Introduction
Most contemporary companies focus on expanding to the international market to capitalize on the available opportunities and increase their market share. This is because expanding to a foreign country increases the customer base leading to amplified productivity and profitability. However, the selected country to invest in should be thoroughly analyzed to determine whether it can generate positive returns (Crespo, Simões, and Fontes, 2020). One of the key organizations that are concentrated on investing in the international market is Amazon. The paper analyzes the chosen company, home, and host country dynamics, the perfect internationalization approach and entry method, and the company’s growth strategy within the foreign market.
Chosen Market Dynamics
It essential to analyze the chosen market to determine the possible threats and opportunities that a company may face to decide whether to enter or not. This generates room to compare the home and chosen market dynamics to identify the notable differences (Crespo, Simões and Fontes, 2020). As a result, this helps in making the right decision to outshine potential competitors.
Chosen Company
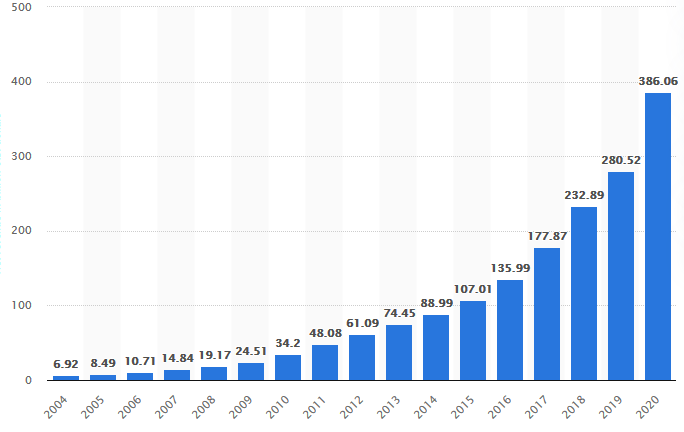
Amazon operates as an international technology organization situated within Washington, the United States, and deals with e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing. The company was established in 1994 and began by vending e-books but grew to offer consumer electronics, online music, and cloud services. Amazon has witnessed growth over the last years, associated with excellent leadership, increased acquisitions, and quality and innovative services and products that align with the customers’ demands. Consequently, during 2016, the revenue was $135.99 billion but increased to $177.87 billion in 2017. The revenue levels increased in 2018 to $232.89 billion, $280.52 billion in 2019, and $386.06 billion in 2020, as shown in figure 1 (Amazon, 2021). The company acts as a major contributor to the economy as it offers employment opportunities to about 1.3 million individuals.
Home and Host Country Dynamics
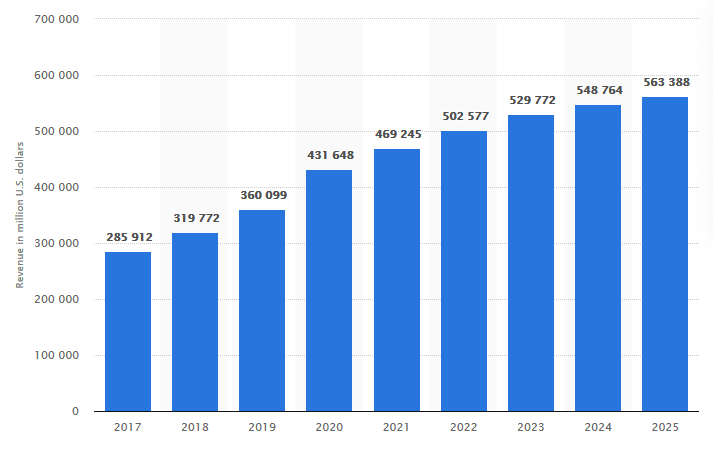
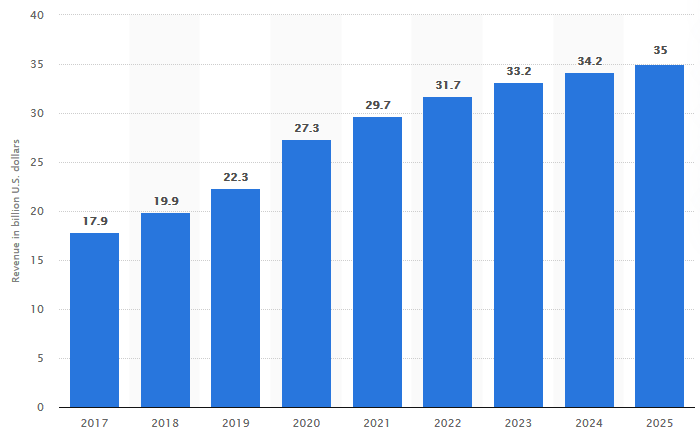
The home country is the United States, which focuses on setting the right atmosphere for businesses to succeed and attain their projected goals. The selected host country is Australia which is situated between South Pacific and Indian Oceans. Amazon operates within the e-commerce industry; therefore, analyzing the market size and growth is crucial to determine its attractiveness and competitiveness. The size of the e-commerce market in the U.S is nearly $432 billion and had been growing since 2017, as demonstrated in figure 2 (IBISWorld, 2021). Conversely, the market size of e-commerce in Australia is approximately $27 billion and has been growing, as disclosed in figure 3. The CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of the e-commerce industry in the United States is projected to be 4.68%, while in Australia, it is expected to be 10.3% (IBISWorld, 2021). This means that Australia has a high growth potential arising from the need to take advantage of the coronavirus impact on online businesses.
