Cause and effect diagrams help us understand processes of bead production at the company. This will enable us identify, explore and graphically display all the possible causes and related problems of bead production. The processes involve four stages. We shall use the information six team members gave in their reports so as to identify categories of cause and effect relations (Rose, 2005).
Cause and effect seeks to identify and define the problem. It also looks at the extent of the problem under scrutiny. The method works better when limited to specific areas. This is because it may be difficult to understand multiple and broad areas in production processes.
The next element of processes of production looks at the major categories of causes. The analysis process identifies that causes of a problem consist of unique sets of varied problems. There are general categories causing problems in the production processes. These categories consist of people, machines, procedures and policies.
However, for effective analysis, the process should only look at the relevant category of causes, which are specific to the problem. For instance, the control chart at Beads R Us analysis shows that the system (machine) is stable and shows predictable results. Therefore, the investigator rules out system-causes and focuses on other categories such as people.
The analysis process decomposes major causes down to several levels. The decomposition process provides a careful analysis of each cause and determines the elements within the category that might cause the problem under investigation. Decomposition process further goes to analyze the sub-elements that might be contributing to the problem.
This process goes on till the investigator is sure that the analysis process is complete. For example, in people-cause problems, the project analysis focuses on variables related to training, apprenticeship period, and motivation, among other elements.
The final process of analysis dwells at identification of root causes. A review of cause and effect diagram reveals multiple occurrences of problem causes. A problem may arise from a variable with multiple occurrences in various production processes.
The Bead R Us production processes reveal no system, performance defects. The system elements interact, but the red beads determine results. The system produces predictable results. Therefore, influence of system on the results in this process is negligible.
At the same time, some factors that are most likely to influence performance, but are not relevant, and have no effect to system performance include excessive inspection, quotas, slogans, exhortations to perform well, rewards and punishments, and management by facilitators. Therefore, a normal system at 85% should determine the performance of a worker, while rest 15% depends on the worker’s effort in performing well. This indicates that there are no aspects of production beyond a worker’s control.
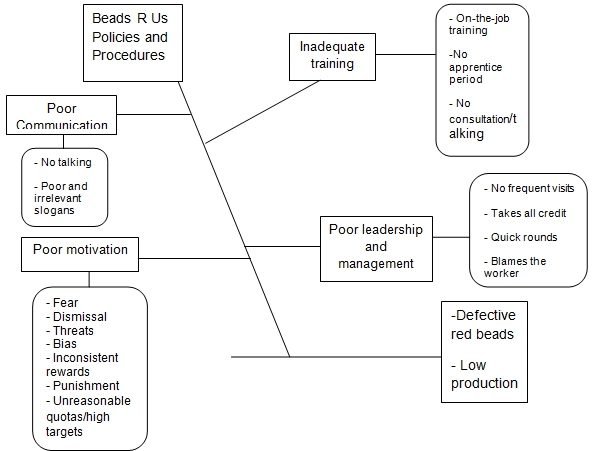
The report of the six team members shows various categories that create problems resulting into defect beads. The report identifies that training is inadequate. The process at Bead R Us does not give new workers any training opportunities. Beads R Us has a policy of on-the-job training whereby new workers join the work force and copy what the next worker is doing.
The company only provides a short training and promises apprenticeship opportunities. The subsequent process breaks the apprenticeship period and workers have no apprenticeship periods. At the same time, new workers who replace dismissed workers get no training but instead join other line of workers.
The report also identifies communication breakdown in Beads R Us. The company policy does not allow workers to ask questions, or talk to each other while on duty. The company administers punishment to workers caught talking. This is rather difficult for new workers who should learn from the job. The company sees talking as frivolous behavior. Therefore, payment is strictly for working not talking.
There is poor management at Beads R Us. Management has a tendency to take all the credit when the process is satisfactory. Conversely, management blames and threatens workers with punishment when there are mishaps.
There is also lack of leadership at Beads R Us. Managers rarely come to the production line. However, when they come, they make quick rounds and tell workers to do well, or else workers will lose their jobs. This approach does not motivate workers.
Workers at Beads R Us work under poor work environment. The place is full of slogans, which workers have trouble understanding. They also do not know how to apply these slogans to improve their outputs. These slogans include Mistakes cost us money, Work hard, keep your job, We’re counting on YOU, and No defect is a good defect.
There are also unreasonable quotas at work. Management assigns quotas which are impossible to achieve. Further to this, the management constantly harps on the quotas and threatens to punish workers who do not make quota. The use of impossible targets only serves to discourage workers.
