Never Waste a Crisis
In the corporate world, one of the principles of success is to never waste a good crisis. This means that any organization should never and under any circumstances fail to take lessons from a challenging situation. Firms should always be learning something new and learn how to adapt to the new reality, and when a necessity arises, they should find ways to eliminate weaknesses and focus on strengths. Moreover, in environments such as medical school or an academic hospital, this means that students and employees see the steps they must take in different situations and learn how to be more flexible and adapt to various circumstances.
Strategy to Achieve the Global Vaccination
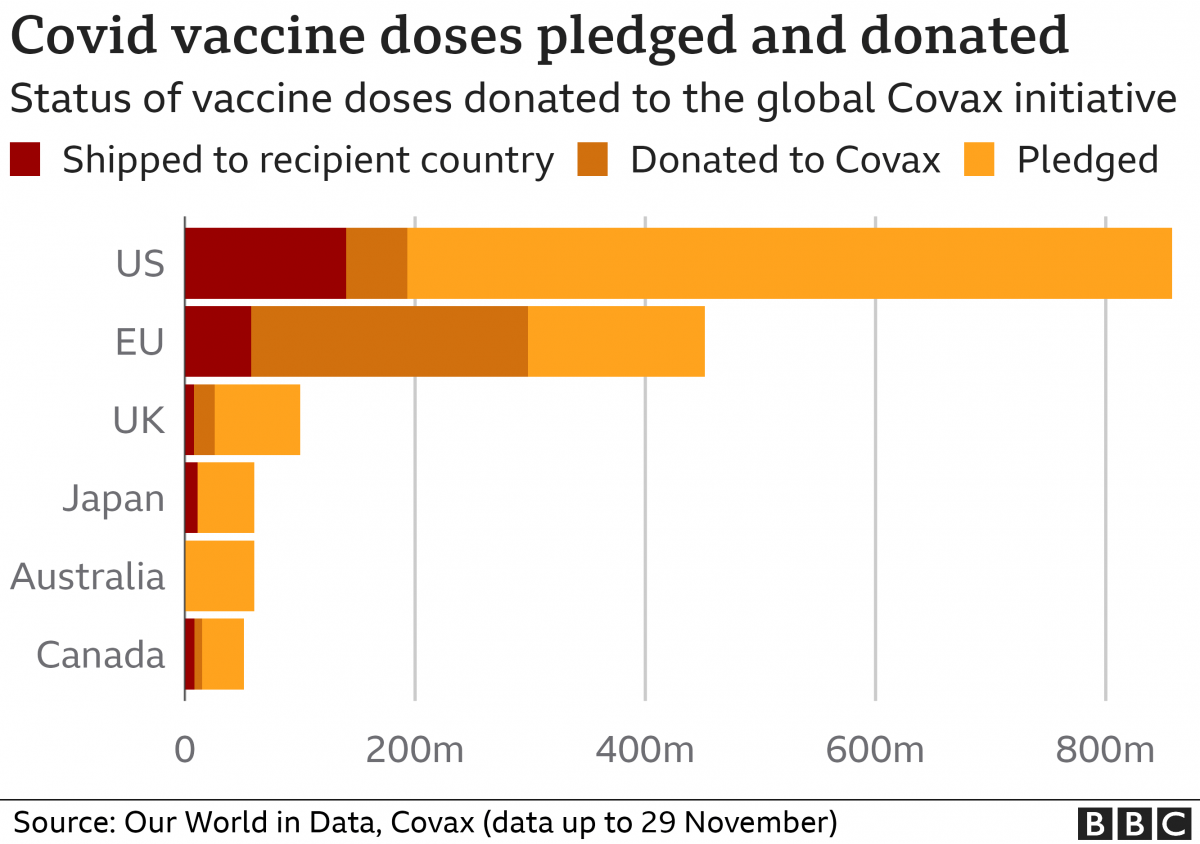
Despite the astounding speed with which highly effective and safe vaccines have been developed, new disease waves continue to strain health systems. Despite the distribution of over 6 billion COVID-19 vaccine doses and a global production rate of 1.5 billion doses per month, the pandemic persists (Nicola et al., 2020). As can be seen from Figure 1, COVID-19 vaccines are mainly donated, and vaccinations are a general recommendation for the public.