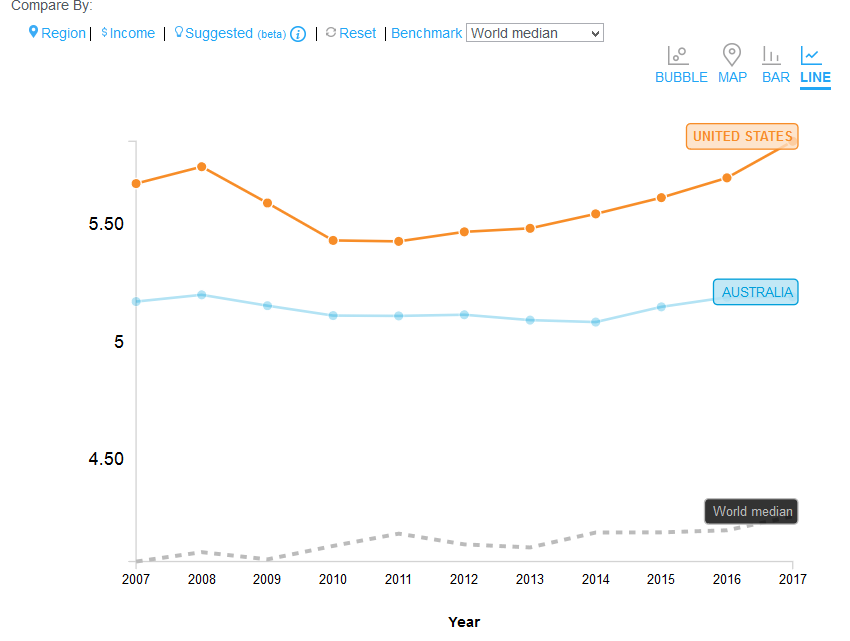
Based on the World Economic Forum Rank, United States is ranked second, revealing how the home market is highly competitive to enhance business growth. Despite ranking 16th within the World Economic Forum, the Australian market is highly competitive to spur growth and innovation within businesses (World Economic Forum, 2021). The Global Competitiveness Index of the U.S is 5.85 while that of Australia is 5.19, as shown in figure 4, thus disclosing that the United States has a higher macroeconomic performance than Australia (The World Bank, 2021). The two countries’ economies are capable of generating prosperity for the citizens to promote good living standards.
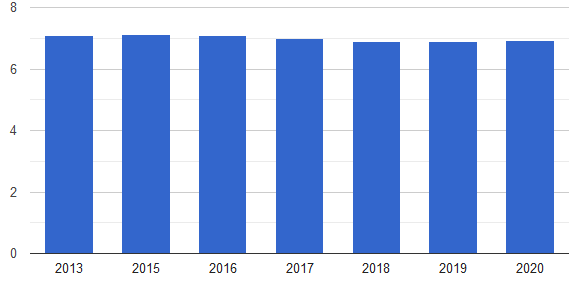
The world happiness report ranks the United States at position 19 while Australia is placed at position 11, inferring that Australians are happier than Americans (Countryeconomy, 2021). The average value of happiness in Australia has slightly dropped from 7.35 points in 2013 to 7.22 points in 2020, while that of the United States dropped from 7.08 in 2013 to 6.94 in 2020, as shown in figures 5 and 6 (The Global Economy, 2021). Consequently, the Australians have high expectations and consider the economy capable of meeting their needs and demands, leading to high happiness.
