Introduction
Amazon.com Inc. is an American multinational technology company that specializes in e-commerce, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence (Amazon, 2023). It was founded in 1994 and has since grown into one of the world’s largest and most valuable companies (Amazon, 2023). Amazon’s core business is its online marketplace, which enables customers to buy and sell products and services. Additionally, Amazon operates several other businesses, including Amazon Web Services, Amazon Prime, and Amazon Studios (Amazon, 2023).
This paper focuses on analyzing Amazon’s financial performance. First, the report focuses on analyzing the company’s balance sheets and income statements for the past three years. After that, the paper focuses on the evaluation of financial ratios.
Annual Reports Analysis
To analyze the changes in the company’s major accounts, a horizontal analysis of Amazon’s balance sheets and income statements for the years 2020-2022 is conducted (Amazon, 2020, 2021, 2022). The summary of changes is provided below.
Table 1. Annual Reports
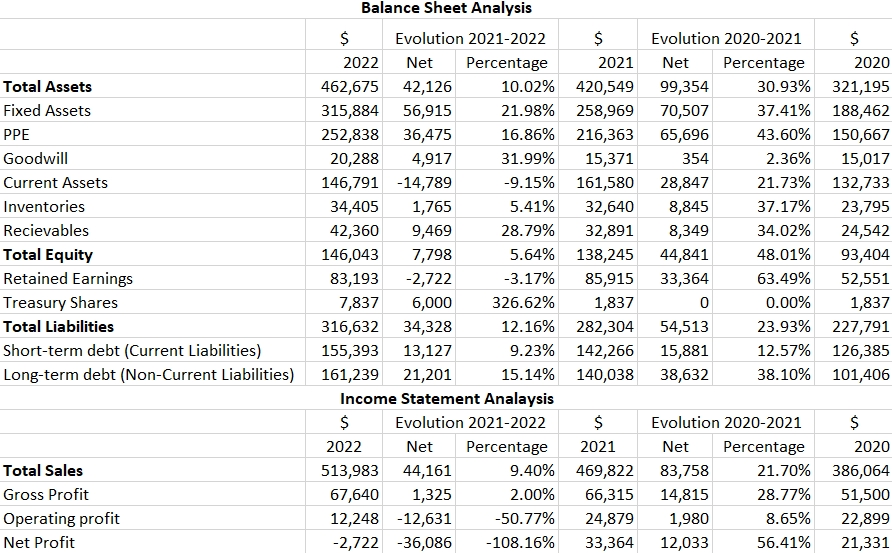
The analysis results showed a significant shift in the company’s assets in 2021. First, it is worth noting that Amazon’s total assets increased by 31% in 2021 compared to 2020, primarily due to the acquisition of Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, which was financed through both debt and equity (Amazon, 2022). As a result, the company’s PPE in 2021 increased by 43.6%, and shareholders’ equity increased by 48% compared to 2020. Additionally, it should be noted that Amazon issued additional shares in 2022, resulting in a 326% increase in treasury shares compared to 2021. Thus, the changes in Amazon’s assets were favorable.
The analysis of the income statement, however, demonstrated that the company’s profitability performance declined in 2022 compared with previous years. In particular, the company’s sales grew by only 9.4% in 2022 compared to 2021, which was disproportionate to the growth of operating expenses and sales costs. As a result, net income fell by 108.16%. In 2021, revenues increased by 21.7%, accompanied by a 56.41% growth in net profit. Therefore, the analysis of the company’s income statement revealed Amazon’s unfavorable performance in terms of revenues and costs in 2022 due to a decline in the e-commerce sector overall (Amazon, 2023).
Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis is a valuable tool for quantitatively analyzing a company’s financial health. It enables investors, managers, decision-makers, and other stakeholders to compare the financial performance of several companies in terms of value, profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and leverage (Tietz & Braun, 2018). Table 2 below presents Amazon’s performance metrics, including the debt-to-equity ratio, current ratio, quick ratio, return on equity, and net profit margin, based on data from Amazon’s annual reports (Amazon, 2021, 2022, 2023).
Table 2. Ratio analysis
The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations using its current assets. A current ratio of 1.0 or higher is generally considered healthy, as it indicates the company has enough current assets to cover its current liabilities (Tietz & Braun, 2018). In this case, the current ratio decreased from 1.14 in 2021 to 0.94 in 2022, indicating that the company’s current assets grew at a slower rate compared to its current liabilities.
The quick ratio is a more conservative measure of a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations, as it only considers the most liquid assets, such as cash, accounts receivable, and short-term investments (Tietz & Braun, 2018). In this case, the quick ratio decreased from 0.91 in 2021 to 0.72 in 2022, indicating that the company’s most liquid assets grew disproportionately in relation to its liabilities. Since both current and quick ratios were below 1, the company could face challenges in fulfilling its immediate financial commitments (Tietz & Braun, 2018).
The net profit margin measures a company’s profitability by calculating the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting all expenses, including taxes and interest (Tietz & Braun, 2018). In this case, the net profit margin decreased from 7.10% in 2021 to -0.53% in 2022, indicating that the company’s expenses increased more rapidly than its revenue.
The debt-equity ratio measures a company’s leverage, or the extent to which it is using debt financing compared to equity financing. A higher debt-equity ratio indicates a higher level of debt relative to equity, which could make the company more vulnerable to financial risk (Tietz & Braun, 2018). In this case, the debt-to-equity ratio increased from 2.04 in 2021 to 2.17 in 2022, suggesting that the company has taken on more debt relative to its equity.
Return on equity (ROE) evaluates a company’s profitability by indicating the percentage of profit generated from shareholders’ equity (Tietz & Braun, 2018). In this case, the return on equity decreased from 0.24 in 2021 to -0.02 in 2022, indicating that the company is not generating sufficient profit to compensate shareholders for their investment.
Conclusion
Overall, the financial ratios suggest that the company’s financial health may have deteriorated from 2021 to 2022, with decreases in the current ratio, quick ratio, net profit margin, and return on equity, as well as an increase in the debt-equity ratio.
References
Amazon. (2021). Annual report 2020. Web.
Amazon. (2022). Annual report 2021. Web.
Amazon. (2023). Annual report 2022. Web.
Tietz, W. M., & Braun, K. W. (2018). Managerial Accounting. United Kingdom: Pearson Education.