Executive Summary
Persimmon PLC is a UK based house building company. It has been in operation since 1972. The company provides housing under three brand names, Westbury Partnerships, Charles Church and Persimmon Homes. The UK housing industry consists of a few dominant firms and many small companies serving small segments of the market.
Persimmon Homes is lucky to be one of the largest dominant firms of this housing industry. For example, according to the last year rates, the company sold close to 10,000 homes; such a result is definitely a huge progress and an immense success.
The external factors, which affect the UK housing industry, have a direct impact on Persimmon PLC. These factors include the economic downturn, lack of financing, sustainability and environmental concerns and government intervention. This paper will discuss those factors in detail.
Persimmon PLC has three major competitors, which are Barratt Developments PLC, Anvil Homes and Bellway Limited. We will compare their performance during 2011 in terms of operations, revenue generation, EPS and several other factors. The outcome shows that the strongest competitor of Persimmon PLC is Barratt Developments PLC. However, Persimmon PLC still has the competitive advantage of the large land banks.
The company draws its competitive advantage from five major sources. They are the land banks, the government partnerships, the brand equity, the scale of operations and a capable management team. This paper will discuss these sources in detail.
The investors have several options open to them if they execute a successful takeover. Michael Porter proposed that companies build competitive advantage using three methods. These are a cost leadership, differentiation and focus.
Introduction
Persimmon PLC is a UK based house building company. It has been in operation since 1972. The company provides housing using three brand names, Westbury Partnerships, Charles Church and Persimmon Homes. Each of these three subsidiary companies focuses on different market segments.
Persimmon Homes’ main occupation which plays a central role in its business is traditional stand-alone houses; Charles Church provides premium housing, while Westbury Partnerships engages in building low-end affordable houses.
This paper will seek to explore the strategic position of Persimmon PLC as well as the options available to a potential investor trying to find the answer to the question if they should be successful in a takeover (De Wit & Meyer, 2004).
The Industry Status and Competition
The UK housing industry consists of a few dominant firms and many small firms serving small segments of the market. Persimmon PLC is lucky one of the largest dominant firms at the market. Such a high position increases its competitive power. The company sold close to 10,000 homes last year. This is quite a high and impressive result in comparison to other market players.
As a matter of fact, Persimmon PLC has three major competitors at the market currently, Barratt Developments PLC, Anvil Homes and Bellway PLC. These three competitive firms hold slightly smaller market shares than Persimmon PLC does. They also compete directly with each of the three Persimmon Brands (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
Bellway PLC focuses on recycling and reclaiming British land. It competes directly with the Westbury Partnerships. However, Bellway PLC has a competitive advantage of its brand name because it is associated with creating sustainability. It sells approximately 5000 homes in a year. This places it in fourth position in the industry. Anvil Homes pays more attention to rural constructions building their houses.
The company is involved in converting barns and other farm structures into family homes. This makes it a direct competitor of Persimmon Homes. However, Anvil Homes has already cut a niche for itself in the country. Moreover, the company also focuses on building cottages.
Barratt Developments PLC builds family houses and apartments. Like Persimmon PLC, the company collaborates with the government to provide affordable housing for citizens. This company is the biggest competitor of Persimmon PLC. Their leadership in innovation has earned them several awards in the industry.
The company is slightly older than Persimmon PLC. It was established in 1958. Barratt Developments PLC also provides a luxury homes collection to rival Persimmons’ Charles Church homes. To spread its risks, Barratt Developments PLC has diversified into the US (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis
Threat of New Entrants
The threat of new entrants in an industry is determined by the economies of scale current players are experiencing, the level of product differentiation and the capital required to begin operations in the industry. The UK housing industry has relatively high barriers of entry.
The large firms such as Barratt and Persimmon already experience huge economies of scale due to widespread operations. They also have the advantage of experience. House building requires specialized machinery. An established firm spreads the use of such machinery over many projects and hence benefits more than a small entrant with only few projects.
Current industry players have employed differentiation to keep out prospective competitors. For example, Persimmon operates under three different brand names, Persimmon homes, Charles Church and Westbury Partnerships.