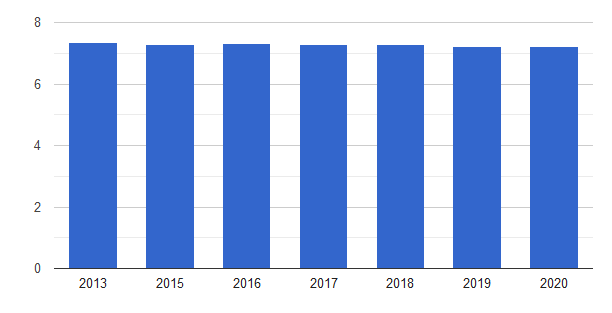
The Global Innovation Index ranks America at 3rd position while Australia ranks 23rd, implying that the United States is more innovative, hence creating more quality products (Global Innovation Index, 2020). Additionally, the Sustainable Development Goals Index ranks the United States at position 31 with a score of 76.43, while Australia is placed at position 37 with a score of 74.87 (Sustainable Development Report, 2021). Lastly, Hofstede’s cultural dimensions for the United States and Australia are as shown in figure 7.
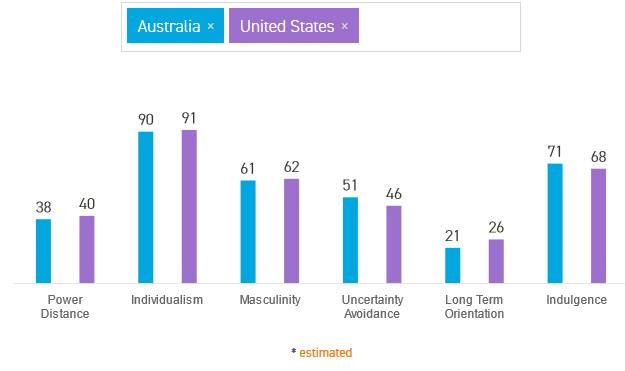
The power distance score for the United States is 40 while Australia scores 38, implying that the two countries have low power distance scores hence value power distribution and decentralized decision-making. The scores for individualism and masculinity are high and almost equal for the two countries revealing that people concentrate on attaining individual goals, material fulfillment, and establish discrete gender roles. The uncertainty avoidance for the U.S is 46, while Australia has a score of 51. Consequently, Australia has a low tolerance for risk-taking and uncertainty, leading to strict regulations compared to the U.S, with high acceptance for risks (Hofstede Insights, 2021). Lastly, the long-term orientation for the two countries is low, while the indulgence score is high.
The environmental scanning and competitive attractiveness regarding the chosen market help individuals in making the right investment decisions. Based on appendix 1, Australia is a good destination to invest in due to its good political and economic stability that boosts the possibility of attaining the anticipated objectives. The high population creates room for a large customer base to increase the sales volume of Amazon in the new market (Lo and Alena, 2018). The high literacy rates offer a chance to acquire a quality workforce that matches the organizational needs. Additionally, the advancement in technology in Australia allows e-commerce to be successful in accessing more customers. The numerous regulations and focus on the environment permit organizations to engage in healthy competition and avoid illegal practices.
The new market appears to be attractive as it can generate high profits and competitive advantage to surpass the potential competitors, as demonstrated in appendix 2. As a result, Amazon should consider capitalizing on the strengths and opportunities in the Australian market to overcome the associated threats and weaknesses, as revealed in appendix 3. This will boost the company’s success in the market and compel it to expand to other new geographical regions.
Internationalization Approach and Method
Internationalization compels organizations to consider operating in the international market while also maintaining their local presence to boost productivity. The internationalization process requires choosing the right country to expand to, carrying out comprehensive market analysis, and identify the correct entry strategy to remain successful (Ciravegna et al., 2019). However, various factors compel organizations to operate within the international market, as shown in figure 8.
