Introduction
Porter’s five forces of competition framework entail the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and competitive rivalry. This tool is useful in the analysis of the competition within industries as well as the profitability of an industry. The strength of the individual Porter’s forces is determined by several variables, which may make it have a low, intermediate, or high effect.
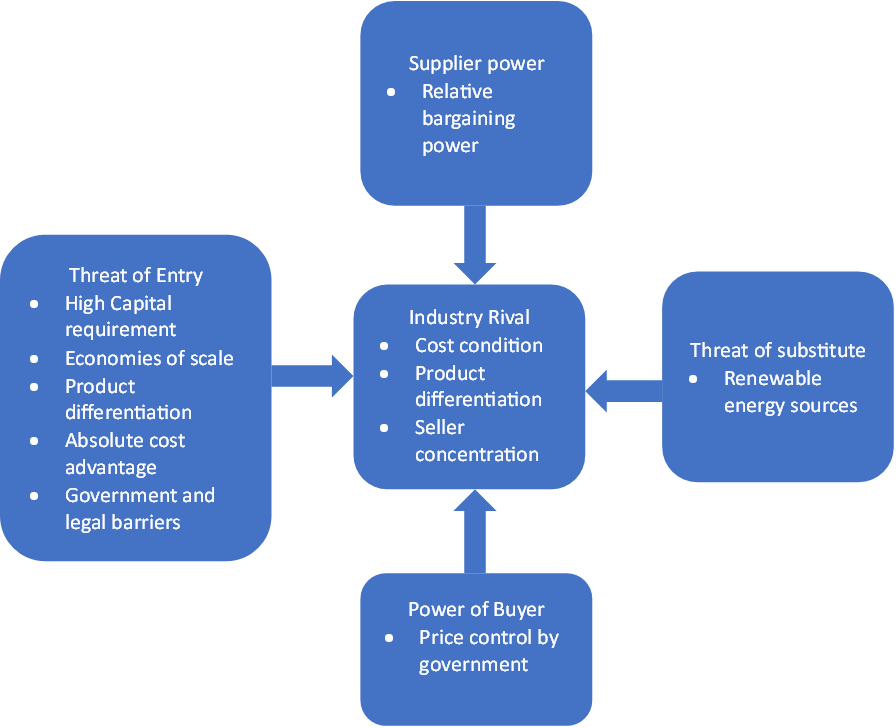
Oil and Gas Industry
The barriers to entry in the oil and gas industry include the high capital requirements. The technology requirement is costly as it is advanced to promote productivity and lower costs, making it challenging for new industries to enter the market (Grant, 2019). Several major oil and gas companies have occupied the industry, making it hard for new entrants to find lucrative oil and gas fields. The threat of substitution results from the increased use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal because their long-term costs are cheaper than oil and gas. However, the sources are affected by weather conditions, such as the availability of sunlight for solar energy.
The bargaining power of buyers for oil products is minimal as products purchased include petroleum and its derivative, whose prices are controlled by the producers. This gives the buyers less power when bargaining for oil and gas products (Bruijl, 2018). Changes in oil structure prices have a global effect because products are homogeneous.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the oil and gas industry is intermediate since they are companies that extract from oil fields. They have regional connections, which enable them to have bargaining power because of the influence they hold. Competitive rivalry oil and gas are major companies that operate globally. Few players in this industry portray how it is competitive, making it difficult to maintain the profit margin (Bruijl, 2018). Furthermore, the government regulates the pricing; hence, the companies cannot set significantly high prices. Figure 1 below shows Porter’s five forces applied to the oil and gas sector.
