ADMC Business Department Quality Policy & the ISO9001:2008 Requirements
ADMC Business Department Quality Policy
Abu Dhabi Men’s College (ADMC) is one of the Abu Dhabi colleges known as the Higher Colleges of Technology (HCT) that provide the learners with the opportunity to study various disciplines in the environment full of advanced learning technologies. ADMC Business Department presents work-relevant, career programs in Business targeted at the development of highly valued skills. This department is considered to be the most innovative one. It has its own Quality Policy that is reviewed annually and sounds as follows:
The Business Department is fully committed to meet all requirements set by HCT and their External Accreditation Bodies, and it integrates all these requirements in an ISO 9001:2008 compliant Quality Management System to promote high-quality program delivery in a transparent, Student-centered working and learning environment where strategic goals, S.M.A.R.T. quality objectives inspire excellence and continuous improvement in all areas of teaching, professional development, applied research and community service (ADMC Business Department, 2014, p. 49).
Requirements of the Standard
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides standard requirements to the quality policy and emphasizes that all organizations that follow ISO 9001:2008 should use them as a guideline when developing the Quality Policy. According to it, top management is expected to ensure that the policy:
- “is appropriate to the purpose of the organization” (ISO, 2008, p. 4). The ADMC Business Department Quality Policy perfectly meets this requirement, as it takes into consideration HCT objectives.
- “includes a commitment to comply with requirements and continually improve the effectiveness of the quality management system” (ISO, 2008, p. 4). It is stated that the department values the requirements, but the improvement of the quality management system is not mentioned even though it is emphasized further.
- “provides a framework for establishing and reviewing quality objectives” (ISO, 2008, p. 4). This requirement is met, and the areas for continuous improvement are defined. Except for that, it is emphasized that the objectives are to be SMART and targeted at excellence encouraging.
- “is communicated and understood within the organization” (ISO, 2008, p. 4). It is mentioned that the Business Department is committed to the requirements and that it will be spread in all areas.
- “is reviewed for continuing suitability” (ISO, 2008, p. 4). The policy is claimed to be reviewed every year, but its content does not include this information.
It can be concluded that the ADMC Business Department Quality Policy meets the requirements provided by ISO (2008), but it would be better to add the information regarding the policy improvement and revision.
Quality Policy for the ADMC Business Department
A new Quality Policy for the ADMC Business department following the ISO 9001:2008 requirements will not face enormous changes because the seniors made it rather efficient. Still, after adding some missing information, it could look as follows:
The Business Department is fully committed to meet all requirements set by HCT and their External Accreditation Bodies, and it integrates all these requirements in an ISO 9001:2008 compliant Quality Management System that will be continually improved to remain effective and suitable and to promote high-quality program delivery in a transparent, Student-centered working and learning environment where strategic goals, S.M.A.R.T. quality objectives inspire excellence and continuous improvement in all areas of teaching, professional development, applied research and community service.
ADMC Business Department Quality Objectives
Two ADMC Business Department Quality Objectives
The ADMC Business Department has a range of quality objectives. The primary two deal with the student and quality satisfaction and effectiveness of the quality management system. They look as follows:
- Quality Objective 1: Improve Student and Faculty Satisfaction
- Quality Indicator 1.1. Student satisfaction with Management, Teaching, Learning, and Support Services. The Business Department uses its own surveys to obtain feedback from its Students. The first measurement will set a base; the next measurements should show certain improvements based on the requirements of a subsequent Management Review. The indicator is if there has been an improvement or not. (KPI = Y/N)
- Quality Indicator 1.2. Faculty Satisfaction with Management, Teaching, Learning, and Support Services. The Business Department uses its own surveys to obtain feedback from its Professors. The first measurement will set a base; the next measurements should show certain improvements based on the requirements of a subsequent Management Review. The indicator is if there has been an improvement or not. (KPI = Y/N)
- Quality Objective 2: Improve the Effectiveness of the Quality Management System
- Quality Indicator 2.1. ISO 9001:2008 Certification Status. The Business Department should achieve ISO 9001:2008 Quality Management and Leadership certification by June 2013 and maintain certification status through successful surveillance visits afterward. (KPI = Y/N).