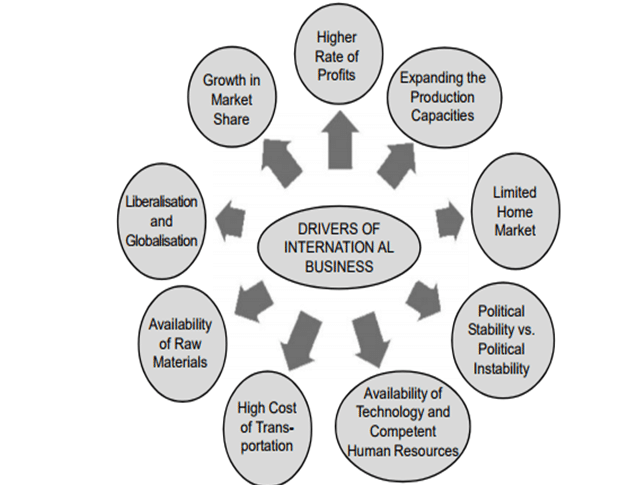
Drivers of Internationalization
One of the internationalization drivers is cost drivers, as most organizations are focused on minimizing their expenses to attain higher profits. The cost drivers mostly arise from favorable logistics that make it easy to reach out to clients. Expanding to the international market may generate scale economies that lead to efficient production due to cheap and quality labor (Ciravegna et al., 2019). Secondly, technological drivers create the need for internationalization as companies choose to capitalize on the new technologies and innovations to meet the projected goals. Thirdly, market drivers compel organizations to operate in the international scene to tap into new and unsaturated markets (Dabić et al., 2019). Lastly, knowledge-related motives enable organizations to engage in internationalization to boost their innovation capabilities, language skills, and research and development processes.
Internationalization Approach
The internationalization approaches entail how organizations would like to operate in the international market to exploit the potential opportunities. This is achieved by adopting the fitting tactic to increase the chances of success in the novel market (Djodat and Knyphausen-Aufseß, 2017). Based on the Bartlett and Ghoshal Model, organizations willing to engage in international operations should utilize local responsiveness and global integration, as shown in figure 9.
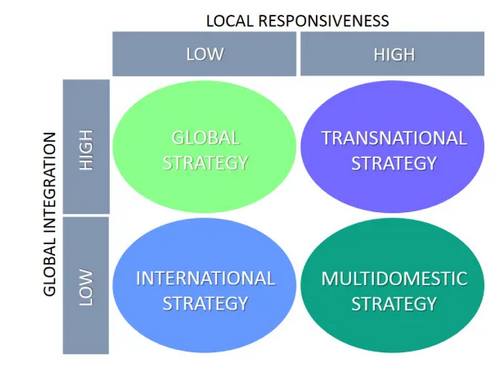
The two critical factors identified by the model yield four strategies that demonstrate how companies can operate their international businesses. The approaches that a company can choose to adopt to remain successful entail transnational, international, global, and multi-domestic approaches (Djodat and Knyphausen-Aufseß, 2017). The strategies are mutually exclusive and determine the appropriate organizational structure a company should adopt to attain efficiency, as shown in figure 10.
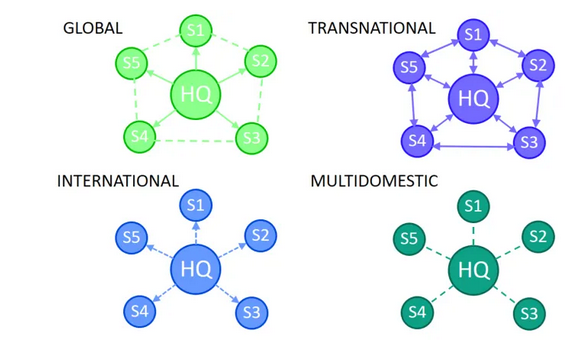
The transnational strategy appears to be the most appropriate strategy to adopt as it compels a company to act as a multi-domestic and global organization. As a result, Amazon should consider acquiring the transnational approach while operating within the Australian market to increase local responsiveness while attaining global integration benefits. This will ensure that the company meets the demands and requirements of local customers in the new market through customization while determining ways of keeping the costs low (Verbeke, Coeurderoy and Matt, 2018). The company will be required to utilize the value chain to produce economies of scale and remain highly adaptive to local demands.
Mode of Entry
The perfect entry mode that Amazon should utilize is a wholly-owned subsidiary, which will entail establishing a subsidiary company in the Australian market entirely owned by the parent company. This will ensure that Amazon retains the strategic and operational control over the new company to enhance smooth and shared decision-making. The foreign-owned subsidiary will be capable of filling some positions with local employees to enhance adaptation to the market to understand the customers better to prevent unnecessary resistance (Ko, 2019). Additionally, the subsidiary will allow sharing of resources to overcome the potential investment challenges while also obtaining guidance from the parent company.