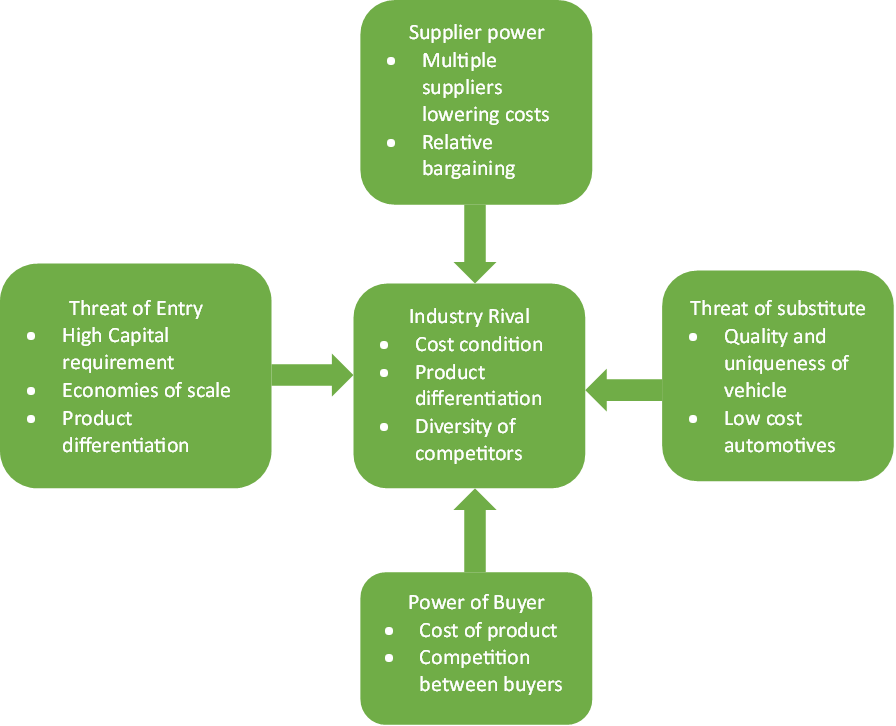
Automotive Industry
The threat of substitute products in the automobile industry is high since the quality and uniqueness of the vehicles drive the industry. Customer loyalty is achieved when products are of superior quality to competitors and are affordable. However, rivals can sell products with the same features at a cheaper cost. The bargaining power of customers is high in the automotive industry as they can demand high-quality products at a forced low price. This is driven by the number of competitors in the market as they rival for profit. Lowering profit gives the company huge sales and attracts many clients.
The bargaining power of suppliers is intermediate since the industry has various suppliers, such as Magna, ZF, Denso, and Bosch, who strive to control the supply market by lowering the prices of products (Grant, 2019). With increased production costs due to expanded material costs, it has become challenging for suppliers and customers to reach a happy medium (Grant, 2019). Key players have built up switching costs, giving them intermediate power.
The threat of new entrants in the automobile industry is driven by uniqueness. This makes it challenging to enter the market as uniqueness comes with a cost that hugely relies on research and development investment (Bruijl, 2018). Competitive rivalry in the automobile industry is significantly high as some laws and regulations have been enacted to ensure fairness. Vehicle quality is also a key factor in the automobile industry, as clients always seek quality products at affordable costs. Figure 2 below shows the application of Porter’s model to the automotive industry.
Profitability in the Oil & Gas Compared to the Automotive Industry
Based on the theory of industry structure, the oil and gas industry is intermediate, while the automotive industry is low in profitability. The oil and gas industry faces a low threat of new entrants because setting up new oil and gas plants requires a massive capital investment. Developing a global supply chain also needs high capital.
Additionally, new companies face the challenge of dominant companies, which makes it hard to enter. This creates a competitive advantage for the companies already operating in this industry. However, high competition in this industry allows them to enjoy intermediate profits.
The industry is also driven by geopolitical factors such as the invasion of Ukraine by Russia and the formation of trade blocs such as BRICS (Isabelle et al., 2020). Furthermore, global pandemics also affect this industry, making them have an intermediate profit in the long run. The threat of substitute products in the oil and gas industry has a low impact on performance.
On the other hand, the automotive industry is low in profitability. This industry faces a threat of substitute products as companies can develop unique products compared to their rivals. Loyalty in the market relies on the quality of products, which makes clients shift their purchases, leading to low profits (Bruijl, 2018).
Consumers also have a high bargaining power, which affects rivalry, leading to the production of quality products as prices reduce. Additionally, the automotive industry faces a significant threat of new entrants as the industry is driven by innovation. Companies with breakthroughs in the automotive industry can enter the market and claim large shares, affecting profitability.