- Quality Indicator 2.2. Continuous Improvement of the Quality Management System. The Business Department should continually improve its Processes and Forms to meet and exceed Faculty expectations about the usefulness and effectiveness of the Quality Management System. Business Department meetings will discuss the QMS every year and make recommendations for improvements, and then a subsequent Management Review will make a decision on the required changes. The indicator is if the change has taken place, or not. (KPI = Y/N) (ADMC Business Department, 2014, p. 51-52).
SMART & ISO 9001:2008 Requirements
The objectives presented by the ADMC Business Department follow the requirements for SMART objectives and ISO 9001:2008 are consistent with the quality policy (ISO 9001 quality objectives, 2015). They are implemented at appropriate levels, which provides an opportunity to meet the Quality Management System requirements and receive student and faculty feedback that can be used for improvement. The objectives are measurable and the formula for assessment is provided (SMART objectives, n.d.).
SMART Quality Objectives for ADMC Business Department
The ADMC Business Department may also consider such SMART objectives as:
- Improve coordination. Department managers should update and add new information to the ADMC’s website monthly on the first Monday and publish it by the next week. After publishing, out-dated information should be archived. Evaluate the webpage on the last Friday each month to ensure that the materials are up-to-date, design meets the ADMC standards, and the site is easy to navigate. Indicator is if there has been improvement and changes, or not. (KPI = Y/N).
- Improve Professional Development Program. Department managers should evaluate student satisfaction with the current Professional Development Program at the end of the semester and adjust it to their needs before the next semester begins. Student satisfaction should be measured again at the end of the following semester to see if the changes altered the situation. Indicator is if there has been improvement, or not. (KPI = Y/N).
Key Processes for Teachers
Policy Statement
The teachers who work at the ADMC Business Department are required to deliver education. In this framework, the teachers are required to follow key processes that are connected with assessment and plagiarism.
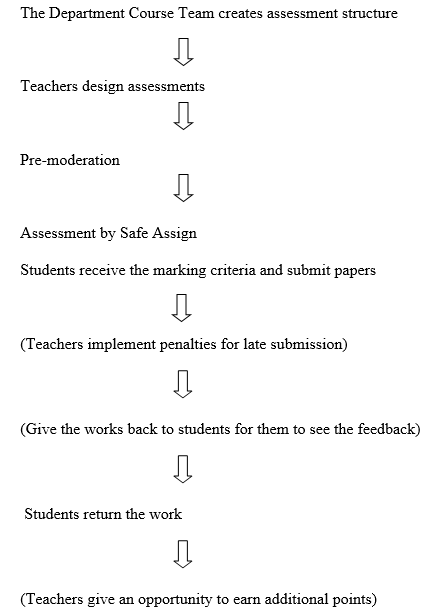
Developing Assessment Instruments – The Department Course Team Leader is the person responsible for the particular structure of assessments. One uses general CSA templates and then transfers the information to the teachers. In case, an educator conducts the course alone, all specifications are to be considered with the Academic Coordinators. The teachers create their own detailed assessments for each section without combining classes.
For Quantitative Courses, Formula Sheets are needed. The assessments and marking schemes as well as assignment instructions are to be signed and uploaded before utilized. It is considered to be a pre-moderation. The teachers should provide the students with the marking criteria detailed enough to allow self-assessment. One can use special rubrics to streamline the work. The Section Calendar should be maintained, and home assignments should be assessed by Safe Assign. A teacher should implement penalties for late submission of the papers without any justification. Paper assignments may be given to the students for them to see the feedback but they are to be returned and kept for a year. A teacher may give an opportunity to earn additional points but only at the end of the semester (ADMC Business Department, 2014, p. 218).
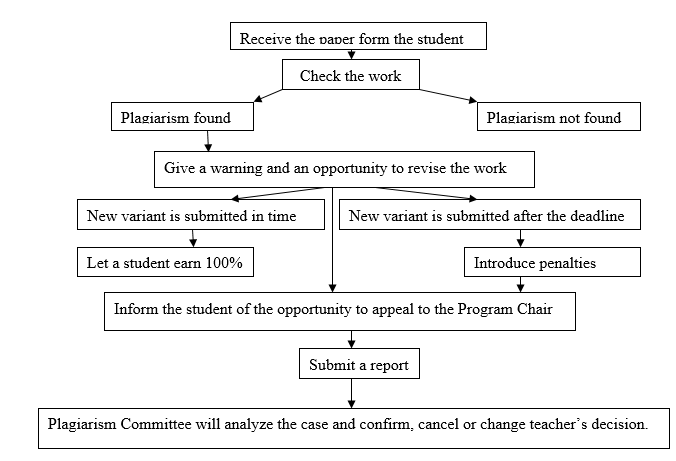
Plagiarism – All teachers are expected to check student’s works on plagiarism and give one a warning if it is found. A student should be given an opportunity to revise the work so that one can earn 100% if a new variant is passed in time. If the work is submitted in a week after the deadline, a student can receive only 95%. If it is submitted later, one can have only 65%.