The strategies of global vaccination should, therefore, be aimed at raising awareness and providing people with more opportunities for vaccination. For instance, the procedure can be marketed by companies to communicate the message to the public, and leaders can serve as role models to their teams. Moreover, companies can create mobile vaccination spots with nurses where teams can become vaccinated.
The Importance of Leadership
The process of influencing or guiding others can be referred to as leadership. Leaders must adapt to changing circumstances and be willing to take the initiative to deal with the issue while maintaining their commitment to their basic principles. Since the future cannot be predicted, it is crucial to back up one’s vision with various adaptable strategies. The ongoing global epidemic has recently presented difficulties for everyone in particular situations. Even though every situation is unique, leaders worldwide confronted three significant challenges: safety, engagement, and support.
A previously unheard-of global humanitarian disaster has evolved due to the coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) pandemic. The clinical manifestations of this disease and the optimal techniques for gastroenterology and endoscopy during this pandemic have been the topic of recent articles and multi-society guidelines. In situations like these, volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity require quick decisions with a significant impact in a position with little information. To keep their organization running smoothly and to ensure the safety and well-being of our patients, leaders must manage these factors, pick up new skills along the way, and contribute to creating various innovative problem-solving techniques.
The Best Leadership Approach
Because they create dynamic teams that welcome change and transform anxiety into success, adaptable leaders get better results. A valuable concept for leadership called adaptive leadership can support people and organizations in being flexible and resilient under challenging circumstances. Adaptive work frequently entails questioning the current quo and