Barratt Plc on the other hand operates under the brand names of Barratt Homes, David Wilson Homes and Ward Homes. Each industry player has differentiated his or her products. This raises the barriers of entry further. There is a high capital requirement for this industry. Thus, the threat of new entrants is made weak by the entry barriers that keep them out.
Threat of Substitute Products
Substitute products serve almost a similar purpose as the industry product but may not be in the same product line. There are few substitutes for housing in the UK. The major alternative for owning homes is renting apartments. With the economic downturn, consumers have been unable to purchase as many houses as they used to. People are now turning to renting upmarket apartments instead.
The industry has recognized this trend and diversified into building these apartments. However, the major customer for such is not the lone homeowner. Usually, large real-estate developers purchase such buildings and rent out units.
The threat of substitute products is low. Apartments may be cheaper than traditional family homes, but those who can afford still prefer to build homes. People have to live somewhere and housing is an essential commodity. Low threat of substitutes increases the industry’s profit potential.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The power of buyers is low. There are very many buyers and the market is fragmented. House buyers seldom make collective purchase decisions in order to minimize costs. Usually, individual families decide what house to buy and which firm to purchase from. Commercial buyers have slightly higher power but they are rare.
Housing is a critical commodity. This gives the supplier an upper hand and reduces the buyer’s bargaining power. The recent problems with financing have driven housing industry firms to create innovative financing options for prospective buyers. This factor has also contributed to low buyer bargaining power.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is high if there are few suppliers and many buyers and if the product supplied is critical to the buyer’s business. In the UK construction industry, there are many independent suppliers. Raw materials can be sourced from within or outside the country. Suppliers often have to submit tenders or bids. The lowest and most convenient bid is chosen.
Skilled construction labourers have high bargaining power. They usually work on contract and seek to maximize their benefit from each contract. Their bargaining power is high because of their specialized knowledge.
Non-skilled workers have low bargaining power. The company can always lay them off and hire other workers. They try to increase their bargaining power by forming unions. Overall, the bargaining power of suppliers in this industry is low.
Competitive Rivalry within the Industry
This is the strongest force in operation within the UK housing industry. There are few dominant firms fighting to maintain their market shares. The smaller firms are competing in market growth. Companies have employed extensive product differentiation to crowd out competition.
They have also invested heavily in research and development. They compete on first mover advantage and innovation. Those who manage to innovate charge competitive prices on their houses. The green housing initiatives are the best example of innovation within the industry. High competitive rivalry reduces an industry’s profit potential.
External Factors and Trends Affecting the UK Housing Industry
Economic Downturn
The global economy suffered a massive downturn in 2008. Recovery has been painfully slow. The European credit crisis has also greatly affected economic conditions in the UK. Consumers are spending less. Unemployment is on the rise.
This has a definite impact on the housing sector. Reduced disposable income means people have less money to spend on housing. This in effect contracts the housing market (Bartlett, Ghoshal &Beamish, 2008).
Government Schemes
The government has tried to encourage home acquisition despite the poor economic conditions. There are several schemes, which have been put in place to facilitate this. They include New Build Home Buy, Open Market Home Buy, Social Home Buy and Cash Incentive Schemes.
The government has forged partnerships with home building companies such as Persimmon PLC and Barratt Developments PLC in order to execute these schemes. These partnerships are opportunities for growth that did not previously exist (Bellway PLC, 2011).
There has also been a tax holiday for stamp duty on new investments. This enabled investors to save between 1250 and 2500 pounds.
This scheme is now ending but it has created increased demand for homes. There are still some buyers rushing to take advantage before it closes in March. Though the housing industry has faced difficult times, it has also received government support to aid its survival and prosperity (Barratt Developments PLC 2011).
