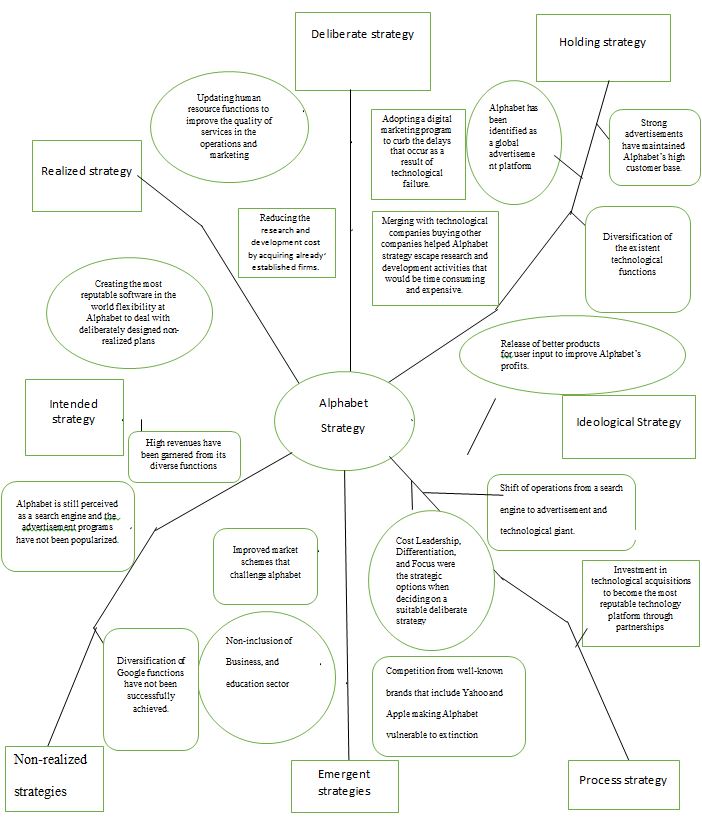
Founded on October 2, 2015, Alphabet is a strategy adopted by Google to diversify internet services by hosting a variety of businesses and software organizations. Initially, Google was a search engine, and a deliberate strategy was adopted to create a parent company to Google that would diversify the platform’s services from a search engine to a digital advertising platform. Developed by the managers, the deliberate strategy involved the acquisition of technological companies, for instance, YouTube, double click, and Nest. Buying and merging other companies helped Alphabet’s strategy escape research and development activities that would be time-consuming and expensive. Alphabet has adopted short- and long-term goals in its operational, resources, and market functions. The operationalization of deliberate and emergent strategies has led to the company’s success and stability. A deliberate strategy is a set of organizational activities that create a company’s identity (Bryson & George, 2020). Through deliberate strategy, Alphabet has been identified as a global advertisement platform.
On the other hand, emergent strategies are the prioritization decisions made by an organization in response to unlikely situations not predicted during the development of deliberate strategy. The deliberate and emergent-making process is a research-intensive process involving the selection of an abstract idea and determining the required resources to operationalize the concept to achieve desired goals. In Alphabet, Cost Leadership, Differentiation, and Focus were the strategic options when deciding on a suitable deliberate strategy.
Alphabet Inc. Strategy Mind Map
Reference List
Bryson, J., and George, B. (2020) Strategic management in public administration. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Politics. Web.