implementing changes that, while necessary, may appear severe. Under this leadership style, managers are tasked with exercising boldness and making thoughtful, occasionally unexpected decisions. These decisions are not made on a whim but out of need. They benefit the organization in some way. Additionally, even though they can seem rash, they must be trained to adapt to their environment.
Leadership Principles – Communication
The number or caliber of communications emanating from a local leader may not have much impact, but it does. The workforce becomes anxious when there is uncertainty, and the leader’s silence will be perceived as negative local news. Communication is crucial to define reality and reinforce a distinct perspective on what is happening and what it implies for the unit individuals who are heading the organization and the region. Communication must be concise, constant, and flexible.
Goals
Despite the fact that the COVID-19 vaccine has been administered more than 6 billion times and is currently produced at a rate of 1.5 billion doses per month worldwide, the pandemic cannot be stopped (Nicola et al., 2020). Serious illness, hospitalization, and mortality have significantly decreased in nations with high vaccination rates; however, vaccine access is unequal worldwide, which is shown in Figure 2, with coverage ranging from 1% to over 70%, primarily dependent on a country’s affluence. (Nicola et al., 2020).
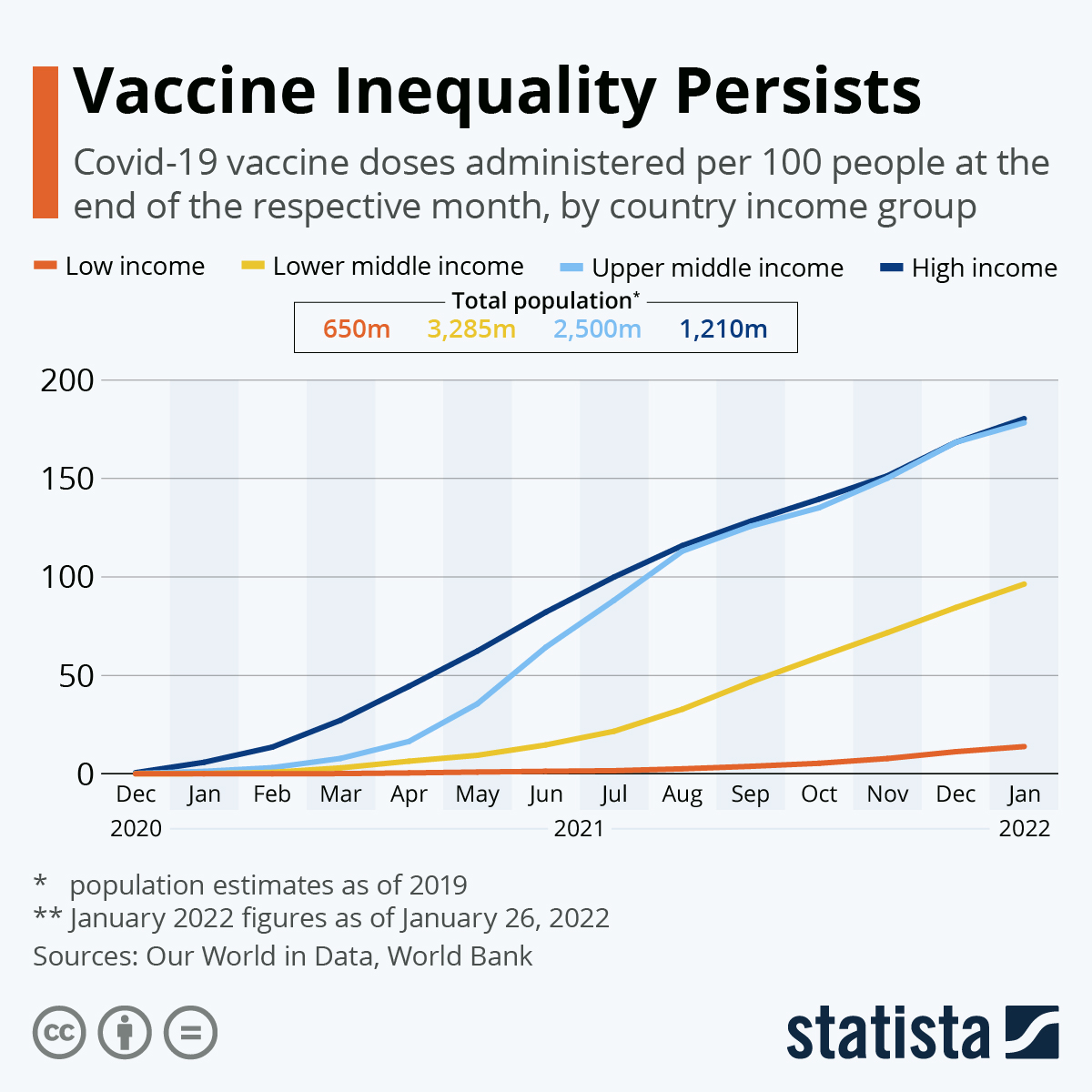
SARS-CoV-2 variants continue to emerge, causing disease outbreaks and delaying or halting the opening of society and economies. Given the continued shortage of vaccines, it is essential to vaccinate in a staged, globally coordinated manner with time-bound coverage targets to have the most impact and equity. By mid-2022, 70% coverage is the goal, supported by technical analyses of disease epidemiology and vaccine attributes (Nicola et al., 2020). It has also been supported by a feasibility assessment that considers requirements for global vaccine production and national absorption capacities, as well as the health and economic imperatives of quickly ending the pandemic.