Company’s Growth in the Foreign Market
The company’s management team should utilize Denison and McKinsey’s 7S models to ensure that the plan remains successful in the foreign market. The Denison model associates the organizational culture with performance measures, thus creating a need for internal and external focus while maintaining flexibility and stability. According to the model, effectiveness in organizations is based on consistency, involvement, adaptability, and mission. The involvement trait requires the company to engage employees in all activities and build teams. The consistency trait compels Amazon to ensure that all activities are integrated and coordinated to produce high levels of commitment within the employees (Wahyuningsih et al., 2019). Additionally, adaptability requires the company to transform the environmental demands into actions to offer value to customers. Lastly, the mission coerces Amazon to set a clear direction and vision to succeed in the new market.
McKinsey’s 7S model demonstrates how different organizational portions work together, thus the need to keep them aligned to achieve effectiveness. The model categorizes the seven factors into soft and hard elements. The soft elements entail style, staff, skills, and shared values and happen to be intangible and are highly impacted by corporate culture (Demir and Kocaoglu, 2019). On the other hand, hard elements include systems, structure, and strategy and are affected by the management.
Conclusion
Expansion to the international market is vital as it allows organizations to reach out to a wider customer base, thus increasing profitability levels and competitive strength. A detailed analysis of the foreign market permits individuals to identify the associated risks and opportunities to make the correct investment decision and avoid losses. Companies willing to engage in internationalization should acquire a suitable strategy for the swift attainment of goals. Additionally, companies should always be guided by international business models to make the correct decisions to remain effective in the foreign market.
Reference List
Amazon (2021) About Amazon. Web.
Ciravegna, L. et al. (2019) “The timing of internationalization – Drivers and outcomes”, Journal of Business Research, 105(1), pp.322–332.
Countryeconomy. World happiness index 2021. Web.
Crespo, N.F., Simões, V.C. and Fontes, M. (2020) “Competitive strategies and international new ventures’ performance: Exploring the moderating effects of internationalization duration and preparation”, BRQ Business Research Quarterly, 23(2), pp.120–140.
Dabić, M. et al. (2019) “Pathways of SME internationalization: a bibliometric and systematic review”, Small Business Economics, 55(1), pp.705–725.
Demir, E. and Kocaoglu, B. (2019). The use of McKinsey s 7S framework as a strategic planning and economic assessment tool in the process of digital transformation. Pressacademia, 9(9), pp.114–119.
Djodat, N. and Knyphausen-Aufseß, D. (2017) “Revisiting Ghoshal and Bartlett’s theory of the multinational corporation as an interorganizational network”, Management International Review, 57(3), pp.349–378.
Global Innovation Index 2020 report. Web.
Helmold, M. et al. (2020) Successful international negotiations: a practical guide for managing transactions and deals. New York, NY: Springer.
Henry, A.E. (2018). Understanding strategic management. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Oxford Univ. Press.
Hofstede Insights (2021) Compare countries – Hofstede insights. Web.
IBISWorld (2021) IBISWorld – e-commerce market research reports & analysis | MarketResearch.com. Web.
Ko, S.J. (2019) “The differing foreign entry mode choices for sales and production subsidiaries of multinational corporations in the manufacturing industry”, Sustainability, 11(15), pp.1–18.
Lo, F.-Y. and Alena, K. (2018) “Entry timing into international markets: evidence from the Taiwanese service industry”, Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 31(1), pp.1059–1077.
Sustainable Development Report (2021) Rankings: The overall performance of all 193 UN member states. Web.
The Global Economy (2021) Global economy, world economy | TheGlobalEconomy.com. Web.
The World Bank (2021) TCdata360: global competitiveness index. Web.
Verbeke, A., Coeurderoy, R. and Matt, T. (2018) “The future of international business research on corporate globalization that never was….”, Journal of International Business Studies, 49(9), pp.1101–1112.
Wahyuningsih, S.H. et al. (2019) “Analysis of organizational culture with Denison’s model approach for international business competitiveness”, Problems and Perspectives in Management, 17(1), pp.142–151.
World Economic Forum (2021) Reports. Web.