Introduction
One of the most acute problems of our time is the increasingly frequent use of alcohol by minors. Free access to alcohol has a negative impact not only on the health and socialization of adolescents but also on their academic performance at school. The study aims to study the effect of alcohol consumption by minors on school graduation rates. This topic is significant for society as alcohol production is developing, and accessibility is becoming freer. This problem should be considered from the perspective of Merton’s anomie theory, as well as through the prism of differential association theory. Although the heads of state seek to regulate the use of alcohol by minors, children still have the opportunity to purchase alcohol, which harms school graduation rates.
Literature Review
The choice of sources is based on collecting information on keywords such as alcohol and minors, as well as on basic phrases such as alcohol consumption and the influence of alcohol on grades. For the analysis, two articles were selected that most accurately respond to the specified search parameters. An article published on the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, 2022) website called Underage Drinking describes that alcohol consumption by minors is typical and has a detrimental effect on children’s academic performance in schools. CDC (2022) claims that alcohol consumption can be prevented by raising taxes on alcohol, ensuring compliance with laws prohibiting the sale of alcohol to minors. These measures will reduce the number of young people addicted to alcohol and prevent a decline in school performance.
National Institute of Health (NIH, n.d.) also studied the problem of alcohol consumption by underage students and wrote the article Underage Drinking. The article describes several important problems that result from alcohol consumption by students. Such issues include physical and psychological problems, the lack of the ability of the brain to develop correctly, and many other problems. The article also suggests ways for different groups to intervene in the lives of young people, for example, the intervention of schools, families, society, and political organizations (NIH, n.d.). The help of all possible groups will make it possible to reduce the number of young minors who consume illegal drinks.
Methodology
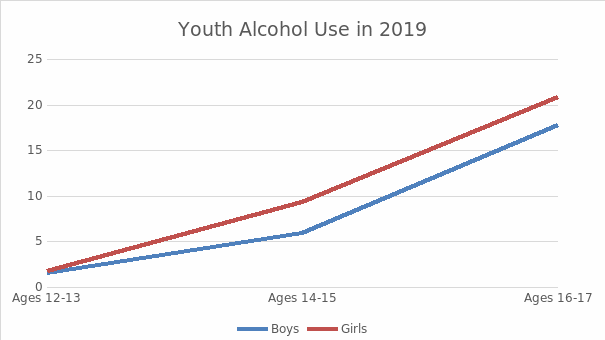
The search for sources was based on a sample of data from various sources from which two of the most suitable were selected. NIH provides information that in 2019, 7 million young people from 12 to 20 years of age consumed alcohol during the last two months (NIH, n.d.). In America, underage alcohol consumption is more common among girls than boys. Thus, at the age of 12-13, 1.7% of girls consumed alcohol, 1.5% of boys aged 14-15, 9.3% of girls and 5.9% of boys, and at the age of 16-17, 20.8% of girls and 17.8% of boys (NIH, n.d.). This information shows that the older teenagers get, the more actively they consume alcohol. The survey was conducted by questioning young people, which made it possible to conduct research and identify the results.
The CDC is based on research also conducted through surveys and questionnaires, which made it possible to collect extensive data and perform the complete study. According to the CDC (n.d.), 29% of young people enrolled in school have consumed alcohol at least once in the last 30 days. These results are frightening because many young people may become addicted to alcohol, which will negatively impact their school performance and learning outcomes. Adolescence is one of the most critical age periods of a person’s life. It is at this time that the child shows a great degree of confrontation with the surrounding world and people. It is typical for such an age to conflict with everyone around them. No restrictions and conflicts were revealed during the study of the literature.
Alcohol consumption by school students refers to deviant behavior, and this type of behavior of adolescents is described in detail in the theory of Robert Merton. The main idea is that the leading cause of crime is the opposition to values highly valued in society and how to achieve them (Messner, 2019). Merton’s theory is based on five types of reactions to matters that are established in the community and also on how they are completed. Usually, these five types of behavior are regarded as following a generally recognized cultural goal that is accepted in society (Messner, 2019). The most chosen means of achieving goals are education and career. Alcohol significantly reduces the likelihood and ability to accomplish this goal.
Another critical theory is the theory of differential association, which consists of processes leading to systematic criminal behavior. These processes, in their form, coincide with the processes leading to law-abiding behavior (Maloku, 2022). Later, the theory was modified, and the main directions were identified. It was exposed that criminal behavior is learned by interacting in the process of communicating with other people (Maloku, 2022). In addition, it was revealed that the specific orientation of motives and aspirations is formed on the basis of assessments of legal norms as favorable or as unfavorable. An essential role in developing personality is played not by contacts with impersonal organizations or institutions but by everyday communication — at school, home, or the place of constant street meetings with friends.
Conclusion
In conclusion, underage alcohol consumption plays a significant role in changing school graduation rates. Based on the conducted research, it can be concluded that the problem of alcohol consumption by minors is urgent and acute. There are various theories, such as Merton’s theory or differential association, which demonstrate that all issues lie in deviant behavior that interferes with achieving goals. The problem of alcohol consumption by students is fundamental and requires the search for practical solutions.
References
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Underage drinking. Web.
Maloku, A. (2020). Theory of differential association. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 9(1), 170-174.
Messner, S., Rosenfeld, R. & Hövermann, A. (2019). Institutional anomie theory: An evolving research program. Handbook on Crime and Deviance. Springer.
National Institute of Health (n.d.). Underage drinking. Web.