Introduction
The strategic and operational choices are some of the managerial decisions that can lead to the growth and development of the firm. The strategic and operational decisions are significant success factors of the firm and determine its growth direction. The strategic and managerial decisions have a direct influence on the firm’s improved competitive advantage.
The paper discusses the managerial decisions made by Apple Inc. that has led to its growth over the years. The focus is on how the firm has used the managerial decisions to respond to the changes in the market structure and competitive environment.
The History of the Company
Apple Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries manufacture and market personal computers, portable digital music players, mobile communication devices and a wide range of software (Apple, 2011). Besides, the firm also offers a wide range of services, peripherals and network solutions to businesses, private and government institutions (Apple, 2011).
Even though the firm was initially formed to manufacture personal computers, over the years, the firm has been involved in different business ventures. The evolution of the firm into a multinational corporation involved in a wide variety of business ventures has been driven mainly by the technological innovations (Apple, 2011).
Over the last decade, the significance of digital devices particularly, the mobile communications and media devices merged. As a result, the firm invested into these newly emerging opportunities and established itself to be the market leader in these product segments.
Apple’s Financial Performance over the Years
Apple Inc. net revenues have been increasing since the revamp of the firm in 2001. Even though the revenues have been fluctuating previously, the constant increases in the firm’s profits since 2001 are evident (Apple, 2011). The profits are estimated to have grown by over 28% during the period. (See the appendices for more details on the firm’s financial performance).
Sources of Risks and Uncertainty in the Firms Operations
Apple Inc. is operating in a risky and uncertain industry. The main sources of risks and uncertainties include competition and economic factors. Constant changes in the consumer demand as well as the purchasing decisions in relation to the firm’s products, the competitive pressures and transformations in the technological innovations are some of the uncertainties the firm is facing (Ashcroft, 2012).
Risks associated with such uncertainties include timely delivery of the firm’s products and services, product development and adaptability to meet the changing consumer demand. Besides, changes in the product pricing and marketing mix as well as increases in the component costs are some of the uncertainties that have greater effect on the firm’s gross and net margins.
The other source of risk is the firm’s dependency on the third-parties for certain components used in the product development. The dependency on the third-parties for product components and logistic services are the main source of inventory risks, which have a direct effect on the products quality, costs and compliance.
The Risks and Financial Indicators
The financial results indicate all the risks and uncertainties the firm has gone through during the financial year. In fact, all the economic risks and uncertainties are extrapolated on the firm’s gross and net profit margins. The risks that directly affect the firm’s operations including the uncertainties associated with the reliance on the third-parties for the provision of the product components, distribution and digital contents.
In fact, the firm’s dependency on the performance of distributors, carriers and other resellers has the effect on the products quality and cost, which in turn affects the firm’s operating profits (Linden, Kraemer & Dedrick, 2008).
Besides risks associated with operations, economic and political uncertainties are also reflected in the firm’s financial results. Most importantly, the economic decline greatly affects the firm’s sales margin. Economic depression reduces the consumption rate and consumer spending on non-basic items.
The economic decline also affects the operations of the other firms that depend on the Apple’s products and services. Essentially, economic decline have a triple effect on the firms sales. Such effects are indicated in the financial results as declining sales, gross, operating and net margins (Linden et al., 2008). For instance, the firm recorded low profit margins during the 2001 economic decline and the 2007-2008 economic recessions.
The Government Regulations that have affected the Firm’s Operations
Apple Inc. is operating in a highly regulated industry not only within the US but also internationally. Apple’s compliance with the government regulations is reflected on its ethical values and corporate culture. Areas where the government regulations affect the firm’s operations are in the patents and copyrights laws as well as labor regulations.
Most of the Apple’s product components are manufactured in international firms operating in countries with low labor costs and poor or exploitative labor laws. The affiliate firms have increased potential of labor violations and misconduct due to lack of direct oversight or differing labor standards.
As a result, Apple incurs extra cost of ensuring that all its product components are manufactured under internationally accepted labor standards and conducts. The violation of labor regulations has resulted in some firms closing their operations or increased financial compensations for the workers.
Such increased expenses have the effect of increasing the cost of the final component delivered to the firm. Besides, the labor issues with some of the firm’s suppliers have a direct effect on the operations of the firm.
The Inputs used in the Production Function
Apple Inc. mainly manufactures personal computers, portable digital music players, mobile communication devices as well as related hardware and software. However, most of the product inputs are not manufactured within the firm’s premises.
In order to succeed in this endeavor, the firm has to secure input components from the supplier firms, which are located within the country or abroad. In most instances, the input components are manufactured in countries with low labor costs. For instance, most of the components that were used in the production of iPad were mainly manufactured in China.
Besides, the inputs used in the production of the major firm’s products are manufactured by the third-party suppliers that are mainly located internationally. The dependence on the third-party suppliers has many challenges. One of the main challenges is the logistical costs, which in effect increases the cost of production.
Product Development and Impact on the Finances
Apple has over time relied upon the development and the introduction of new and innovative products to the market. The development and introduction of new products is the main driver and the cause of increased demand. Over the last decade the firm has introduced variety of the products including the iPod, iPhone and iPad.
The launch of such products has caused a tremendous increase in the firm’s sales and profit margins (Kim & Mauborgne, 2005). For instance, the introduction of the new products into the market has caused the firm’s revenues to increase from $5 billion to over $108 billion within ten years.
The launch of Ipod caused an increased in the gross margins by over 40%. Similarly, the launch of iPad caused a leap in the operating profit to 32% in 2011.
