Antidumping laws are put in place to alter the existing pricing policies used by the foreign firms. Basically, the laws are made with a view to protecting domestic firms from foreign pricing that are seen as having a negative economic impact on the local industry. The anti dumping restrictions are carried out when the foreign firms are providing goods are services at much lower price than the costs incurred by the host country in the production of the same product.
The imposition of large tariffs or duties on the importing companies normally has some benefits and consequences to the host nation. The essay is an analysis of the costs and benefits that a country like the US would have on putting antidumping laws on a country like China.
Dumping has been defined by economists and other scholars as the behavior where exports are sold at a lower price which is relatively low compared to the same price at the exporting nation market price (Araujo, Marcio, and Steinfatt 13). This affects the local industry since its products are not bought as a cheaper and perfect substitute is available. The remedy of this through the application of anti-dumping policy has both welfare and distribution effects. This is illustrated in figure 1 below.
Figure1: The simple market: perfect Substitutes
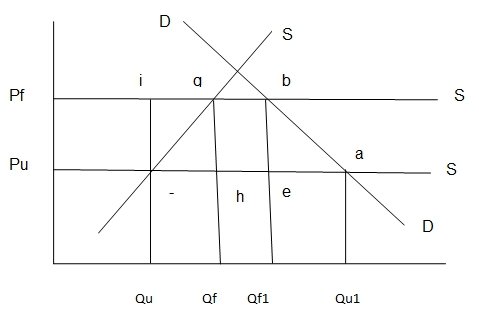
Source: Diane publishing company (1997, p.5-12).
The assumption made is that the dumped imports have perfect substitute in the US.
u- Unfair trade practice
R-remedy
f- Fair value
D-domestic demand
Sd- domestic supply
Unfair competition of solar reduces the domestic production from level Qf to Qf. The changes as a result of unfair trade “result to changes in prices and quantities in turn imply adverse effects for employment, investment, and profits for the domestic industry” (5-12).
Consumers are able to consumer cheaper quantities in large volumes. Anti dumping policy by US makes the domestic industry regain initial sales (Qf) as the imports decline (QfQf1). When domestic product increases, investment, employment, and profits from US companies will increase. The associated welfare effects include consumers losing cheaper products as the producers enjoy profits. Consequently, prices increase, thereby affecting the consumer surplus (5-13). On the other hand, the producer surplus increases.
The antidumping laws protect American solar companies from unfair competition. The assumptions made are that the distorting market practices by foreign importing companies protect American companies from unfair competition consequences (Lindsey 2). However, the laws have negative consequences to the welfare of the American citizens.
For instance, the large number of Americans acquiring the solar panels will be affected. This is because antidumping laws have tariffs, meaning that prices would increase beyond the means of American buyers. Secondly, many American employees who work in the Chinese solar terminal will be rendered jobless. This will increase the unemployment rate, increase inflation, and reduce GDP as there will be a deficit in the balance of payments.
In conclusion, antidumping policy ensures that the welfare of the host company is supported. This is achieved through fair competition. The US solar distribution channels will be affected by the anti dumping duty. This means that consumer demand will not be sustained by American production. This would cause an artificial consumer demand deficit that could have been sustained by the foreign importers.
Works Cited
Araujo, José, Tavares, Carla Macario and Karsten, Steinfatt.” Antidumping in the Americas”. Santiago: Chile. United Nations Publications. 2001. Print.
Diane Publishing Company. “Economic Effects of Antidumping & Countervailing Duty Orders & Suspension Agreements”. Diane Publishing, 1995. Print.
Lindsey, Brink. The U.S. Antidumping law rhetoric versus reality. The Cato Institute’s Center for Trade Policy Studies.1999. Print.