Finally, the six team members noticed that rewards are inconsistent and inequitable. For instance, two workers can have the same results, but one gets rewarded while the other does not. The management rewards a worker for excellence performance today and punishes the same worker for poor performance the next day. There are instant and on-the-spot bonus and immediate Employee of the Day tag to complement the best worker. The following day, the management fired the staff for poor performance.
Fig. 1: Cause and Effect diagram of categories of major causes of problems at Beads R Us
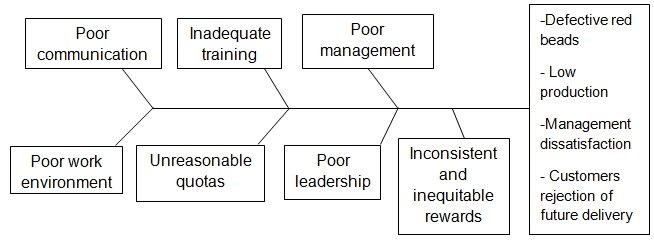
Fig. 2: Decomposition of category of policies and procedures at Beads R Us
Beads R Us produces high-quality plastic for commercial purpose. The production processes follow the red bead experiment the six team members cover. The process involves workers producing by dipping a paddle into a bin of beads, and they withdraw fifty at a time. The company process considers red beads to be defective.
Any withdrawal below fifty beads makes the management count the missing beads as defective. Beads R Us gets their supplies from Bead World. Beads World is among the top world suppliers. The supplier makes sure that they eliminate all the defective beads before delivering to Beads R Us (Rose, 2005).
This process of producing defective beads has made the management dissatisfied with the number of defects in the production process. At the same time, one of the major customers has informed Beads R Us that it will reject any future deliveries with defective beads of fifty in a single packet.
The production process of red beads includes these three elements, people (workers), materials (red and white spherical beads) and processes. In this regard, any shortcoming may arise from the three elements above.
It is necessary to note that before Beads World makes deliveries, it removes all the defective beads. Therefore, the materials do not have any defects. This makes them not to be a source of any shortcoming in the production processes. Likewise, the experiment shows that the system is performing within the expected range. The only thing that determines the system performance is the percentage of red beads in the bead mix.
For instance, the performance of 0.23 percent defects is within the normal system performance. However, if the system has any defect, then the company should stop blaming the workers. The 85/15 rule states that a system performance is responsible for 85 percent a worker’s output while the rest 15 percent depends on the individual worker. Any system shortcoming influence on production is beyond the control of the worker.
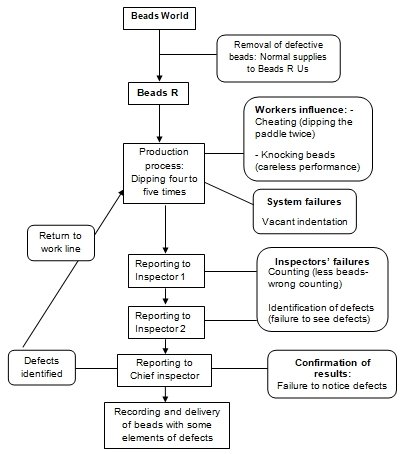
The production processes involve workers dipping the paddle into the container and producing a sample of fifty beads. The process goes on four to five times in order to simulate the number of working days. Every worker produces one sample each day. The workers report to the inspector who counts the defects (red beads or a vacant indentation). The workers then report to the second inspector, who further counts and looks for more defective beads.
The inspectors report to the chief inspector, who then checks the results of the inspectors. Any same results indicate agreement. The chief inspector records the number in the recorder. However, if there is any variance, the chief inspector counts the defects and puts the number in the recorder, then orders the workers to dump the beads back in the container and return to work. The recorder shows all workers performances by day.
The production processes also involve people (managers and workers). These people influence the production processes of beads. Workers get brief training with a promise of an apprenticeship period. Workers then join the production line with no period of apprenticeship. New workers who replace the dismissed workers also get no training. The facilitator then sets a high target of more than one red bead per day.
There are praises for good performances based on a very low number of defects, and condemnation or punishment for poor performances with dismissal. This involves a very high number of defects. This only serves to reduce workers motivation. They have no job security. Occasionally, the facilitator may use irrelevant slogans and urge the workers to perform better. However, after a couple of days with inconsistent and poor performances, the facilitator threatens workers with dismissal.
The point is that workers cannot meet their quotas of more than one defect per paddle. The participants include senior management team who the facilitator point out their poor performances to the rest of the work force. At the end of the workdays, the facilitator ends the operation and informs workers to collect their severance pay on their way out. A worker still has influence over results through careless acts. A worker may knock beads from the paddle during production. At the same time, a worker may also cheat by dipping the paddle twice.