Pricing and Price Behaviors
The firm believes in premium prices and mainly targets the high-end markets. However, like most high-tech products, the firm’s product prices continue to decline over time. In other words, the product prices are normally high during and immediately after the launch. However, the prices will continue to decrease with time (Linden et al., 2008).
Competition is the major factor that contributes to the decline of prices. Most of the competing firms are likely to produce similar and low-cost products. Such competing firms enjoy the cost advantages in their production process. As a result, they produce cheap, efficient and competing products that in many ways drive down the prices of the original products.
Demand Elasticity of the Products
Even though the products have different elasticity, the demand for most of the firm’s products can be described as price elastic. In fact, most of the Apple products have close price elasticity considering marginal revenues and costs (Douglas, 2012).
The implication is that the changes in prices would not significantly change the quantity demanded (Douglas, 2012). In other words, if the firm were to change the prices of products from the current levels, the percentage change in quantity demanded would be higher compared with the percentage change in prices. The majority of the clients would not make purchases when the prices are changed.
The consumer behavior towards the firm’s products reflects the purchasing decisions of the majority within the industry. As such, Apple would lose out to competing products from other firms when prices are changed. As such, competing firms in the industry will take advantage of the price elasticity and produce cheap products and claim a larger market share.
For instance, Samsung produces cheap iPads and Smartphones compared with that of Apple. Price elasticity is significant in the pricing decisions especially in an industry that is highly competitive. However, the concept of price elasticity is only applicable when other factors are kept constant.
The Firms Profitability and the Industry Influences
The strategic financial and managerial decisions have resulted in in an increase in net revenues since the revamp of the firm in 2001. From 2001, the firm’s revenues have increased from a bout $5 billion to over $108 billion in 2011. The gross profit margins have increased from a bout 23% to over 40%. The operating profits have jumped from a loss of $344 million in 2001 to over $33 billion in 2011.
The Company’s current return on investments is about 44%, return on sales of a bout 32% with net assets of about $77 billion. Further, the Firm is boasting of market Capitalization of a bout $592 billion and an enterprise value of about $550 billion. In fact, the improved revenues have enabled the firm to gain financial capabilities (See appendix on more of the firms Revenues)
The Industry Influences on the firms Costs, Operations and Profitability
The technology industry in which the firm is operating is highly competitive. The industry structure and dynamics has enabled the firm to come up with strategies that has effectively improved its competitive advantage. Increased competition coupled with changes in the technological innovation has a direct effect on the prices of the firm’s products, which in effect increases the cost of production.
Increased costs of production and cumulative reduction in the prices squeeze the firm’s profits. Generally, the increased competition and the industry dynamics have a direct effect on the costs, operations and profitability of the firm.
The Competitive Environment, Market Power and Strategic Behavior
As indicated, the firm is operating in a highly competitive environment. The intense competition has a profound effect on the operations, marketing and pricing strategies. As a result, the firm has entered in the strategic alliances, in the design, manufacture and marketing of certain products. Such alliances enabled the firm to mitigate the competitive risks.
Apple unique products still place it at exceptional competitive position over the rivals. One way through which the firm can sustain its competitiveness is through continuous offering of unique and quality products. The changing trends in the competitive landscape require firms to develop distinctive capabilities that will differentiate its products from the competitors.
Apple Inc. has managed to create a demand for its products through innovative approach, which has provided the firm with increased power over pricing.
The Pricing and Production Decisions
Even though the pricing strategy of the firm is aimed at placing the products at the highest competitive edge in the high-end market, the cost of product is also considered. In other words, the unit prices are considered where the marginal revenues equal the marginal costs. Generally, the firms pricing and production decisions, take into consideration the micro-economic theories of production and consumption.
Conclusion
The strategic and managerial decisions influence the firms operations, which in turn enables it to survive in a highly competitive environment. As can be observed in the case of Apple Inc., the strategic and managerial decisions has resulted in distinctive capabilities and increased competitive advantage. The appropriate strategic and managerial decisions have enabled the firm to survive the industry dynamics, technological transformations and financial difficulties.
References
Apple (2011). Apple’s library. Web.
Ashcroft, J. (2012). Apple from iPod to iPad, a case study on the corporate strategy. Famington Hills, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Douglas, E. J. (2012). Managerial economics. San Diego: Bridgepoint Education, Inc.
Kim, W. C., & Mauborgne, R. (2005). Blue ocean strategy – How to create uncontested market space and make the competition irrelevant. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing.
Linden, G., Kraemer, K., & Dedrick, J. (2008). Who captures value in a global innovation network? The case of Apple’s iPod. Communications of the ACM, 52(3), 140–144.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Apple’s Net Sales from 2001 financial year to 2013 financial year
Appendix 2: Apple’s revenue growth trends from FY 2001 to FY 2013
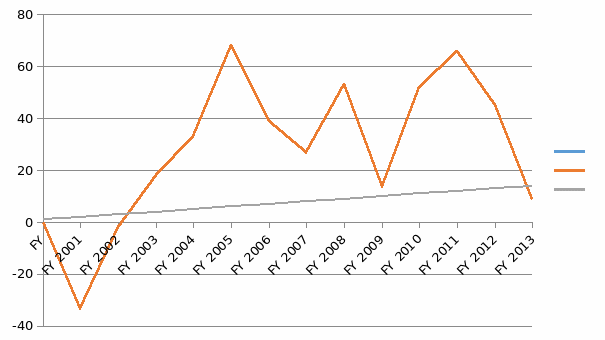
Appendix 3: Apple Inc. financial data