If the plagiarism was detached twice in a raw, a teacher should cancel the assessment at all and mark it as 0. Then this educator informs the student of the opportunity to appeal to the Program Chair. If the student agrees, the teacher will submit a Report, and Plagiarism Committee will analyze the case and confirm or cancel teacher’s decision. It may also change this decision and suspend or dismiss the student (ADMC Business Department, 2014, p. 222).
Process Map
Assessment
Plagiarism
Following the Processes
Personally I believe that the teachers who work at the ADMC Business Department follow these processes perfectly. They all have access to the detailed information about the processes and the way they should be maintained. This work is cooperative that is why each teacher coordinates one’s actions with other professionals. Moreover, the educators are provided with templates for the reports, which streamlines their work. Finally, the processes are controlled by the seniors.
Guidelines for Appling the ISO9000 Certification
Steps to Achieve Certification
It is extremely important for every organization to prove that its products and services are of the high quality to receive customer’s trust, improve performance and achieve international quality recognition. ISO certification ensures that the company operates decently and follows the requirements of ISO 9001:2008. It can be gained from various certification bodies after the accomplishment of a particular procedure.
The certification process is rather long and it consists of nine steps:
- Top management commitment. Company’s top management team should decide to implement a quality management system and allocate resources needed for this (human, time, finances).
- Establishment of a quality team. A core team should be formed and a management representative appointed.
- Training and Awareness. A training plan should be established: awareness – for all workers, documentation – for the core team, internal auditors – minimum for three employees of the core team. Training programs can be conducted within a company or outside it.
- Review current systems & conduct gap analysis. Compare existing business systems with the requirements of the quality system and find out what is missing.
- Create the quality manual. Design quality policy, objectives and procedures.
- Implement the quality system and do the internal audit. Identify a start date and ensure that the training has been completed in 30 days. Evaluate documentation and processes.
- Conduct management review and on-site audit. Apply for certification, submit quality manual, pay charges, conduct management review meeting and ask certification body to do an on-site audit.
- Perform external audits. At first, the auditor will evaluate the situation and identify the gaps that should be filled. Then, one will assess the implementation and effectiveness of the system and conclude if the company passed certification. Some recommendations may be made.
- Certification. If the quality system meets the requirements of ISO 9001, a recommendation letter will be received and followed by the original certificate (Landerville, 2013).
Advice for Choosing Accreditation Body
There are different certification bodies, and companies are free to choose which one to appeal. In order to make a right decision, the organization should spend some time evaluating various opportunities. First of all, several accreditation bodies should be considered. It would be advantageous to compare them to each other so that their advantages and disadvantages can be identified. The organization should make sure that the certification body utilizes a relevant CASCO standard.
Then it is critical to check if it is accredited because it is one more proof of competence. The organization can refer to the national accreditation body to receive more detailed information and assistance. It is also possible to refer to the international accreditation forum.
Training
To achieve certification, the organization will need to provide training programs to ensure employee competence (ISO, 2008). Awareness training will make all workers understand the necessity of quality certification and its benefits. The employees will find out what changes they are going to face and how they can help the organization to achieve its quality objectives. Documentation training will make the core team efficient about the way different records will be maintained in regard to the instructions. Except for that several employees will be taught how to conduct internal audits and evaluate compliance. In this way, three training programs, including those that are web-based and held in classrooms, will be needed as a part of certification procedure (ISO 9000 training, n.d.).
References
ADMC Business Department. (2014). Quality Manual Version 5.0. Retrieved from ISO. (2008). Quality management systems – Requirements. Web.
ISO 9000 training. (n.d.). Web.
ISO 9001 quality objectives. (2015). Web.
Landerville, T. (2013). 9 steps to implementing ISO 9000. Web.
SMART objectives. (n.d.). Web.