Structural Features of the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has various structural features, including vehicle production, global capacity, fixed cost and large-scale economies, key technology controlled by suppliers, internationalization by domestic producers, and new producers of electric vehicles. Vehicle production in the United States faces stiff competition involving key companies. In 2022, based on the sales of the vehicles, Ford was first with 1,764,267, Toyota was second with 1,755,552, and Chevrolet was third with 1,512,875 (Statista, 2023). This portrays that vehicle productivity in this industry is significantly high as the number of vehicles produced by key competitors has a small variation.
The automotive industry has a large global capacity due to exit barriers. In 2021, the global automotive market share was approximately $2.86 U.S. trillion, which is expected to expand (Statista, 2022). Companies in this industry are supported by the government, making them compete effectively. This industry has a high fixed cost and large scale of economies, which promote its production process. This enables the producers to save on the cost of production as workers are assigned specific roles in the industry.
Key suppliers in the automotive industry include Hyundai Mobis, Bosch, Magna, and Denso. They connect consumers to factories and have a wealth of data crucial for the industry’s performance. Technology controlled by suppliers is crucial in increasing efficiencies and providing an accurate timeline to clients.
Electric vehicle production has gradually increased in the automobile industry in the U.S. In 2019, Tesla led the production of 439,000 electric vehicles (Arrieche, 2023). Lucid Motors was second with 7,180 vehicles, followed by Rivian, whose debut was in 2021, delivering 12,278 (Arrieche, 2023). Electric vehicle share continues to expand with new companies entering the industry.
Impact of Structural Changes
The structural changes in the automobile industry significantly impact competition and profitability. For instance, internationalization by domestic producers enables companies operating in this industry to expand their market share. This has a huge effect on the industry’s profitability and competition as companies such as Ford, Chevrolet, and Toyota tend to serve a wider market (Grant, 2019). The development of electric vehicles drives competition as user preferences keep on changing. This enables the companies that have invested in electric vehicles to gain high profits as they serve new markets that prefer electric vehicles based on their uniqueness. This also creates competition as consumers may want to try out electric vehicles.
The structural changes in oil and gas have a negative impact on the performance of this industry. The extensive use of renewable energy affects the market share of this industry (Gong, 2020). Green energy creates awareness of the significance of reducing pollution by changing energy consumption, which reduces the overreliance on oil and gas. Exploration of offshore oil and gas creates room for the entrance of new players in the oil industry, creating competition (Gong, 2020).
The automobile industry is not attractive for investment as other major competitors in the market have large shares in the U.S. Companies such as Ford, Chevrolet, and Toyota have the largest shares compared to other competitors in the market (Statista, 2023). Although the Electric vehicle market is growing, its usage is lower than that of conventional vehicles.
Conclusion
The oil and gas industry makes higher profits than the automotive industry. The profitability in the oil and gas sector is determined by the competitive advantage that the companies have in the market. This is driven by the low threat of product substitution, which generates intermediate profits. The automobile industry relies on the uniqueness of products, which makes it susceptible to structural changes such as the development of electric vehicles and environmental policies.
References
Arrieche, A. (2023). Biggest Electric vehicle companies: What you need to know. Biggest Electric Vehicle Companies | What You Need to Know. Web.
Bruijl, G. H. (2018). The relevance of Porter’s five forces in today’s innovative and changing business environment. SSRN Electronic Journal, 4(1), 1–22. Web.
Gong, B. (2020). Analysis on the structural changes in the global oil and gas industry and its trend. Shale Energy Revolution, 3–17. Web.
Grant, R. M. (2019). Contemporary strategy analysis (10th ed.). Wiley.
Isabelle, D., Horak, K., McKinnon, S., & Palumbo, C. (2020). Is Porter’s five forces framework still relevant? A study of the capital/labour intensity continuum via mining and IT industries. Technology Innovation Management Review, 10(6), 28–41. Web.
Statista. (2022). Global Automotive Manufacturing Market Size 2022. Web.
Statista. (2023). U.S.: Best-selling car brand 2022. Web.