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
There is a shift in all industries towards environmental friendly operations. The housing industry has also been affected by this trend. People want houses that have the minimum possible negative influence on the environment. Global warming and the resultant climate change have caused consumers to be more conscious in their purchasing (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
Companies are now forced to invest heavily in Research and Development to create innovative green housing solutions. Such innovations could reduce the amount of waste sent to landfill, increase recycling, create energy efficient homes and create renewable energy. The current industry leaders are also leaders in innovation and environmental consciousness.
There are various certifications and awards issued annually to encourage this trend. Companies literally compete for these since it proves to consumers that they are doing something about the situation. The Code for Sustainable Homes serves this purpose in the UK. Many industry players have adopted this principles based approach (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
Financing
The Global Financial Crisis in 2008 resulted in the collapse of major banks such as The Lehman Brothers. The banks that survived put a tighter leash on lending to avoid similar pitfalls. This means that consumers today find it harder to obtain mortgages.
Very few people can afford to pay cash upfront for investment in housing. Thus, reduction in the availability of mortgages also results in a smaller housing market (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
Increased rates of unemployment prevent people from having a constant source of income. Without a payslip or any collateral, it is difficult to obtain a mortgage and thus own a home. The housing industry has to come up with creative solutions to assist their customers purchase houses (Johnson, Whittington & Scholes, 2011).
Performance of Persimmon PLC Compared to Competitors
This section of the essay will compare Persimmon’s performance to two of its major competitors: Bellway PLC and Barratt Developments PLC. The third major competitor, Anvil Homes is a private company. This company’s financial information is not publicly available.
The figures all relate to the 2011 financial year. Different aspects of performance will be measured. The Persimmon PLC figures are double the half-year results issued in November 201. These are the most current figures. The assumption is that all revenues and expenses accrue evenly over the year.
Revenue
Revenue measures the amount of income a company is generating, especially from operations. In this measure, Barratt Developments PLC performed better than both Persimmon PLC and Bellway. Barratt Developments PLC sold almost 30% more than Persimmon PLC (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
This is a huge margin. Barratt Developments PLC has the advantage of innovation and strong brand recognition. It has also diversified greatly. Persimmon PLC should come up with strategies to close this gap (Barratt Developments PLC, 2011).
Dividend
The dividend indicates the return shareholders receive for their investment during that period. For shareholders, the higher the dividend, the better. Bellway PLC paid out the highest dividend at 12.5p, followed by Persimmon PLC at 8p, and finally, by Barratt Developments PLC at 5p (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
However, some shareholders view non-payment of high dividend as a sign that the company is investing the profits for long-term share price growth. This could be the strategy adopted by both Persimmon PLC and Barratt Developments PLC (Barratt Developments PLC, 2011).
Operating Profit
This is a clear indicator of how much the company is profiting from its operations. It is the difference between the revenue and operating costs. Barratt Developments PLC posted the highest operating profit at 127.3 Million Pounds. It was closely followed by Persimmon PLC with 119.4M. Bellway’s operating profit of 50.144M was barely half of Persimmon’s (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
The difference in the Persimmons and Barratt Developments PLC operating profit is 8%. The difference in their revenues was 30%. This means that either Barratt Developments PLC has very high operating expenses or Persimmon PLC is more efficient in managing its costs. If the latter is true, then Persimmon PLC has some competitive advantage over Barratt Developments PLC.
Houses Legally Completed
The number of houses legally completed is a measure of the operational efficiency and productivity of the company. These companies compete based on houses sold. The more houses a company can complete, the more it can sell. The result is higher revenues and thus profits (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
Barratt Developments PLC is leading with 11,171 houses legally completed. Persimmon PLC is in second place having completed 8,878 houses. This is 80% of the work done by Barratt Developments PLC. This difference could explain the 30% difference in revenue.
Persimmon PLC should expand its capacity to enable it complete the same number of houses as Barratt Developments PLC. Technology can be used to speed up the cost of construction (Anvil Homes, 2012).
Land Bank
The land bank refers to the amount of land a company has that is available for construction. It represents capacity to expand. Land is also an asset, which appreciates.
The more land in the land bank, the higher the value of this asset. Persimmon PLC is leading in this department by a very small margin. The company should keep acquiring more land in prime areas to widen the gap between them and their competitors. Bellway PLC is trailing with 18,086 plots.