Primary Targets
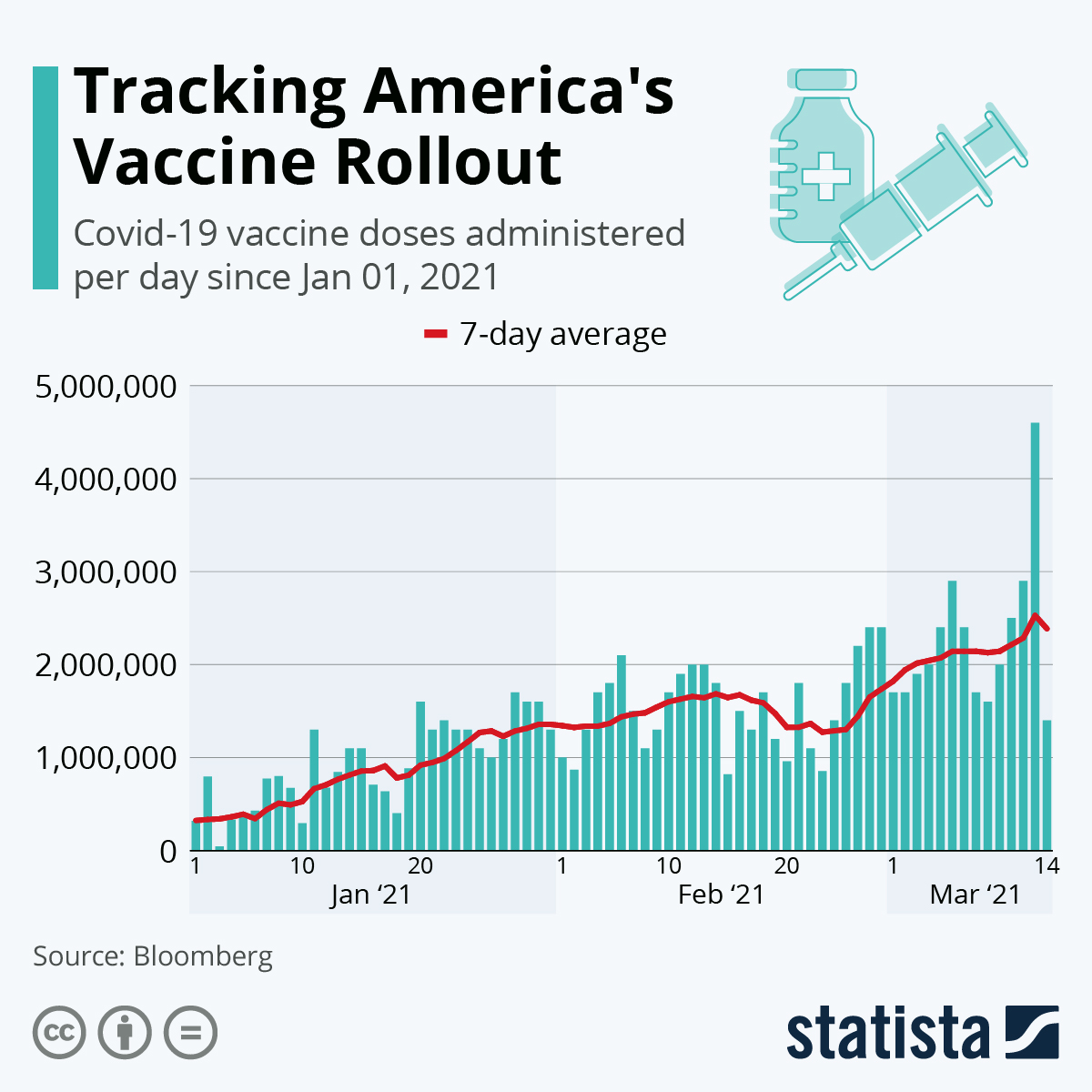
Fifty-six countries, or 20% of the world’s population, still need to reach the 10% coverage goal by the end of September 2021 (Nicola et al., 2020). Seventy nations had already surpassed the 40% coverage goal as of the end of September (Nicola et al., 2020). This makes it even more vital to take the necessary steps to ensure that the remaining nations, particularly those with coverage levels below 10%, are on track to reach the 40% mark by the end of December 2021 (Nicola et al., 2020). As seen from Figure 3, vaccination was rising in 2021. However, the COVID-19 vaccinations’ potential to halt the pandemic can only be achieved if all nations act swiftly and together, making the best possible use of the finite but expanding vaccine supply.
Expectations Management
To preserve a perception of fairness, it is essential to openly explain choices to workers and provide them the option to offer feedback wherever possible. A leader could state that this choice is not motivated by biases or favoritism toward people with more excellent protection positions. Instead, the option satisfies the practical requirement to keep a core group of officers in good health as backups in case of future absenteeism. One will be able to control expectations better.
Tactical Approaches
Tactics, which are additionally frequently referred to as initiatives, should be strategies that are tailored to the institution’s requirements and finances while also being influenced by standard operating procedures. When it comes to global vaccination, the tactical approaches should be aimed at disseminating information regarding the advantages of this procedure, lower risks of mortality, anda robust immune system. Therefore, the tactical approach that will be used involves expanding the marketing team so that the company can spread the information.
