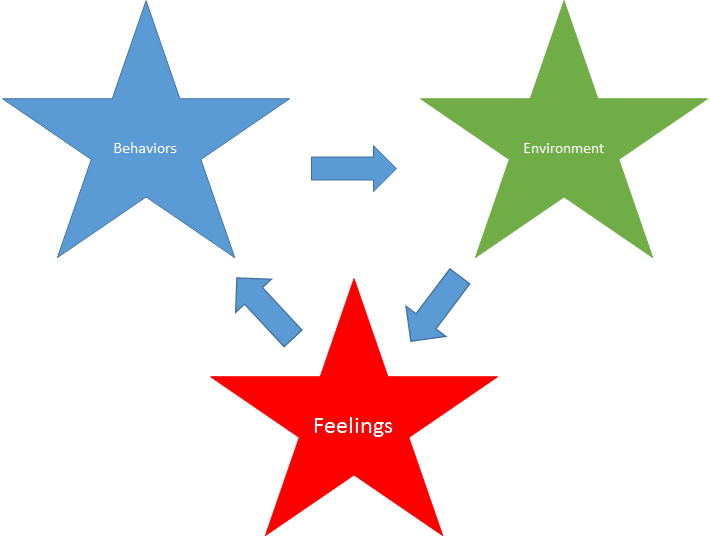
The All Employee Survey (AES) is a tool utilized by business companies, government bodies, and non-profitable organizations to estimate job satisfaction, organizational assessment, and organizational culture (“Employee census,” n.d.). The data provided by this framework enables a rigorous HR analysis of the existing company structure, which allows improving various organizational parameters, such as turnover rates, capabilities for vertical mobility, and others. As it is possible to see in Figure 1, the AES framework is based on three major factors, such as the feelings, the behaviors, and the environment. The questionnaires grade the performance of leaders and departments depending on the overall score in each of these issues (USCB, n.d.). The purpose of this paper is to summarize the scores of an AES survey in a healthcare setting.
Summary of the Survey
The survey was completed by 27 employees out of 38, achieving a 71% response rate. These numbers allow the survey to represent the majority of the healthcare center’s workers. The framework identified three major planning priorities, such as the workload (22%), coworker relationships (15%), and communications (7%). The overall questionnaire was split to judge the performance of the unit based on behaviors, environment, and feelings subgroups.
The AES questionnaire evaluated numerous parameters. The behaviors subgroup included workgroup cooperation, diversity acceptance, conflict resolution, respect, and psychological safety. Supervisor-specific items included trust, reasoning, respect, and favoritism, as well as goal evaluations, support development, facilitation of life-work balance, goal setting, recognition, accountability, and the ability to directly address worker concerns.
The environment subgroup was comprised of relationships and workplace characteristics. The primary items were as follows: reprisals, collaboration, civility, servant leadership index, workload, innovation, development, decisional involvement, data use, employee-driven improvement, and workplace performance. Lastly, the feelings subgroup included work engagement, disengagement, customer satisfaction, information sharing between leaders and supervisors, exhaustion, depersonalization, high burnout, reduced personal achievement, and reduced turnover intent.
The unit results have proven to be exceedingly impressive. The overall scores in all three subcategories were exceeding those of the comparison rollup group by a large margin. Based on the feelings subcategory, all employees in the unit were much more engaged and satisfied with their performance when compared to the basis group. In addition, the overall turnover intent was reduced, in comparison to the last year. However, the burnout and turnover indicators remained largely similar to the basis group, showing that the work pressure did not subside.
In terms of the environment, the group showed significantly better results in all parameters, when compared to the base group. However, there were no increases when compared to the last year, showing that no radical changes have been implemented. The same could be said for the behavior subsection, which saw better results in all parameters. However, it must be noted that the AES score for supervisor addressing concerns was lower than the last year, meaning that their efforts in that regard have faltered, though not by much. The unit cohesion and preference towards working together remained largely above the norm.
Conclusions
The AES framework is an efficient tool for constructing questionnaires to be used for investigating the performance of companies, departments, and individual units. As it was evidenced in this paper, it can also be implemented in non-profit organizations, such as healthcare departments and hospitals. The unit analyzed in this paper showed above-average performance when compared to the basis group, and has been doing so consistently for some time. There is room for improvement, however, namely in reducing stress, turnover rates, and supervisor addressing concerns.
References
Employee census. (n.d.). Web.
United States Census Bureau (USCB). (n.d.). Are you in a survey? Web.