Earnings Per Share
The EPS indicates how productive the investment by shareholders has been during the year. It depends on how management has employed such resources. A high EPS indicates more productive the resources. EPS is obtained by dividing the net profit by the total number of shares (Persimmon PLC, 2011).
Barratt Developments PLC is leading with a huge margin. All factors constant, this means that it is earning the highest return for its shareholders. Bellway is the second, with an EPS that is almost 50% of Barratt’s EPS. Finally, Persimmon PLC is trailing with an EPS of 31p.
A low EPS could be attributed to a high number of shares. If this is the cause, then Persimmon PLC should reduce its use of equity financing and use more debt instead. This will help reduce shareholder dissatisfaction over low EPS.
Competitive Advantage
Persimmon PLC has several sources of competitive advantage. The first is the large land banks, which the company controls. Currently, Persimmon PLC has the largest land banks among its competitors. These land banks represent expansion capacity.
This means that given the right conditions, the company can grow to be much larger than its competitors are. The gap between the competitors and Persimmon PLC in terms of land banks is not very significant. The company should purchase more plots to widen the gap and thereby strengthening their competitive advantage (Bartlett, Ghoshal & Beamish, 2008).
Secondly, Persimmon PLC has an established brand name. The Charles Church brand is associated with up-market luxury homes. Prospective homeowners seeking luxury homes are likely to hire this company due to its brand name. This name can be enhanced by advertising in exclusive places. The major threat to this brand is the rival Barratt brand.
Westbury Partnerships and Persimmon Homes are also well known in the country. They have cut out niches for themselves in the property market. Their major competition is the small industry players. The company should seek to personalize these brands to the consumers in order to increase brand equity (Mintzberg, Lampel & Ghoshal, 2003).
Thirdly, the company has excellent sustainability policies. If properly implemented, these policies could lead the company to greater heights. They respond to operational, environmental and stakeholder needs. In the operational sector, the company seeks to minimize its operational wastes and recycle where possible (Haberberg & Rieple, 2007). This will reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Persimmon PLC also seeks to build sustainable communities. This goal recognizes the human need for social interactions. It also bears in mind that these communities are Persimmon’s customers and therefore revenue sources. Persimmon PLC also tries to build the capacity of its workers. This policy recognizes the fact that people make a company (Hitt, Ireland & Hoslisson, 2008).
The government is the biggest consumer in any economy. Persimmon PLC has partnerships with the government to promote home ownership. In the NewBuy scheme, the Government backs 95% of the mortgage to enable new homeowners acquire houses.
This has increased the customer base for the Westbury partnerships division. Such associations with the government help to create a positive image for the company and enhance its brand equity (Barney, 2002).
Persimmon PLC has a large scale of operations. This is a source of competitive advantage since it allows the company to benefit from economies of scale (Kay, 1993). Persimmon PLC can achieve great efficiencies in construction due to learning curve effect. They can also negotiate for bulk discounts from suppliers. Economies of scale help to reduce costs hence increase operating margin
Finally, the company has a capable and experienced management team. The company management is divided into the Northern, Central and Southern Divisions. They each have a regional Chairman, financial Director and Chief Executive. This team meets regularly to strategize and plan.
The workers on the ground are also well trained. This is one of Persimmon’s sustainability policies. The capability built in these people offers great competitive advantage as noted by Barney (2002).
Persimmon Swot Analysis
A swot analysis examines both internal and external factors that are critical to a firm’s success. This analysis will aid in making strategic choices.