Potential Pitfalls
However, there might be potential pitfalls when it comes to expanding teams within the organization. For instance, the biggest pitfall is a lack of financial stability in terms of employee pay. Without paying at least the average market pay, a company cannot expect the employees to be efficient and motivated. Moreover, when expanding the team, the pitfall of poor department structure can occur. At this point, it is necessary to pay attention to the clear hierarchy and a list of responsibilities to ensure high performance.
Realistic Views
When reviewing the topic of vaccination, it must be understood that there can be external and internal threats to success. For instance, among the internal threats are low morale and motivation of the employees to vaccinate. When corporate culture does not promote the cohesiveness of the teams and their cooperation, it can be challenging to influence and motivate them. Therefore, without proper respect and collaboration, it will be challenging to communicate the necessity of vaccination to the team.
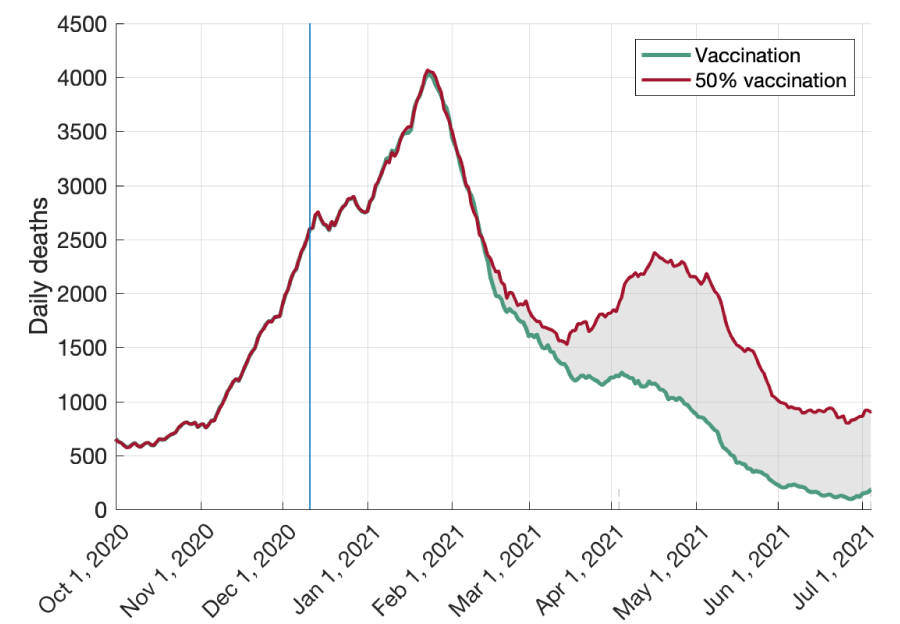
However, when it comes to external threats to the success of the initiative, it must be noted that vaccine hesitancy can result from a lack of awareness and a decreasing global trend of vaccination and disease spreading if employees are exposed to the news that stresses the decreasing trend of Covid-19 infection, they can be more reluctant to vaccinate, and in Figure 4, one can see the decreasing trend of daily deaths, which can lead to excessive optimism. Therefore, it is important to maintain the dissemination of information regarding the benefits of vaccination. As for measuring success, companies should focus on using questionnaires to learn about employees’ attitudes, with more positive feedback being the most effective metric.
The Importance of Analysis and Communication
Especially when it comes to new tasks and responsibilities, the employees must comprehend the current administrative position and have a clear vision of success. Effective communication is essential for leaders. Communication should be timely and pertinent. It is crucial to refrain from unduly diverting employees from mission-critical work; instead, concentrate on inclusion to ensure everyone is heard and seen.
During an emotionally charged situation that causes anxiety and worry, conversations may not go well. Everyone is under pressure because they are living in unprecedented times. It is possible that difficult discussions would not be planned, and the leader would be unable to prepare. Talking about important topics rather than avoiding them is essential since issues and demands continuously change.
Reference
Nicola, M., Sohrabi, C., Mathew, G., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Griffin, M., Agha, M., & Agha, R. (2020). Health policy and leadership models during the COVID-19 pandemic: A review. International Journal of Surgery, 81, 122-129. Web.