Fig. 3: Flow chart to identify any shortcomings in the production processes of beads
According six team members findings, the production processes of beads at Beads R Us face several challenges. The primary sources of these challenges are mainly company’s policies and procedure, workers and managers, and occasional system failures. Therefore, any recommendation must address the above issues. All these factors contribute to the production and delivery of defective beads to customers.
Training and staffing is a major problem in Beads R Us. New recruits join the production line without any initials training or apprenticeship period. According to the results and company’s policy on talking, on-the-job training may not be effective for workers who must learn from others so as to perform.
Beads R Us must make training and staffing of its workers a part of its core overall strategies in building a reliable workforce. The company must identify the target results and changes that it wants from the behavior, knowledge, and attitude of its workers. Training and staffing must identify the current situation with regard to workers, system, and the nature of the work. Therefore, barrier to productivity at Beads R Us can better be eliminated by training (Dobson, 2001).
There is poor work environment. The company slogans and management fads are a source of constant threats and menace to workers. Likewise, workers have a problem understanding the fads and have no idea to implement them to improve production. These fads and slogans only serve to demotivate workers.
Therefore, the company must review its policies to enhance job satisfaction among workers. Beads R Us management fads tend to enhance a sense of inconsistency, which destabilize and disrupt workers performance. Slogans also have short lives and no longer relevant for motivation. The company must address motivators and hygiene factors like achievement, policies, recognition, wages and benefits, work relationships, challenges and working conditions. At the same time, the policy must allow for open communication among workers.
Leadership and management are poor. Managers tend to take credit for better performances and blame workers for poor performances with threats of punishment and dismissal. Inspectors rarely come, but when they do, they make quick rounds and threaten workers. The company is using management by wandering or walking-around approach.
This method works better when it promotes organization’s fluidity and supports the company model. However, it has failed at Beads R Us. Beads R Us should adopt management by objectives approach. The company must establish its mission statement to address issues concerning business, customers, value to customers, future of the business, and what the business should do. Management by objectives also specifies the business domain under which it will operate.
At the same time, it should motivate workers so that they also feel that their work is vital for the company. The company must stress its major policies that the management and workers must honor, such as valuing teamwork, and efficient production and valuing customers. Objectives must address issues of production, sales growth, profitability, innovation to reduce defective beads, market share, and others.
Beads R Us must understand the role of inspection. Inspection is necessary in quality management. Inspectors must check for beads at the end of production to ensure that they conform to specification. They must do this before the company delivers beads to the paying customer in order to avoid any rejections.
Management must use the results of inspection to deliver the beads, return beads to production processes, or discard the defective beads. Inspection at Beads R Us must play the roles of ensuring that the process goes as planned, with few nonconforming beads at the end of the production process.
Beads R Us should introduce in-process inspection in order to identify any defective beads before they result into lose of customers and costly reworks. Inspection must look at the physical characteristics of beads, examine beads for completeness (vacant indentation), and number.
There is also the issue of unreasonable quotas. Management at Beads R Us give targets which no one has ever achieved. At the same time, management harps on the quotas and threatens workers who do not achieve them. In this regard, Beads R Us must set realistic quotas, quantifiable and consistent. Management can then turn these objectives into specific action lists and measurement criteria for workers and managers.
The objectives must create a benchmark for evaluation purposes, which should be used for corrective purposes and changes in the production processes of beads. However, they must watch over tight focus on numbers. Otherwise, it will lead to management by fear as Dr. Deming calls it.
This will enhance short-term performances and ignore long-term planning objectives, and increases reliance of aspects of bead production that the inspectors can measure and ignores quality. This will reduce workers cheating and careless performances. Therefore, right management focuses will eliminate defects in the production processes of beads (Dobson, 2001).
Beads R Us has a policy of inconsistent and inequitable reward systems. Workers can have the same results, but one gets reward while the other one does not. A worker gets rewarded today for exceptional performance and dismissed the following day for poor performances. On-the-spot bonus and immediate pin declaring employee of the day are not effective in motivating. Poor performances must be corrected.
However, there should be some discipline to correct poor performance. If discipline fails to restore a worker’s performance to an acceptable level, then the management must use termination. The management should exercise discipline in the workplace, but with caution. Beads R Us must be consistent in the offenses that need discipline. Attacking nonperformance of a single worker and ignoring others results into conflict.
References
Dobson, M. S. (2001). Project Management for the Technical Professional. Pennsylvania: Project Management Institute, Inc.
Rose, K. H. (2005). Project Quality Management: Why, What and How. Florida: J. Ross Publishing, Inc.