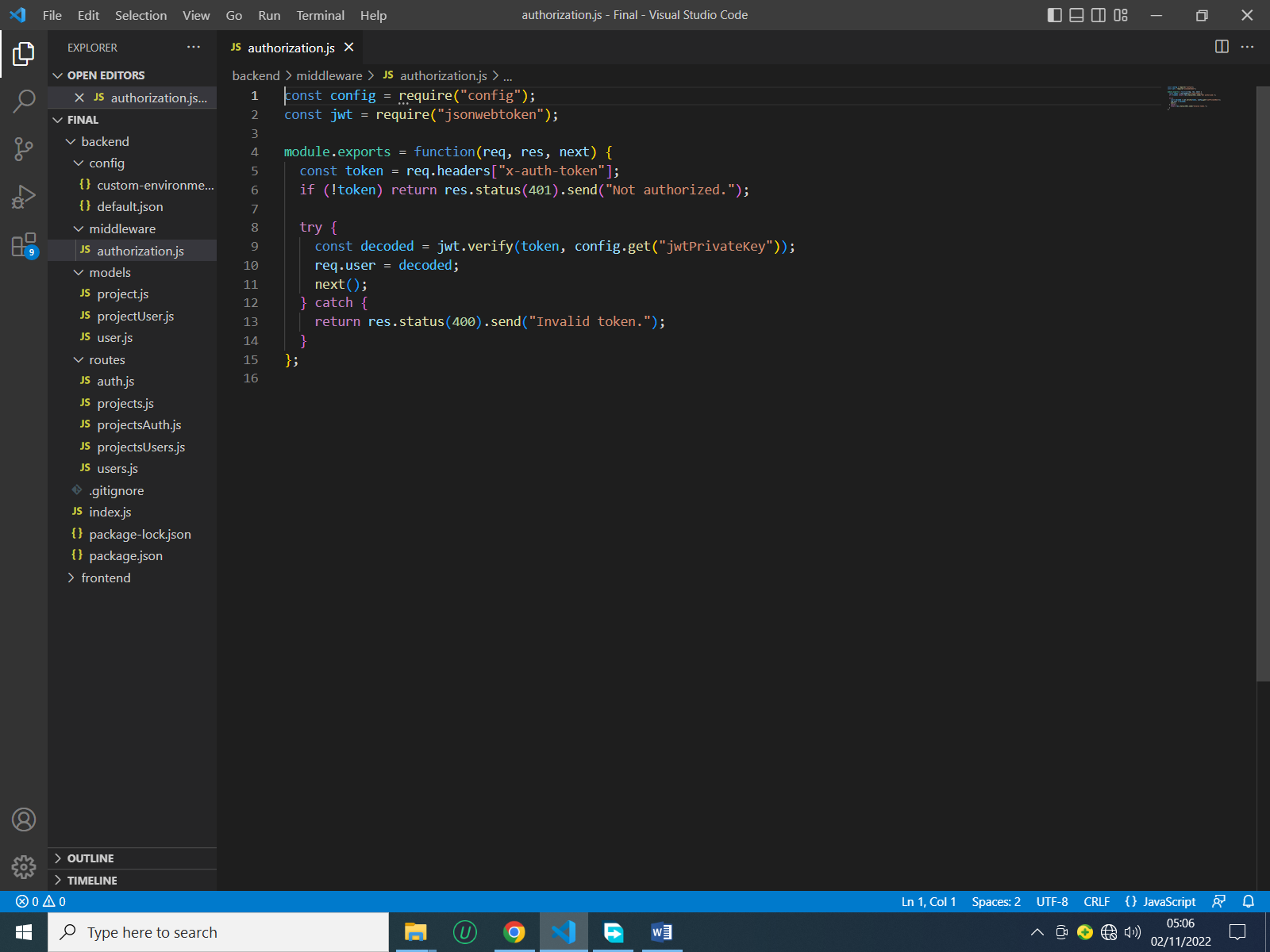
Software Components
The system is comprised of two main components: the front end and the back end. The front end is a collection of interfaces that consume the backend APIS. The backend comprised the server, database connection, and database records.
Testing and Evaluation
In software development, testing refers to the method of assessing a software system to determine if it currently satisfies the necessary requirements or not. In the assessment process, the characteristics of the new software are examined for compliance with specifications in regard to any unmet needs, flaws or mistakes, security, dependability, and efficiency. The project was subjected to two types of testing: functional and nonfunctional tests.
Functional Testing
A program is tested for its functionality, ability, and degree of executing its intended purposes with regard to the user requirements. As the name suggests, functional testing evaluates whether a system carries out its expected purposes in the manner justified in the project charter. In this case, the system was subjected to unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT). In unit testing, different project parts were tested to assess whether they carried out their intended purposes. Such tests were carried out at the method, object, and class levels. Since the project uses different frameworks and libraries, it was assumed that they were bug-free for them to be incorporated into the project. Any instances detected were fixed before proceeding to the next development phases. This ensured the project performance and functionality were as per the requirements gathered from the target users and stakeholders. The second level of functional testing was integration testing. This kind of evaluation assesses the performance of different system modules as they interact with each other. For instance, the consumption of API endpoints, database connection, tabulation, security verification, validation, and authentication. The communication and interaction between different system modules registered errors, misconfigurations, and faults that were corrected accordingly. The tests were carried out manually, lopping through all major modules and interfaces until the developers were confident with the results. User acceptability tests are carried out in the final stages of development. The tests encompassed 20 users who evaluated the system interface, ease of use, validity of results, response speed, and general user experience. The users returned positive feedback, implying that the system met the target client’s needs.
Nonfunctional Testing
Nonfunctional tests evaluate the behavior and characteristics of a software system. The tests are primarily built on nonfunctional requirements and do not necessarily affect what the system should do, but how it should achieve its target goals. In this context, the system was passed through performance, endurance, and usability tests. Performance tests were carried out to evaluate the speed, responsiveness, and scalability of the system under predetermined working conditions. The conditions were based on disk space, memory, and internet speed. The optimal performance was obtained at 100MB free disk speed, 1GB memory space, and 10kbps internet speed. The tests did not consider any other running applications on the test computer. The system was designed to accommodate up to 2000 active users, which is a manageable load for standard systems.