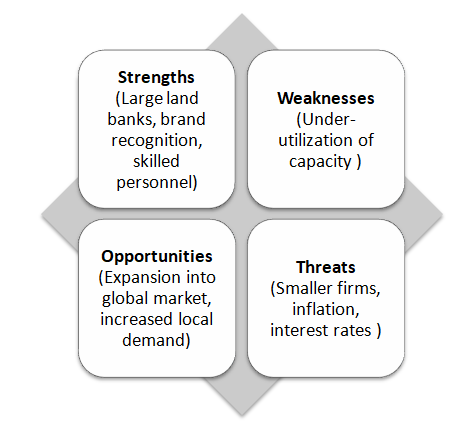
Strengths
Persimmon has large land banks that are available for development. It can use this resource to increase market share in the industry. Their brand is also recognized countrywide. This brand equity is an important intangible asset. Persimmon has a highly skilled management team and Board of Directors. They provide leadership to the company.
Weaknesses
Weaknesses are factors under the company’s control, which can prevent it from achieving corporate goals. Persimmon is underutilizing its land banks. The company may lose market share by failing to develop its land. The company also constructs houses at a slower rate than its competitor Barratt does. This could be due to internal inefficiencies.
Opportunities
Persimmon can take advantage of globalization to enter foreign markets. The company can use its experience in UK as leverage. The demand for luxury housing is also increasing. Persimmon has an opportunity to expand its Charles Church division.
Threats
The macro-economic environment is the greatest threat to Persimmon. Rising interest rates will make it difficult for prospective customers to obtain mortgages. The company may also have trouble accessing credit. Inflation may force consumers to spend less and reduce persimmon’s revenue.
Strategic Options
The investors have several options open to them if they execute a successful takeover. Michael Porter proposed that companies build competitive advantage using three methods. These are cost leadership, differentiation and focus.
Differentiation
This is the most appropriate option for Persimmon PLC. The company has already started operating along these lines. The investors would seek to create brand loyalty by providing special features in their housing products. This brand loyalty will create repeat purchases and referrals. This will increase Persimmon’s sales and profitability.
This strategy is appropriate because the company already has three different established brands. The investors can create other brand s to compete with their current brands. The purpose of such a move will be to crowd out competition. A differentiation strategy also provides options for the company. In case one product line is failing, the company can still profit from the others.
Focus
The investors can adopt a focus strategy. This means they work to meet the needs of only one specific segment of the market. In Persimmon’s case, they would need to divest in two divisions and retain one, preferably the Charles Church line. This line serves the high-end market, which is less prone to market fluctuations.
A focus strategy requires high specialization. The company would have to invest in Research and Development to meet the needs of the chosen target market.
Cost Leadership
This strategy requires Persimmon PLC to maximize construction and operational efficiency in order to minimize costs. The company will end up selling products at a lower price than competitors sell.
Such a strategy will appeal only to low-end consumers and the government. If the investors adopt this strategy, they cannot sell to the high-end homeowners. This may result in reduced revenues.
Reference List
Anvil Homes. 2012. Web.
Barney, J. 2002, Gaining and Sustaining Competitive Advantage. Pearson, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Barratt Developments PLC 2011, Annual Report 2011. Web.
Barratt Developments PLC 2011, Sustainability Report 2011. Web.
Bartlett, C. A., Ghoshal, S. & Beamish, P. 2008, Trans-national Management: Text, Cases, and Readings in Cross-Border Management, McGraw-Hill, London.
Bellway 2011, Annual Report 2011. Web.
De Wit, B. & Meyer, R. 2004, Strategy: Process, Content, Context, Thomson International Business Press, London.
Haberberg, A. & Rieple, A. 2007, Strategic Management: Theory and Application, Oxford University Press (SMTA), London.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D. & Hoslisson, R. E. 2008, Strategic Management Competitiveness and Globalization, Thomson, London.
Johnson, G., Whittington, R. & Scholes, K .2011, Exploring Strategy Text & Cases, FT Prentice Hall, New York.
Kay, J. 1993, Foundations Of Corporate Success – How Business Strategies Add Value, Oxford University Press, London.
Mintzberg, H., Lampel, J. & Ghoshal, S. 2003, The Strategy Process, Concepts Contexts Cases, Oxford University Press, London.
Persimmon PLC 2011, Annual Report 2010. Web.
Persimmon PLC 2011, Annual Report 2011. Web.
Persimmon PLC 2011, Sustainability Report 2010. Web.